动态规划 -- 钢条切割
动态规划(Dynamic Programming)
什么是动态规划,我们要如何描述它?
动态规划算法通常基于一个递推公式及一个或多个初始状态。当前子问题的解将由上一次子问题的解推出。
动态规划和分治法相似,都是通过组合子问题的解来求解原问题。分治法将问题划分成互不相交的子问题,递归求解子问题,再将他们的解组合起来,求出原问题的解。与之相反,动态规划应用于子问题重叠的情况,即不同的子问题具有公共的子子问题。在这种情况下,分治算法会做出许多不必要的工作,它会反复的求解那些公共子问题。而动态规划算法对每个子子问题只求解一次,将结果保存到表格中,从而无需每次求解一个子子问题都要重新计算。
钢条切割利润最大化问题描述:
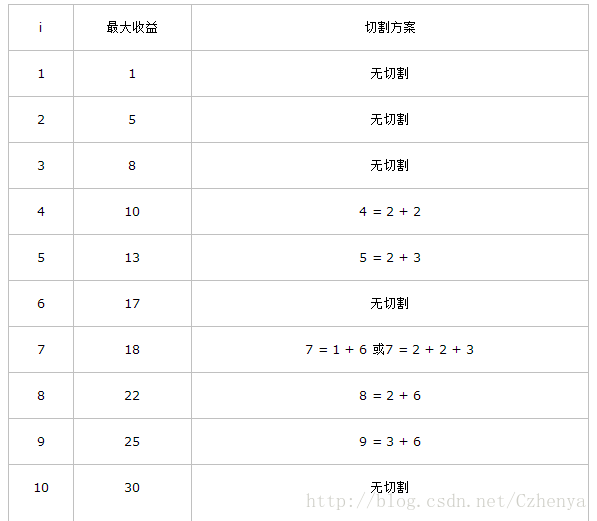
给出下面一个钢条的长度(int类型)和对应的价格表,求出给定长度n米(int类型)的钢条如何切割才能获得最大收益。
| 长度(m) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | … | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 价格($) | 1 | 5 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 17 | 17 | 20 | 24 | 30 | … | P |
代码实现:
using System;
namespace _4_1_1动态规划_钢条切割_递归
{ /*一公司购买长钢条,将其切为短钢条出售, * 假设切割没有成本,公司希望知道最佳的切割方案! * 假设我们知道一段长度为i的钢条的价格为pi(i = 1,2,3...), * 钢条长度均为整英寸,下面给出一个价格表: * //索引代码钢条的长度,值代表价格 * int[] p = { 0, 1, 5, 8, 9, 10, 17, 17, 20, 24, 30 }; * 给定一长度为n的钢条和一张价格表(i =1, 2,3...n),求切割钢条的方案, * 使的利润最大,可以不进行切割 */ class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //索引代码钢条的长度,值代表价格 int[] p = { 0, 1, 5, 8, 9, 10, 17, 17, 20, 24, 30 }; Console.WriteLine(UpDown(1, p)); Console.WriteLine(UpDown(2, p)); Console.WriteLine(UpDown(3, p)); Console.WriteLine(UpDown(4, p)); Console.WriteLine(UpDown(5, p)); Console.WriteLine(UpDown(6, p)); Console.WriteLine(UpDown(7, p)); Console.WriteLine(UpDown(8, p)); Console.WriteLine(UpDown(9, p)); Console.ReadKey(); } /// <summary> /// 钢条切割递归算法 /// </summary> /// <param name="n">要切割的长度</param> /// <param name="p">索引代码钢条的长度,值代表价格</param> /// <returns></returns> public static int UpDown(int n,int[] p) { if (n == 0) return 0; int MaxPrice = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { int tempmaxPrice = p[i] + UpDown(n - i, p); if (tempmaxPrice > MaxPrice) { MaxPrice = tempmaxPrice; } } return MaxPrice; } }
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
运行结果:

递归优化:
优化思路也和简单:当我们使用递归解决问题的时候,会发现相同的问题会执行多次,比如我们求长度为5的最大利润的时候,就会把长度为4 的最大利润也求出来,而求长度为6的最大利润时,还需要把长度为5,长度为4的最大利润在求一次,,,如果可以长度为n的最大利润可以保存下来,那么程序运行起来就会快很多了,,,优化代码如下:
namespace _4_1_2动态规划_钢条切割_递归优化
{ class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //索引代码钢条的长度,值代表价格 int[] p = { 0, 1, 5, 8, 9, 10, 17, 17, 20, 24, 30 }; //用于保存所求长度的最大利润, int[] result = new int[p.Length+1]; Console.WriteLine(UpDown(1, p,result)); Console.WriteLine(UpDown(2, p,result)); Console.WriteLine(UpDown(3, p,result)); Console.WriteLine(UpDown(4, p,result)); Console.WriteLine(UpDown(5, p,result)); Console.WriteLine(UpDown(6, p,result)); Console.WriteLine(UpDown(7, p,result)); Console.WriteLine(UpDown(8, p,result)); Console.WriteLine(UpDown(9, p,result)); Console.ReadKey(); } /// <summary> /// 钢条切割递归算法 /// </summary> /// <param name="n">要切割的长度</param> /// <param name="p">索引代码钢条的长度,值代表价格</param> /// <returns></returns> public static int UpDown(int n, int[] p,int[] result) { if (n == 0) return 0; //如果计算了长度为n的最大值,那么就不会再次计算 if (result[n] != 0) return result[n]; int MaxPrice = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { int tempmaxPrice = p[i] + UpDown(n - i, p,result); if (tempmaxPrice > MaxPrice) { MaxPrice = tempmaxPrice; } } result[n] = MaxPrice; return MaxPrice; } }
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
动态规划的方法进行求解
上面的方法之所以效率很低,是因为它反复求解相同的子问题。因此,动态规划算法安排求解的顺序,对每个子问题只求解一次,并将结果保存下来。如果随后再次需要此子问题的解,只需查找保存的结果,不必重新计算。因此动态规划的方法是付出额外的内存空间来节省计算时间。
自底向上法
首先恰当的定义子问题的规模,使得任何问题的求解都只依赖于更小的子问题的解。因而我们将子问题按照规模排序,按从小到大的顺序求解。当求解某个问题的时候,它所依赖的更小的子问题都已经求解完毕,结果已经保存。
代码实现:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace _4_1_3动态规划_钢条切割_自底向上
{ class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //索引代码钢条的长度,值代表价格 int[] p = { 0, 1, 5, 8, 9, 10, 17, 17, 20, 24, 30 }; //用于保存所求长度的最大利润, int[] result = new int[p.Length + 1]; Console.WriteLine(BottomUp(1, p, result)); Console.WriteLine(BottomUp(2, p, result)); Console.WriteLine(BottomUp(3, p, result)); Console.WriteLine(BottomUp(4, p, result)); Console.WriteLine(BottomUp(5, p, result)); Console.WriteLine(BottomUp(6, p, result)); Console.WriteLine(BottomUp(7, p, result)); Console.WriteLine(BottomUp(8, p, result)); Console.WriteLine(BottomUp(9, p, result)); Console.ReadKey(); } public static int BottomUp(int n,int[] p,int[] result) { for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { //取得钢条长度为i的时候最大利润 int maxPrice = -1; for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) { int tempmaxPrice = p[j] + result[i - j]; if (tempmaxPrice>maxPrice) { maxPrice = tempmaxPrice; } } result[i] = maxPrice; } return result[n]; } }
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
文章来源: czhenya.blog.csdn.net,作者:陈言必行,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:czhenya.blog.csdn.net/article/details/78927096
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)