IPython基础使用_Round2
目录
前言
上篇博文中记录了Setup Python环境和Iptyhon,以及Ipython的特性和部分基础功能。现在继续更深入的学习Ipython的特殊功能,以及Ipython的魔力函数—Magic
软件环境
- 系统
- Ubuntukylin 14.04
- 软件
- Python 2.7.6
- Ipython 4.0.0
Ipython的字符串处理
Ipython内嵌grep()函数,可以实现类似awk、grep指令的功能
a). 获取要处理的文本内容
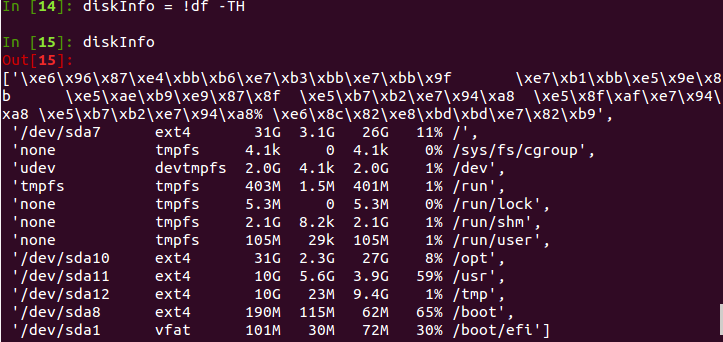
b). 对文本进行行过滤
contentsInfo.grep(“lineFilter”)
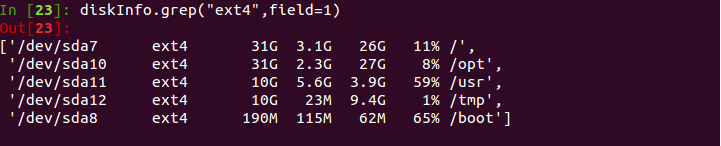
c). 行过滤后再进行的列过滤
contentsInfo.grep(“lineFilter”).fields(rangeArray)
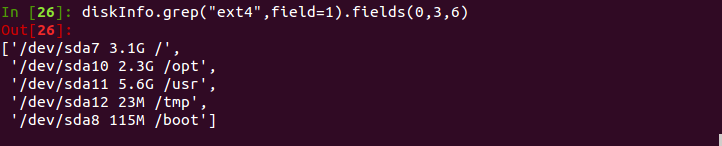
也可以直接进行列过滤contentsInfo.fields(rangeArray)
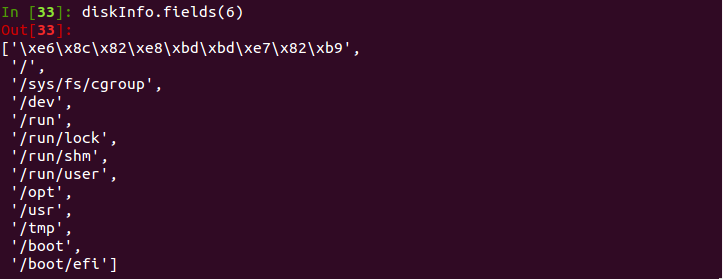
e). 对进行过滤后的Out[ ]作选择操作
Ipython的魔力函数—Magic
Magic是Ipython内置的丰富的函数库,一般以%开头,支持查看函数的源代码,Magic是Ipython主要内容,为编程提供了很好的便捷性能。其中Magic有两种类型,分别是%:line magic和%%:call magic。前者针对处理一行代码,反之,后者处理多行代码。
%lsmagic — Output所有魔力函数
In [39]: %lsmagic
Out[39]:
Available line magics:
%alias %alias_magic %autocall %autoindent %automagic %bookmark %cat %cd %clear %colors %config %cp %cpaste %debug %dhist %dirs %doctest_mode %ed %edit %env %gui %hist %history %install_default_config %install_ext %install_profiles %killbgscripts %ldir %less %lf %lk %ll %load %load_ext %loadpy %logoff %logon %logstart %logstate %logstop %ls %lsmagic %lx %macro %magic %man %matplotlib %mkdir %more %mv %notebook %page %paste %pastebin %pdb %pdef %pdoc %pfile %pinfo %pinfo2 %popd %pprint %precision %profile %prun %psearch %psource %pushd %pwd %pycat %pylab %quickref %recall %rehashx %reload_ext %rep %rerun %reset %reset_selective %rm %rmdir %run %save %sc %set_env %store %sx %system %tb %time %timeit %unalias %unload_ext %who %who_ls %whos %xdel %xmode
Available cell magics:
%%! %%HTML %%SVG %%bash %%capture %%debug %%file %%html %%javascript %%latex %%perl %%prun %%pypy %%python %%python2 %%python3 %%ruby %%script %%sh %%svg %%sx %%system %%time %%timeit %%writefile
Automagic is ON, % prefix IS NOT needed for line magics.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
可以看见Ipython拥有丰富的内置函数。下面着重介绍常用的几个。
查看Magic的源码
In [69]: %edit??
- 1
??:查看函数、指令、对象的详细信息,包括用法、函数的源代码等
?:查看函数、指令、对象、变量的更加详细使用方法、文档,但不包括函数的源代码
%env 显示系统环境变量
In [40]: %env
- 1
%history 查看指令执行历史记录
In [41]: %history -n
- 1
%pwd 显示当前目录路径
IpythonShell中的pwd是%pwd的链接,而%pwd是系统Bash中pwd的链接。Ipython中大部分可以直接使用的系统指令都是经过了这样的处理后才能使用。
In [42]: %pwd
Out[42]: u'/usr/local/src/pyScript'
In [43]: pwd
Out[43]: u'/usr/local/src/pyScript'
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
%pycat 语法高亮显示一个Python程序文件
In [45]: %pycat pyFile.py
- 1
%save 将历史指令筛选并保存到文件中
常%save 结合 %history 、%edit 指令一起使用。
%save fileName commandsNnmber
先将历史记录保存到文件中
In [54]: %save testSave 1-3 14-15 24 27-30
File `testSave.py` exists. Overwrite (y/[N])? y
The following commands were written to file `testSave.py`:
portInfo = get_ipython().getoutput(u'netstat -lpntu')
portInfo
portInfo.grep("tcp")
diskInfo = get_ipython().getoutput(u'df -TH')
diskInfo
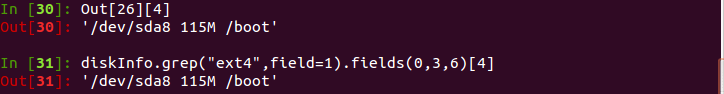
diskInfo.grep("ext4",field=1).fields(0)
diskInfo.grep("ext4",field=1).fields(0,3,6)[0]
Out[1]
Out[26]
Out[26][4]
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
再编辑保存了历史指令的testSave文件,可以非常方便的将调试的指令写入到文件中,再作进一步的处理。
In [56]: %edit testSave.py # coding: utf-8 portInfo = get_ipython().getoutput(u'netstat -lpntu') portInfo portInfo.grep("tcp") diskInfo = get_ipython().getoutput(u'df -TH') diskInfo diskInfo.grep("ext4",field=1).fields(0) diskInfo.grep("ext4",field=1).fields(0,3,6)[0] Out[1] Out[26] Out[26][4]
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
%run 在IPython执行一个脚本
在IPython中因无法使用python指令来执行一个.py的脚本,所以IPython也内嵌了一个%run函数来代替python command。其中run是%run的链接,所以有下面两种方式,而且还提供能多个选项来满足开发需求。
In [8]: run test.py
My Name is Jmilk!
In [9]: %run test.py
My Name is Jmilk!
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
a). -t 输出程序执行的CPU timings, -Nx (x为数字)指定程序重复执行的次数。
In [10]: run -t test.py
My Name is Jmilk!
IPython CPU timings (estimated):
User : 0.00 s.
System : 0.00 s.
Wall time: 0.00 s.
In [12]: run -t -N2 test.py
My Name is Jmilk!
My Name is Jmilk!
IPython CPU timings (estimated):
Total runs performed: 2
Times : Total Per run
User : 0.00 s, 0.00 s.
System : 0.00 s, 0.00 s.
Wall time: 0.00 s.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
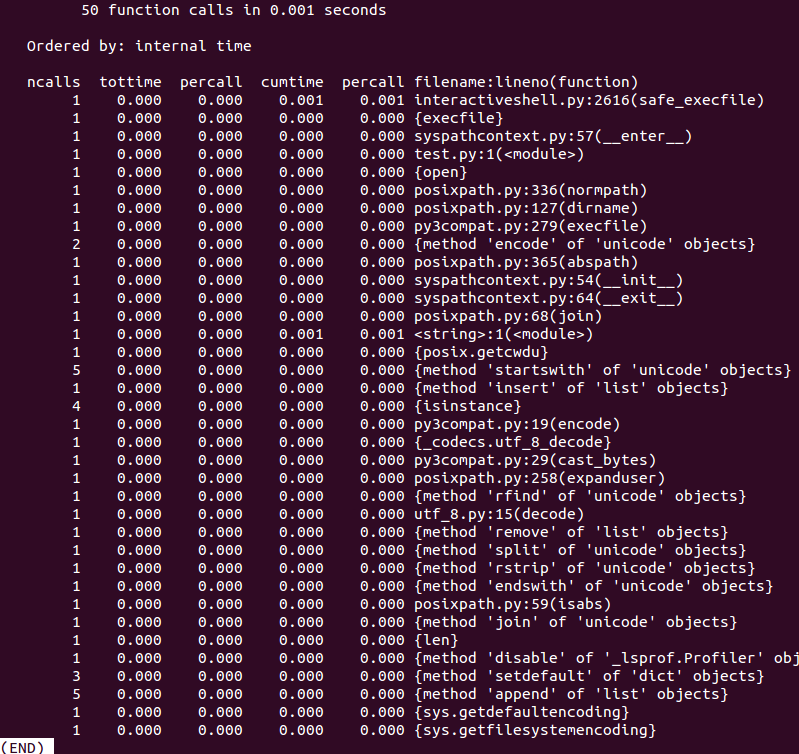
b). -p 开启Python profiler(Python 程序性能调优)
In [18]: run -t -N2 -p test.py
My Name is Jmilk!
- 1
- 2
可以显示详细的程序运行时资源使用量的参数。
c). -d 进入ipdb控制台中,-bx(x为数字)指定行数打断点。是一个不错的程序调试平台。
In [19]: run -d test.py
Breakpoint 1 at /usr/local/src/pyScript/test.py:1
NOTE: Enter 'c' at the ipdb> prompt to continue execution.
> /usr/local/src/pyScript/test.py(1)<module>()
1---> 1 print "My Name is Jmilk!"
ipdb>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
上述%run函数的几个选项都非常值得深入学习,在以后会继续为大家介绍。
%timeit 测试一条指令执行的时间
%timeit 函数默认会重复执行10000次此条指令,并取出3个最佳的结果来计算平均值,从而得出一条指令执行所需要的时间。
In [23]: %timeit [i*i for i in range(1000)]
The slowest run took 5.67 times longer than the fastest. This could mean that an intermediate result is being cached
10000 loops, best of 3: 160 µs per loop
- 1
- 2
- 3
a). -n 指定重复执行的次数,默认为10000。-p 显示出详细的高精度时间。
In [31]: %timeit -n 100 [i*i for i in range(1000)]
100 loops, best of 3: 231 µs per loop
In [34]: %timeit -p 1000 [i*i for i in range(1000)]
1000 loops, best of 3: 162.34493255615234375 µs per loop
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
b). -r 指定取多少个最佳结果来计算平均值,默认为3个。
In [26]: %timeit -p 1000 -r 4 [i*i for i in range(1000)]
10000 loops, best of 4: 162.2743129730224609375 µs per loop
- 1
- 2
%bookmark 记忆路径
In [36]: %bookmark workspace /usr/local/src/pyScript/
In [39]: cd workspace
(bookmark:workspace) -> /usr/local/src/pyScript/
/usr/local/src/pyScript
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
注意的是,使用%bookmark的定义的路径无法使用 !cd 来进入。既系统Shell不是别%bookmark定义的变量。
%file 创建并编辑一个文件
In [58]: %%file testFile.py
def myFuncation(): name = 'Jmilk' print "My name is %s" % name
if __name__ == '__main__': myFuncation() ....:
Overwriting testFile.py
In [59]: run testFile.py
My name is Jmilk
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
Python 和 shell 的结合
在Shell中使用Python变量
可以在定义Python变量后,使用$符来结合Shell command和Python variable。需要注意的是,mkdir其实是%mkdir的链接,既本质上是IPython 的内嵌函数%mkdir 可以识别variable “folder” 。
In [62]: folder = 'testVariable'
In [63]: mkdir $folder
In [65]: cd $folder
/usr/local/src/pyScript/testVariable
#反之,指令:!cd $folder 则无法执行
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
将Shell 的结果赋值给Python vairable。
vairable = !shellCommands
In [83]: import re
In [84]: portInfo = !netstat -lpntu | grep "tcp"
In [86]: portInfo
Out[86]:
['tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:11211 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 2259/memcached ',
'tcp 0 0 127.0.1.1:53 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1468/dnsmasq ',
'tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1761/sshd ',
'tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:631 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 5483/cupsd ',
'tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:15672 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 2428/beam.smp ',
'tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:55672 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 2428/beam.smp ',
'tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:3260 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1823/tgtd ',
'tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:54531 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 2428/beam.smp ',
'tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:3306 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1975/mysqld ',
'tcp6 0 0 :::80 :::* LISTEN 2845/apache2 ',
'tcp6 0 0 :::4369 :::* LISTEN 2332/epmd ',
'tcp6 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN 1761/sshd ',
'tcp6 0 0 ::1:631 :::* LISTEN 5483/cupsd ',
'tcp6 0 0 :::3260 :::* LISTEN 1823/tgtd ',
'tcp6 0 0 :::5672 :::* LISTEN 2428/beam.smp ']
In [88]: for i in portInfo: print re.sub(r"0","J",i) ....: tcp J J 127.J.J.1:11211 J.J.J.J:* LISTEN 2259/memcached
tcp J J 127.J.1.1:53 J.J.J.J:* LISTEN 1468/dnsmasq tcp J J J.J.J.J:22 J.J.J.J:* LISTEN 1761/sshd tcp J J 127.J.J.1:631 J.J.J.J:* LISTEN 5483/cupsd tcp J J J.J.J.J:15672 J.J.J.J:* LISTEN 2428/beam.smp tcp J J J.J.J.J:55672 J.J.J.J:* LISTEN 2428/beam.smp tcp J J J.J.J.J:326J J.J.J.J:* LISTEN 1823/tgtd tcp J J J.J.J.J:54531 J.J.J.J:* LISTEN 2428/beam.smp tcp J J J.J.J.J:33J6 J.J.J.J:* LISTEN 1975/mysqld tcp6 J J :::8J :::* LISTEN 2845/apache2 tcp6 J J :::4369 :::* LISTEN 2332/epmd tcp6 J J :::22 :::* LISTEN 1761/sshd tcp6 J J ::1:631 :::* LISTEN 5483/cupsd tcp6 J J :::326J :::* LISTEN 1823/tgtd tcp6 J J :::5672 :::* LISTEN 2428/beam.smp
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
将Shell commands的结果赋值给Pyhon variable后,可以将此List类型的变量再作后期的处理。其中re(regular expression) module在Python中实现正则表达式的功能。re.sub(substitute)则是实现正则表达式的替换功能。
到此IPython的基本介绍也完成了,IPython是一个非常有意思的东西,他所能实现的功能,总会给你惊喜。当然,,这也需要失时间去熟悉他。往后会结合Python的语法和代码实现来继续学习IPython。
Jmilk
文章来源: is-cloud.blog.csdn.net,作者:范桂飓,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:is-cloud.blog.csdn.net/article/details/48194487
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)