数据结构 — 双向链表
【摘要】 目录
文章目录
目录双向链表双向链表结点的数据结构双向链表的操作集合应用示例创建双向链表清理双向链表查询链表结点更新链表结点的数据插入链表结点删除结点打印链表数据
双向链表
双向链表(Double linked list)是在操作系统中常用的数据结构,它的每个数据结点中都有两个指针,分别指向直接后继和直接前驱,其结点组成如下:
双向链表,所谓...
目录
双向链表
双向链表(Double linked list)是在操作系统中常用的数据结构,它的每个数据结点中都有两个指针,分别指向直接后继和直接前驱,其结点组成如下:

双向链表,所谓 “双向” 值其支持 “顺序和逆序” 查找,如下图:
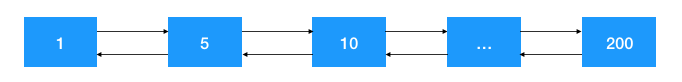
所以双向链表也常被称之为环(Ring),常用于作为网络数据报文的内存缓存空间,因为双向链表具有两个特征:
- 支持顺序和逆序查找,肯定能把数据报文遍历完。
- 成环状,即:内存空间固定,不会因为数据报文的多少而造成内存越界。
双向链表的缺点是不支持按某个值或区间的快速查找,也不支持数据的快速插入,所以不十分适用于需求灵活的逻辑控制场景(e.g. 数据库)。
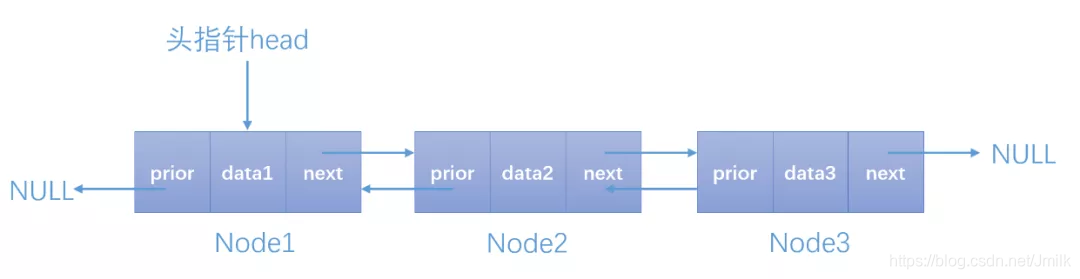
双向链表结点的数据结构
typedef int data_type; // 4B
typedef struct dlist_node_s { data_type data; // 4B + 4B(填充) struct dlist_node_s* prior; // 8B struct dlist_node_s* next; // 8B
} dlist_node_t;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
双向链表的操作集合
- dlist_create:(构造函数)创建双向链表
- dlist_find:查询链表结点
- dlist_change:更新链表结点的数据
- dlist_insert:插入链表结点
- dlist_delete:删除链表结点
- dlist_print_int:输入链表结点的数据
- dlist_distory:(析构函数)清理双向链表
应用示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define DL_LEN 5
typedef int data_type; // 4B
typedef struct dlist_node_s { data_type data; // 4B + 4B(填充) struct dlist_node_s* prior; // 8B struct dlist_node_s* next; // 8B
} dlist_node_t;
enum { SUCCESS, FAIL
};
int list[DL_LEN] = {5, 2, 0, 13, 14};
static int dlist_create(dlist_node_t** dlist)
{ printf("dlist_create.\n"); *dlist = (dlist_node_t*)malloc(sizeof(dlist_node_t)); if (NULL == *dlist) { printf("Allocation dlist_node_t failed.\n"); return FAIL; } (*dlist)->prior = NULL; (*dlist)->next = NULL; (*dlist)->data = list[0]; /* 开始,链表的第一个结点 head 就是链表本身,后续再不断增加新的结点。 */ dlist_node_t* head = *dlist; for (int i=1; i<DL_LEN; i++) { /* 初始化新的结点。 */ dlist_node_t* new_node = (dlist_node_t*)malloc(sizeof(dlist_node_t)); new_node->next = NULL; new_node->prior = head; // 新结点的 prior 为 head new_node->data = list[i]; head->next = new_node; // head 的 next 为新结点 /* 头指针向后移动一个结点,循环添加直到双向链表的所有结点都构造完成。 */ head = head->next; } return SUCCESS;
}
static void dlist_distory(dlist_node_t* dlist)
{ dlist_node_t* temp = dlist; while (temp) { temp = temp->next; if (NULL != temp) { free(temp->prior); } }
}
static int dlist_find(dlist_node_t* dlist, int* idx, data_type find_data)
{ printf("dlist_find: %d.\n", find_data); int pos = 0; // position dlist_node_t* temp = dlist; while (temp) { if (find_data == temp->data) { idx = &pos; return SUCCESS; } else { temp = temp->next; pos++; } } printf("Data %d not exist.\n", find_data); return FAIL;
}
static int dlist_change(dlist_node_t* dlist, int idx, data_type new_data)
{ printf("dlist_change, index: %d, new_data: %d.\n", idx, new_data); if (idx > DL_LEN) { printf("Position out of bounds.\n"); return FAIL; } /* 使用 temp 来移动链表位置,不能直接移动 dlist,dlist 始终执行链表的起始位置,即索引为 [0] 的结点。 */ dlist_node_t* temp = dlist; /* 移动到预期的 idx 结点。 */ for (int i=1; i<idx; i++) { temp = temp->next; } /* 更新。 */ temp->data = new_data; return SUCCESS;
}
static int dlist_insert(dlist_node_t* dlist, int idx, data_type insert_data)
{ printf("dlist_insert, index: %d, insert_data: %d\n", idx, insert_data); /* 构造一个新的结点。 */ dlist_node_t* new_node = (dlist_node_t*)malloc(sizeof(dlist_node_t)); new_node->next = NULL; new_node->prior = NULL; new_node->data = insert_data; if (idx > (DL_LEN + 1)) { printf("Position out of bounds.\n"); // 新结点的位置不连续 return FAIL; } /* 头部插入。 */ if (1 == idx) { dlist->prior = new_node; // 步骤 1 new_node->next = dlist; // 步骤 2 dlist = new_node; // 步骤 3 } else { dlist_node_t* temp = dlist; for (int i=1; i<idx; i++) { temp = temp->next; } /* 中间插入。 */ if (temp->next != NULL) { new_node->next = temp->next; // 步骤 1 new_node->prior = temp; // 步骤 2 temp->next->prior = new_node; // 步骤 3 temp->next = new_node; // 步骤 4 } else { temp->next = new_node; // 步骤 1 new_node->prior = temp; // 步骤 2 } } return SUCCESS;
}
static int dlist_delete(dlist_node_t* dlist, data_type del_data) { printf("dlist_delete, del_data: %d\n", del_data); dlist_node_t* temp = dlist; while (temp) { if (del_data == temp->data) { temp->next->prior = temp->prior; temp->prior->next = temp->next; free(temp); return SUCCESS; } else { temp = temp->next; } } printf("dlist_delete not exist.\n"); return FAIL;
}
static void dlist_print_int(dlist_node_t* dlist)
{ dlist_node_t* temp = dlist; int idx = 0; while (temp) { printf("index: %d - data: %d\n", idx, temp->data); temp = temp->next; idx++; }
}
int main(void)
{ /** * 这里不能直接定义使用双重指针 **dlist, * 因为这样会导致 *dlist 的类型没有定义,从而无法进行下一步的 malloc 内存分配, * 应该: * 1. dlist_node_t* dlist; * 2. &dlist 入参 * 3. 在函数内再使用 dlist_node_t** dlist 变量 */ dlist_node_t* dlist; if (FAIL == dlist_create(&dlist)) { printf("dlist_create ERROR.\n"); exit(1); } dlist_print_int(dlist); int idx = 0; if (FAIL == dlist_find(dlist, &idx, 13)) { printf("dlist_find ERROR.\n"); exit(1); } dlist_print_int(dlist); if (FAIL == dlist_change(dlist, 1, 666)) { printf("dlist_change ERROR.\n"); exit(1); } dlist_print_int(dlist); if (FAIL == dlist_insert(dlist, 2, 2020)) { printf("dlist_insert ERROR.\n"); exit(1); } dlist_print_int(dlist); if(FAIL == dlist_delete(dlist, 13)) { printf("dlist_delete ERROR.\n"); exit(1); } dlist_print_int(dlist); dlist_distory(dlist); return 0;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
创建双向链表
创建一个双向链表:5,2,0,13,14。
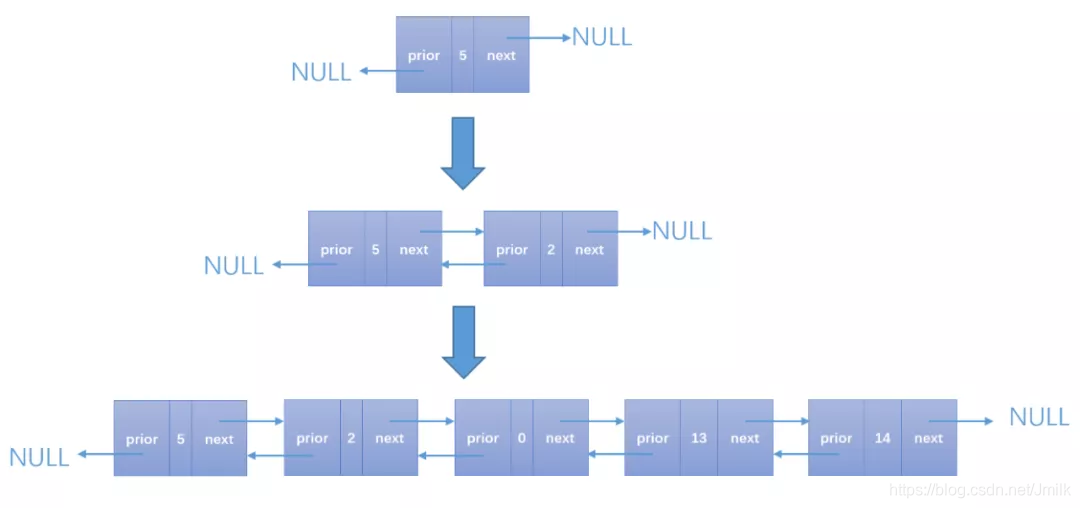
static int dlist_create(dlist_node_t** dlist)
{ printf("dlist_create.\n"); *dlist = (dlist_node_t*)malloc(sizeof(dlist_node_t)); if (NULL == *dlist) { printf("Allocation dlist_node_t failed.\n"); return FAIL; } (*dlist)->prior = NULL; (*dlist)->next = NULL; (*dlist)->data = list[0]; /* 开始,链表的第一个结点 head 就是链表本身,后续再不断增加新的结点。 */ dlist_node_t* head = *dlist; for (int i=1; i<DL_LEN; i++) { /* 初始化新的结点。 */ dlist_node_t* new_node = (dlist_node_t*)malloc(sizeof(dlist_node_t)); new_node->next = NULL; new_node->prior = head; // 新结点的 prior 为 head new_node->data = list[i]; head->next = new_node; // head 的 next 为新结点 /* 头指针向后移动一个结点,循环添加直到双向链表的所有结点都构造完成。 */ head = head->next; } return SUCCESS;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
清理双向链表
static void dlist_distory(dlist_node_t* dlist)
{ dlist_node_t* temp = dlist; while (temp) { temp = temp->next; if (NULL != temp) { free(temp->prior); } }
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
查询链表结点
双向链表不支持快速查询,所以只能循环遍历匹配查询。匹配成功后,返回结点的索引号。
static int dlist_find(dlist_node_t* dlist, int* idx, data_type find_data)
{ printf("dlist_find: %d.\n", find_data); int pos = 0; // position dlist_node_t* temp = dlist; while (temp) { if (find_data == temp->data) { idx = &pos; return SUCCESS; } else { temp = temp->next; pos++; } } printf("Data %d not exist.\n", find_data); return FAIL;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
更新链表结点的数据
static int dlist_change(dlist_node_t* dlist, int idx, data_type new_data)
{ printf("dlist_change, index: %d, new_data: %d.\n", idx, new_data); if (idx > DL_LEN) { printf("Position out of bounds.\n"); return FAIL; } /* 使用 temp 来移动链表位置,不能直接移动 dlist,dlist 始终执行链表的起始位置,即索引为 [0] 的结点。 */ dlist_node_t* temp = dlist; /* 移动到预期的 idx 结点。 */ for (int i=1; i<idx; i++) { temp = temp->next; } /* 更新。 */ temp->data = new_data; return SUCCESS;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
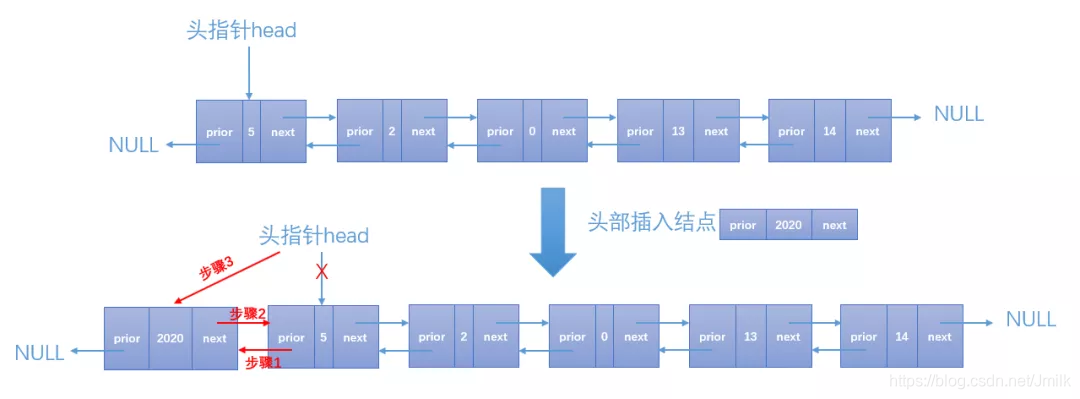
插入链表结点
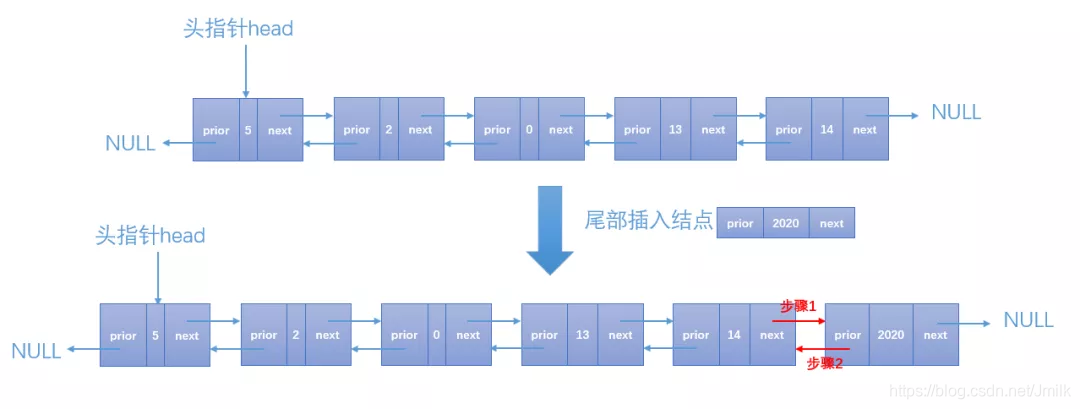
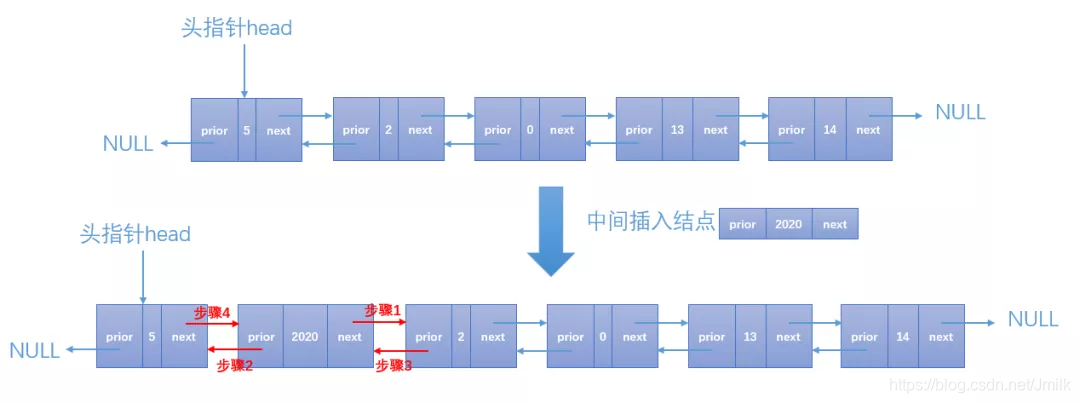
插入一个链表的节点有 3 种情况:
- 头部插入

- 尾部插入

- 中间插入

static int dlist_insert(dlist_node_t* dlist, int idx, data_type insert_data)
{ printf("dlist_insert, index: %d, insert_data: %d\n", idx, insert_data); /* 构造一个新的结点。 */ dlist_node_t* new_node = (dlist_node_t*)malloc(sizeof(dlist_node_t)); new_node->next = NULL; new_node->prior = NULL; new_node->data = insert_data; if (idx > (DL_LEN + 1)) { printf("Position out of bounds.\n"); // 新结点的位置不连续 return FAIL; } /* 头部插入。 */ if (1 == idx) { dlist->prior = new_node; // 步骤 1 new_node->next = dlist; // 步骤 2 dlist = new_node; // 步骤 3 } else { dlist_node_t* temp = dlist; for (int i=1; i<idx; i++) { temp = temp->next; } /* 中间插入。 */ if (temp->next != NULL) { new_node->next = temp->next; // 步骤 1 new_node->prior = temp; // 步骤 2 temp->next->prior = new_node; // 步骤 3 temp->next = new_node; // 步骤 4 } else { temp->next = new_node; // 步骤 1 new_node->prior = temp; // 步骤 2 } } return SUCCESS;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
删除结点
tatic int dlist_delete(dlist_node_t* dlist, data_type del_data) { printf("dlist_delete, del_data: %d\n", del_data); dlist_node_t* temp = dlist; while (temp) { if (del_data == temp->data) { temp->next->prior = temp->prior; temp->prior->next = temp->next; free(temp); return SUCCESS; } else { temp = temp->next; } } printf("dlist_delete not exist.\n"); return FAIL;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
打印链表数据
static void dlist_print_int(dlist_node_t* dlist)
{ dlist_node_t* temp = dlist; int idx = 0; while (temp) { printf("index: %d - data: %d\n", idx, temp->data); temp = temp->next; idx++; }
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
文章来源: is-cloud.blog.csdn.net,作者:范桂飓,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:is-cloud.blog.csdn.net/article/details/105918103
【版权声明】本文为华为云社区用户转载文章,如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)