Go 语言编程 — gorm 数据库版本迁移
目录
前言
本文示例为 GORM V2.0 版本。
AutoMigrate
GORM 的 AutoMigrate() 方法用于自动迁移 ORM 的 Schemas。所谓 “迁移” 就是刷新数据库中的表格定义,使其保持最新(只增不减)。
AutoMigrate 会创建(新的)表、缺少的外键、约束、列和索引,并且会更改现有列的类型(如果其大小、精度、是否为空可更改的话)。但不会删除未使用的列,以保护现存的数据。
// 初始化一张表
db.AutoMigrate(&User{})
// 初始化多张表
db.AutoMigrate(&User{}, &Product{}, &Order{})
// 创建表的同时进行表属性配置
db.Set("gorm:table_options", "ENGINE=InnoDB").AutoMigrate(&User{})
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
在 2.0 版本中,AutoMigrate 还会自动创建数据库表的约束,包括:外键约束。这在 1.9 版本中,则需要显示的通过 sql tag 来完成。
2.0 还支持在初始化时禁用此功能:
db, err := gorm.Open(sqlite.Open("gorm.db"), &gorm.Config{
DisableForeignKeyConstraintWhenMigrating: true,
})
- 1
- 2
- 3
示例
以 SQLite 数据库存储为例。
- V1 Schema
type Product struct {
gorm.Model
Code string
Price string
}
// 初始化 V1
db.AutoMigrate(&Product{})
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
其在数据库的存储格式为:

- V2 Schema:新增了一个 Age 字段
type Product struct {
gorm.Model
Code string
Price string
Age string
}
// 更新 V2
db.AutoMigrate(&Product{})
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
数据库会自动为 products 表新增 age 列,旧数据记录的 age 列值为空(NULL),新数据记录的 age 列值可以不为空:
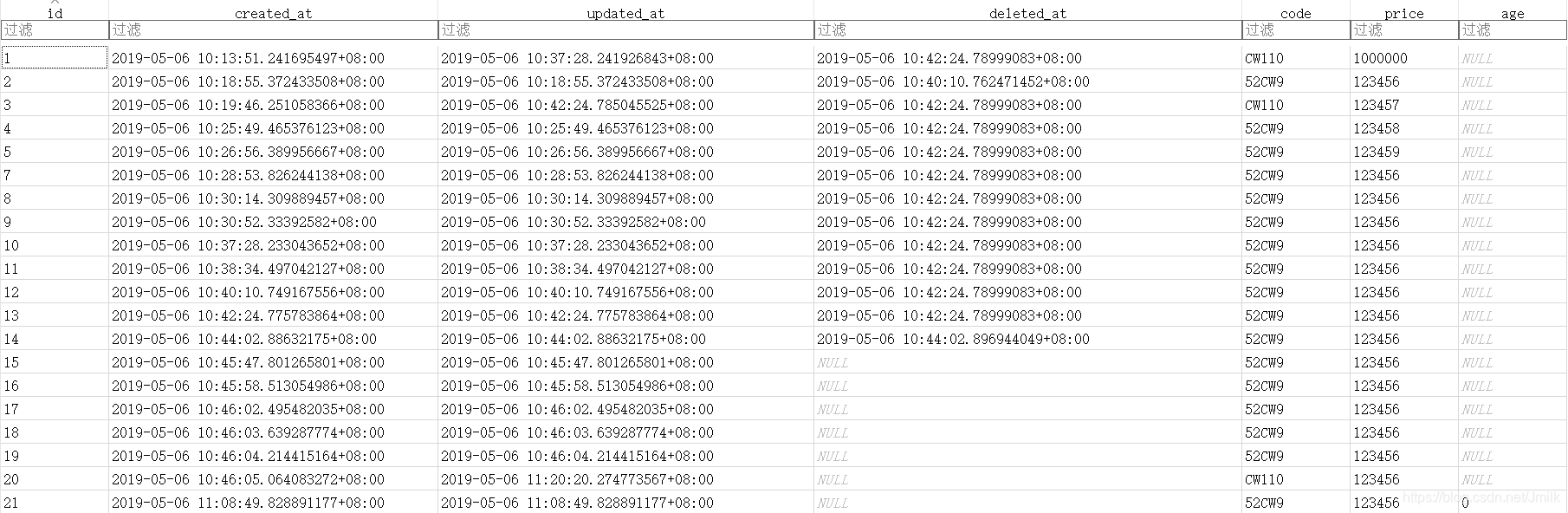
- V3 Schema:删除了 Price 和 Age 字段
type Product struct {
gorm.Model
Code string
}
// 更新 V3
db.AutoMigrate(&Product{})
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
数据库不会自动为 products 表删减 price 和 age 列,旧数据记录依旧存在且可以使用,新数据纪录的 price 和 age 的列值为空(NULL):
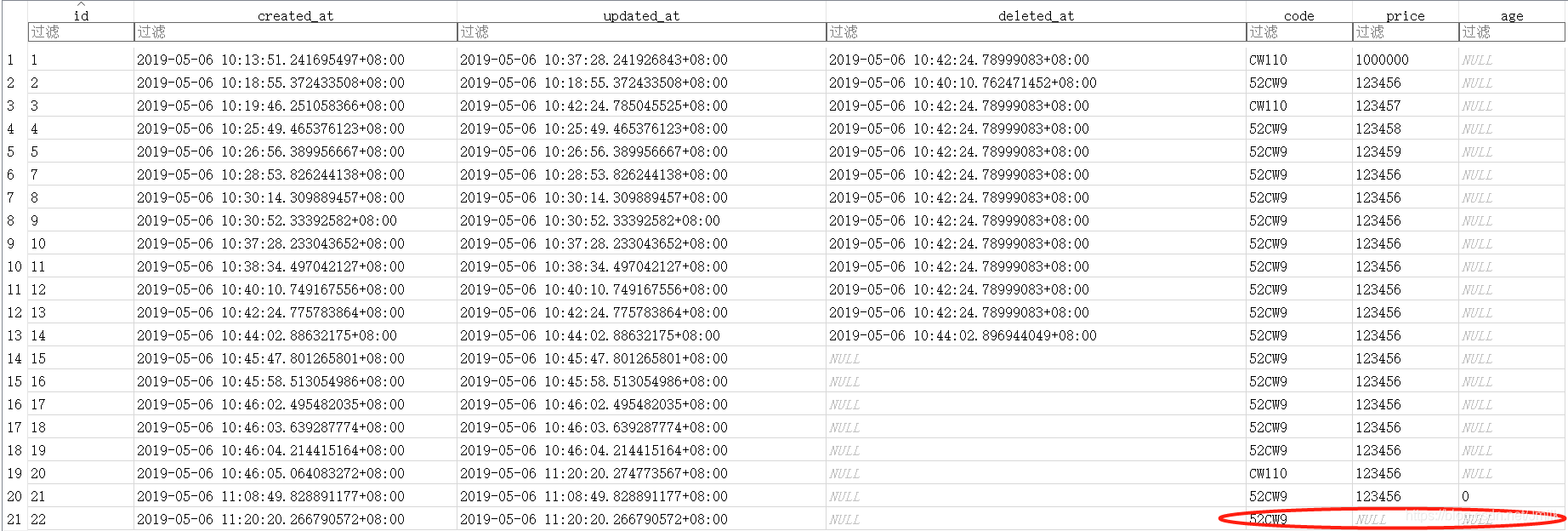
Migrator 接口(DDL 操作方法)
如果 AutoMigrate 还不足以满足特殊的需求,那么 GORM 还提供了 Migrator 接口,可用来为 ORM Schemas 实现自定义的迁移逻辑。
Migrator 还为不同类型的数据库提供了统一的 API 抽象,例如:SQLite 不支持 ALTER COLUMN、DROP COLUMN 等 SQL 子句,所以当我们调用 Migrator API 试图修改表结构时,GORM 会自定为在 SQLite 创建一张新表、并复制所有数据,然后删除旧表、重命名新表。
再例如:旧版本的 MySQL 不支持 rename 列、索引,GORM 也会基于当前的 MySQL 的版本执行不同 SQL。
type Migrator interface {
// AutoMigrate
AutoMigrate(dst ...interface{}) error // Database
CurrentDatabase() string
FullDataTypeOf(*schema.Field) clause.Expr // Tables
CreateTable(dst ...interface{}) error
DropTable(dst ...interface{}) error
HasTable(dst interface{}) bool
RenameTable(oldName, newName interface{}) error // Columns
AddColumn(dst interface{}, field string) error
DropColumn(dst interface{}, field string) error
AlterColumn(dst interface{}, field string) error
HasColumn(dst interface{}, field string) bool
RenameColumn(dst interface{}, oldName, field string) error
MigrateColumn(dst interface{}, field *schema.Field, columnType *sql.ColumnType) error
ColumnTypes(dst interface{}) ([]*sql.ColumnType, error) // Constraints
CreateConstraint(dst interface{}, name string) error
DropConstraint(dst interface{}, name string) error
HasConstraint(dst interface{}, name string) bool // Indexes
CreateIndex(dst interface{}, name string) error
DropIndex(dst interface{}, name string) error
HasIndex(dst interface{}, name string) bool
RenameIndex(dst interface{}, oldName, newName string) error
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
表操作
// 为 `User` 创建表
db.Migrator().CreateTable(&User{})
// 将 "ENGINE=InnoDB" 添加到创建 `User` 的 SQL 里去
db.Set("gorm:table_options", "ENGINE=InnoDB").CreateTable(&User{})
// 检查 `User` 对应的表是否存在
db.Migrator().HasTable(&User{})
db.Migrator().HasTable("users")
// 如果存在表则删除(删除时会忽略、删除外键约束)
db.Migrator().DropTable(&User{})
db.Migrator().DropTable("users")
// 重命名表
db.Migrator().RenameTable(&User{}, &UserInfo{})
db.Migrator().RenameTable("users", "user_infos")
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
列操作
type User struct {
Name string
}
// 添加 name 字段
db.Migrator().AddColumn(&User{}, "Name")
// 删除 name 字段
db.Migrator().DropColumn(&User{}, "Name")
// 修改 name 字段
db.Migrator().AlterColumn(&User{}, "Name")
// 检查字段是否存在
db.Migrator().HasColumn(&User{}, "Name")
type User struct {
Name string
NewName string
}
// 重命名字段
db.Migrator().RenameColumn(&User{}, "Name", "NewName")
db.Migrator().RenameColumn(&User{}, "name", "new_name")
// 获取字段类型
db.Migrator().ColumnTypes(&User{}) ([]*sql.ColumnType, error)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
约束操作
包括基本的数据完整性约束类型。
type UserIndex struct {
Name string `gorm:"check:name_checker,name <> 'jinzhu'"`
}
// 创建约束
db.Migrator().CreateConstraint(&User{}, "name_checker")
// 删除约束
db.Migrator().DropConstraint(&User{}, "name_checker")
// 检查约束是否存在
db.Migrator().HasConstraint(&User{}, "name_checker")
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
索引操作
type User struct {
gorm.Model
Name string `gorm:"size:255;index:idx_name,unique"`
}
// 为 Name 字段创建索引
db.Migrator().CreateIndex(&User{}, "Name")
db.Migrator().CreateIndex(&User{}, "idx_name")
// 为 Name 字段删除索引
db.Migrator().DropIndex(&User{}, "Name")
db.Migrator().DropIndex(&User{}, "idx_name")
// 检查索引是否存在
db.Migrator().HasIndex(&User{}, "Name")
db.Migrator().HasIndex(&User{}, "idx_name")
type User struct {
gorm.Model
Name string `gorm:"size:255;index:idx_name,unique"`
Name2 string `gorm:"size:255;index:idx_name_2,unique"`
}
// 修改索引名
db.Migrator().RenameIndex(&User{}, "Name", "Name2")
db.Migrator().RenameIndex(&User{}, "idx_name", "idx_name_2")
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
数据库版本控制
需要注意的是,GORM 虽然提供了不错的数据库迁移功能,但是距离理想的 “版本控制” 仍有距离。不支持,包括:版本记录、版本回退、版本选择。这些都需要开发者自行封装。
参考文档
https://gorm.io/zh_CN/docs/migration.html
https://davidchan0519.github.io/2019/05/06/gorm-automigrate/
文章来源: is-cloud.blog.csdn.net,作者:范桂飓,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:is-cloud.blog.csdn.net/article/details/108967581
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)