leetcode 刷题142 143
【摘要】 每天都要刷几题leetcode
看到了大神的代码,毫不犹豫拷贝下来
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution(object):...
每天都要刷几题leetcode
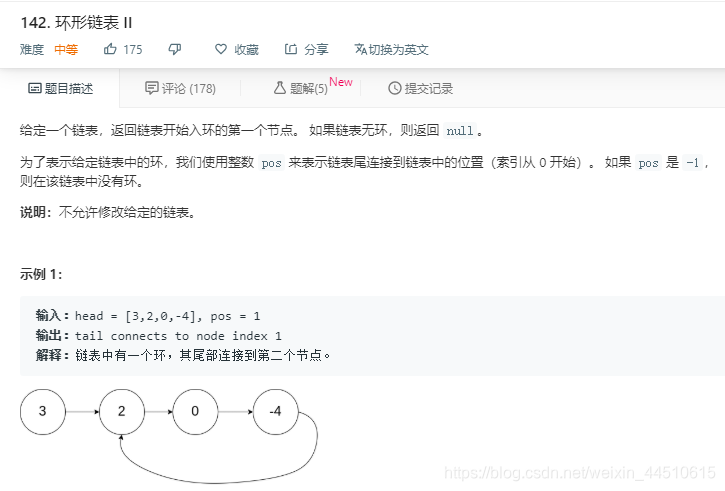

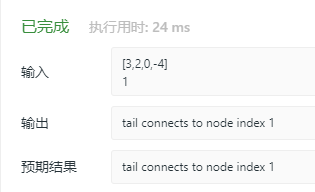
看到了大神的代码,毫不犹豫拷贝下来
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution(object): """ 原理:首先初始化快指针 fast = head.next.next 和 slow = head.next, 此时快指针走的路长为2, m慢指针走的路长为1,之后令快指针每次走两步, 慢指针每次走一步,这样快指针走的路长始终是慢指针走的路长的两倍, 若不存在环,直接返回None, 若存在环,则 fast 与 slow 肯定会在若干步之后相遇; 性质1: 设从head需要走 a 步到达环的入口,如果环存在的话, 再走 b 步可以再次到达该入口(即环的长度为b), 如果存在环的话,上述描述的 快指针 fast 和 慢指针slow 必然会相遇,且此时slow走的路长 小于 a + b(可以自行证明),设其为 a + x, 当快慢指针相遇时,快指针已经至少走完一圈环了, 不妨设相遇时走了完整的m圈(m >= 1),有: 快指针走的路长为 a + mb + x 慢指针走的路长为 a + x 由于快指针fast 走的路长始终是慢指针的 2倍,所以: a + mb + x = 2(a + x) 化简可得: a = mb - x ------------- (*) 当快指针与慢指针相遇时,由于 <性质1> 的存在, 可以在链表的开头初始化一个新的指针, 称其为 detection, 此时 detection 距离环的入口的距离为 a, 此时令 detection 和 fast 每次走一步, 会发现当各自走了 a 步之后,两个指针同时到达了环的入口,理由分别如下: detection不用说了,走了a步肯定到刚好到入口 fast已经走过的距离为 a + mb + x,当再走 a 步之后, fast走过的总距离为 2a + mb + x,带入性质1的(*)式可得: 2a + mb + x = a + 2mb,会发现,fast此时刚好走完了 整整 2m 圈环,正好处于入口的位置。 基于此,我们可以进行循环,直到 detection 和 fast 指向同一个对象,此时指向的对象恰好为环的入口。 """ def detectCycle(self, head): """ :type head: ListNode :rtype: ListNode """ # 首先初始化快指针和慢指针,确保快指针走的路的长度是慢指针长度的2倍 if head and head.next: fast = head.next.next slow = head.next else: return None # 说明无环 # 进行循环,首先让快指针和慢指针第一次相遇 while fast: if fast != slow: # 快指针走两步 if fast.next: fast = fast.next.next else: return None # 说明无环 # 慢指针走一步 slow = slow.next else: detection = head while detection != slow: # 此时由于slow和fast是一样的,用哪个都行 slow = slow.next detection = detection.next return detection
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
我这个垃圾
class Solution(object): def detectCycle(self, head): """ :type head: ListNode :rtype: ListNode """ l = [] while head and head not in l: l.append(head) head = head.next return head
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
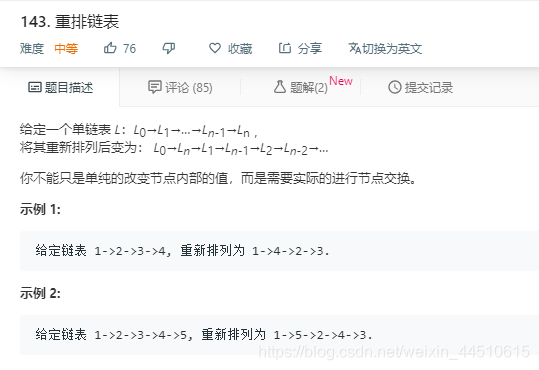
**
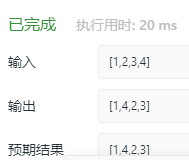
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution(object): def reorderList(self, head): """ :type head: ListNode :rtype: void Do not return anything, modify head in-place instead. """ if head is None or head.next is None: return #快慢指针找到链表中点s f = s = head while f and f.next: s = s.next f = f.next.next #中点之后的链表反转 p = c = s n = c.next while n: p = c c = n n = n.next c.next = p #c为末尾节点,双指针分别从头结点和末尾节点重构链表 n1 = h1 = head n2 = h2 = c while h1 != h2 and h1.next != h2: n1 = h1.next n2 = h2.next h1.next = h2 h2.next = n1 h1 = n1 h2 = n2 h2.next = None
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution(object): def reorderList(self, head): if not head or not head.next: return L = [] while head: L.append(head) head = head.next for i in range(len(L)//2): L[i].next = L[len(L)-i-1] L[len(L)-i-1].next = L[i+1] L[i+1].next = None
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
文章来源: maoli.blog.csdn.net,作者:刘润森!,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:maoli.blog.csdn.net/article/details/90975492
【版权声明】本文为华为云社区用户转载文章,如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)