DGL & RDKit | 基于Attentive FP可视化训练模型原子权重
【摘要】 DGL具有许多用于化学信息学、药物与生物信息学任务的函数。
DGL开发人员提供了用于可视化训练模型原子权重的代码。使用Attentive FP构建模型后,可以可视化给定分子的原子权重,意味着每个原子对目标值的贡献量。
基于Attentive FP可视化训练模型原子权重
环境准备
PyTorch:深度学习框架DGL:基于PyTorch的库,支持深度学习以处理图形RDK...
DGL具有许多用于化学信息学、药物与生物信息学任务的函数。
DGL开发人员提供了用于可视化训练模型原子权重的代码。使用Attentive FP构建模型后,可以可视化给定分子的原子权重,意味着每个原子对目标值的贡献量。
基于Attentive FP可视化训练模型原子权重
环境准备
- PyTorch:深度学习框架
- DGL:基于PyTorch的库,支持深度学习以处理图形
- RDKit:用于构建分子图并从字符串表示形式绘制结构式
- MDTraj:用于分子动力学轨迹分析的开源库
导入库
-
%matplotlib inline
-
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-
import os
-
from rdkit import Chem
-
from rdkit import RDPaths
-
-
import dgl
-
import numpy as np
-
import random
-
import torch
-
import torch.nn as nn
-
import torch.nn.functional as F
-
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
-
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
-
from dgl import model_zoo
-
-
from dgl.data.chem.utils import mol_to_complete_graph, mol_to_bigraph
-
-
from dgl.data.chem.utils import atom_type_one_hot
-
from dgl.data.chem.utils import atom_degree_one_hot
-
from dgl.data.chem.utils import atom_formal_charge
-
from dgl.data.chem.utils import atom_num_radical_electrons
-
from dgl.data.chem.utils import atom_hybridization_one_hot
-
from dgl.data.chem.utils import atom_total_num_H_one_hot
-
from dgl.data.chem.utils import one_hot_encoding
-
from dgl.data.chem import CanonicalAtomFeaturizer
-
from dgl.data.chem import CanonicalBondFeaturizer
-
from dgl.data.chem import ConcatFeaturizer
-
from dgl.data.chem import BaseAtomFeaturizer
-
from dgl.data.chem import BaseBondFeaturizer
-
-
from dgl.data.chem import one_hot_encoding
-
from dgl.data.utils import split_dataset
-
-
from functools import partial
-
from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score
代码来源于dgl/example
DGL开发人员提供了用于可视化训练模型原子权重的代码。
使用Attentive FP构建模型后,可以可视化给定分子的原子权重,意味着每个原子对目标值的贡献量。
-
def chirality(atom):
-
try:
-
return one_hot_encoding(atom.GetProp('_CIPCode'), ['R', 'S']) + \
-
[atom.HasProp('_ChiralityPossible')]
-
except:
-
return [False, False] + [atom.HasProp('_ChiralityPossible')]
-
-
def collate_molgraphs(data):
-
"""Batching a list of datapoints for dataloader.
-
Parameters
-
----------
-
data : list of 3-tuples or 4-tuples.
-
Each tuple is for a single datapoint, consisting of
-
a SMILES, a DGLGraph, all-task labels and optionally
-
a binary mask indicating the existence of labels.
-
Returns
-
-------
-
smiles : list
-
List of smiles
-
bg : BatchedDGLGraph
-
Batched DGLGraphs
-
labels : Tensor of dtype float32 and shape (B, T)
-
Batched datapoint labels. B is len(data) and
-
T is the number of total tasks.
-
masks : Tensor of dtype float32 and shape (B, T)
-
Batched datapoint binary mask, indicating the
-
existence of labels. If binary masks are not
-
provided, return a tensor with ones.
-
"""
-
assert len(data[0]) in [3, 4], \
-
'Expect the tuple to be of length 3 or 4, got {:d}'.format(len(data[0]))
-
if len(data[0]) == 3:
-
smiles, graphs, labels = map(list, zip(*data))
-
masks = None
-
else:
-
smiles, graphs, labels, masks = map(list, zip(*data))
-
-
bg = dgl.batch(graphs)
-
bg.set_n_initializer(dgl.init.zero_initializer)
-
bg.set_e_initializer(dgl.init.zero_initializer)
-
labels = torch.stack(labels, dim=0)
-
-
if masks is None:
-
masks = torch.ones(labels.shape)
-
else:
-
masks = torch.stack(masks, dim=0)
-
return smiles, bg, labels, masks
-
-
atom_featurizer = BaseAtomFeaturizer(
-
{'hv': ConcatFeaturizer([
-
partial(atom_type_one_hot, allowable_set=[
-
'B', 'C', 'N', 'O', 'F', 'Si', 'P', 'S', 'Cl', 'As', 'Se', 'Br', 'Te', 'I', 'At'],
-
encode_unknown=True),
-
partial(atom_degree_one_hot, allowable_set=list(range(6))),
-
atom_formal_charge, atom_num_radical_electrons,
-
partial(atom_hybridization_one_hot, encode_unknown=True),
-
lambda atom: [0], # A placeholder for aromatic information,
-
atom_total_num_H_one_hot, chirality
-
],
-
)})
-
bond_featurizer = BaseBondFeaturizer({
-
'he': lambda bond: [0 for _ in range(10)]
-
})
-
-
train_mols = Chem.SDMolSupplier('solubility.train.sdf')
-
train_smi =[Chem.MolToSmiles(m) for m in train_mols]
-
train_sol = torch.tensor([float(mol.GetProp('SOL')) for mol in train_mols]).reshape(-1,1)
-
-
test_mols = Chem.SDMolSupplier('solubility.test.sdf')
-
test_smi = [Chem.MolToSmiles(m) for m in test_mols]
-
test_sol = torch.tensor([float(mol.GetProp('SOL')) for mol in test_mols]).reshape(-1,1)
-
-
train_graph =[mol_to_bigraph(mol,
-
node_featurizer=atom_featurizer,
-
edge_featurizer=bond_featurizer) for mol in train_mols]
-
-
test_graph =[mol_to_bigraph(mol,
-
node_featurizer=atom_featurizer,
-
edge_featurizer=bond_featurizer) for mol in test_mols]
-
-
def run_a_train_epoch(n_epochs, epoch, model, data_loader,loss_criterion, optimizer):
-
model.train()
-
total_loss = 0
-
losses = []
-
-
for batch_id, batch_data in enumerate(data_loader):
-
batch_data
-
smiles, bg, labels, masks = batch_data
-
if torch.cuda.is_available():
-
bg.to(torch.device('cuda:0'))
-
labels = labels.to('cuda:0')
-
masks = masks.to('cuda:0')
-
-
prediction = model(bg, bg.ndata['hv'], bg.edata['he'])
-
loss = (loss_criterion(prediction, labels)*(masks != 0).float()).mean()
-
#loss = loss_criterion(prediction, labels)
-
#print(loss.shape)
-
optimizer.zero_grad()
-
loss.backward()
-
optimizer.step()
-
-
losses.append(loss.data.item())
-
-
#total_score = np.mean(train_meter.compute_metric('rmse'))
-
total_score = np.mean(losses)
-
print('epoch {:d}/{:d}, training {:.4f}'.format( epoch + 1, n_epochs, total_score))
-
return total_score
-
-
model = model_zoo.chem.AttentiveFP(node_feat_size=39,
-
edge_feat_size=10,
-
num_layers=2,
-
num_timesteps=2,
-
graph_feat_size=200,
-
output_size=1,
-
dropout=0.2)
-
-
train_loader = DataLoader(dataset=list(zip(train_smi, train_graph, train_sol)), batch_size=128, collate_fn=collate_molgraphs)
-
test_loader = DataLoader(dataset=list(zip(test_smi, test_graph, test_sol)), batch_size=128, collate_fn=collate_molgraphs)
-
-
loss_fn = nn.MSELoss(reduction='none')
-
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=10 ** (-2.5), weight_decay=10 ** (-5.0),)
-
n_epochs = 100
-
epochs = []
-
scores = []
-
for e in range(n_epochs):
-
score = run_a_train_epoch(n_epochs, e, model, train_loader, loss_fn, optimizer)
-
epochs.append(e)
-
scores.append(score)
-
model.eval()
导入用于分子可视化依赖库
-
import copy
-
from rdkit.Chem import rdDepictor
-
from rdkit.Chem.Draw import rdMolDraw2D
-
from IPython.display import SVG
-
from IPython.display import display
-
import matplotlib
-
import matplotlib.cm as cm
定义可视化函数
- 代码来源于DGL库。
- DGL模型具有get_node_weight选项,该选项返回图形的node_weight。该模型具有两层GRU,因此以下代码我将0用作时间步长,因此时间步长必须为0或1。
-
def drawmol(idx, dataset, timestep):
-
smiles, graph, _ = dataset[idx]
-
print(smiles)
-
bg = dgl.batch([graph])
-
atom_feats, bond_feats = bg.ndata['hv'], bg.edata['he']
-
if torch.cuda.is_available():
-
print('use cuda')
-
bg.to(torch.device('cuda:0'))
-
atom_feats = atom_feats.to('cuda:0')
-
bond_feats = bond_feats.to('cuda:0')
-
-
_, atom_weights = model(bg, atom_feats, bond_feats, get_node_weight=True)
-
assert timestep < len(atom_weights), 'Unexpected id for the readout round'
-
atom_weights = atom_weights[timestep]
-
min_value = torch.min(atom_weights)
-
max_value = torch.max(atom_weights)
-
atom_weights = (atom_weights - min_value) / (max_value - min_value)
-
-
norm = matplotlib.colors.Normalize(vmin=0, vmax=1.28)
-
cmap = cm.get_cmap('bwr')
-
plt_colors = cm.ScalarMappable(norm=norm, cmap=cmap)
-
atom_colors = {i: plt_colors.to_rgba(atom_weights[i].data.item()) for i in range(bg.number_of_nodes())}
-
-
mol = Chem.MolFromSmiles(smiles)
-
rdDepictor.Compute2DCoords(mol)
-
drawer = rdMolDraw2D.MolDraw2DSVG(280, 280)
-
drawer.SetFontSize(1)
-
op = drawer.drawOptions()
-
-
mol = rdMolDraw2D.PrepareMolForDrawing(mol)
-
drawer.DrawMolecule(mol, highlightAtoms=range(bg.number_of_nodes()),
-
highlightBonds=[],
-
highlightAtomColors=atom_colors)
-
drawer.FinishDrawing()
-
svg = drawer.GetDrawingText()
-
svg = svg.replace('svg:', '')
-
if torch.cuda.is_available():
-
atom_weights = atom_weights.to('cpu')
-
return (Chem.MolFromSmiles(smiles), atom_weights.data.numpy(), svg)
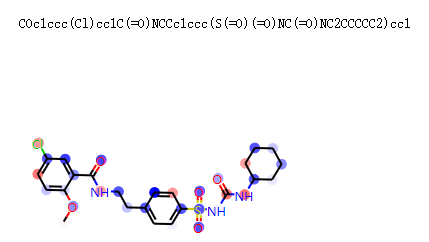
绘制测试数据集分子
该模型预测溶解度,颜色表示红色是溶解度的积极影响,蓝色是负面影响。
-
target = test_loader.dataset
-
for i in range(len(target)):
-
mol, aw, svg = drawmol(i, target, 0)
-
display(SVG(svg))
。。。。。
参考资料
1. https://github.com/dmlc/dgl/tree/master/apps/life_sci
2. https://github.com/dmlc/dgl/blob/master/python/dgl/model_zoo/chem/attentive_fp.py
3. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acs.jcim.9b00387
文章来源: drugai.blog.csdn.net,作者:DrugAI,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:drugai.blog.csdn.net/article/details/104868996
【版权声明】本文为华为云社区用户转载文章,如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)