【Linux C编程】第八章 文件操作相关函数
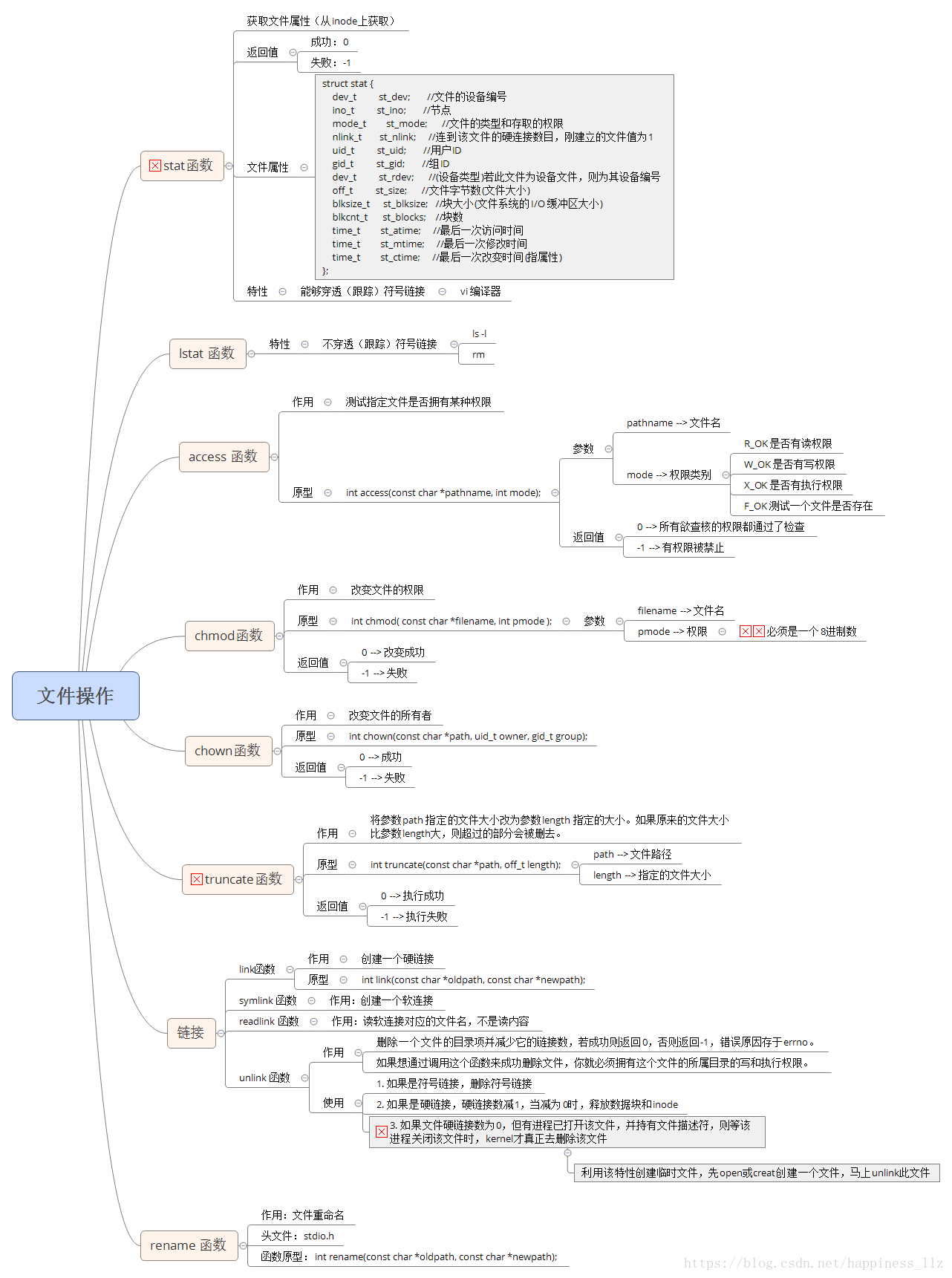
一、整体大纲
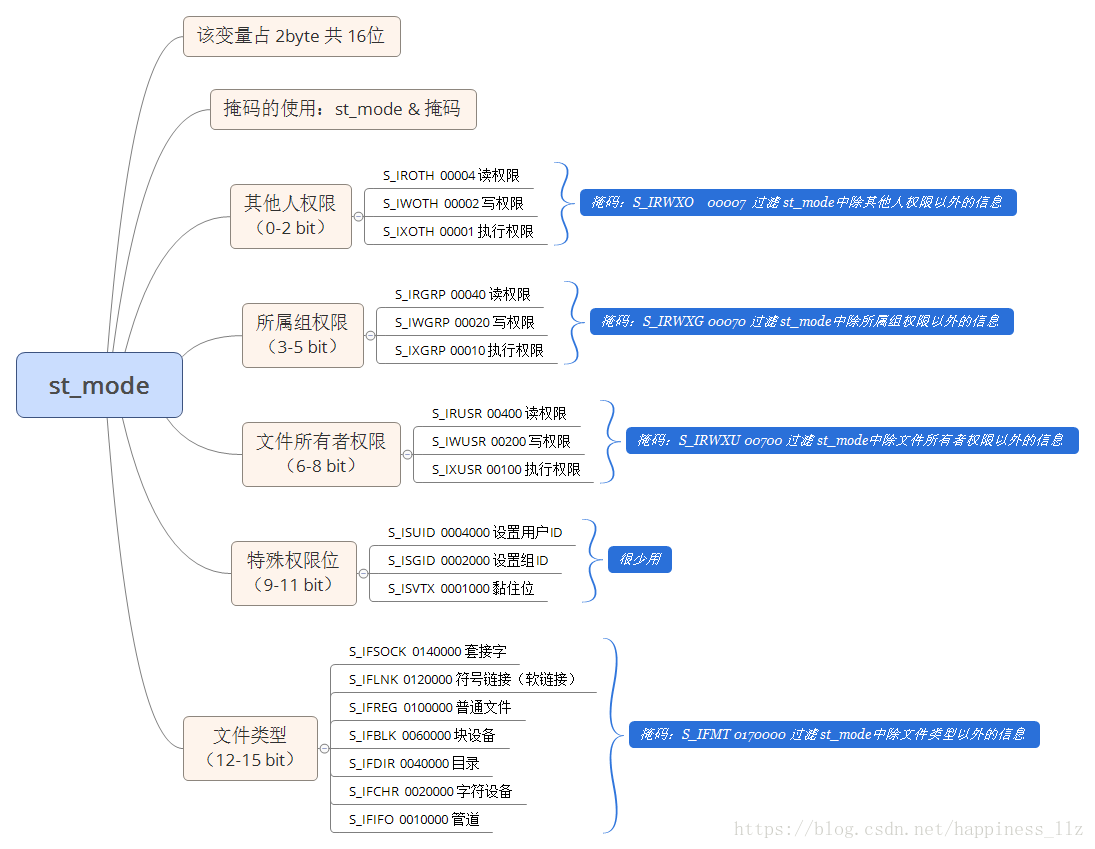
st_mode整体介绍:
二、 Linux文件操作相关函数
1. stat
- 作用:获得文件信息,也可以获取文件大小。
- 头文件
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>- 函数原型
int stat(const char *path, struct stat *buf);
int fstat(int fd, struct stat *buf);
int lstat(const char *path, struct stat *buf);- 参数说明:
path文件名
buf传出参数,定义结构体struct stat sb; &sb
- 返回值
失败:返回-1,设置errno
成功:返回0
注意: stat碰到链接,会追溯到源文件,穿透!!!lstat并不会穿透。
stat结构体:struct stat {
dev_t st_dev; /* ID of device containing file */
ino_t st_ino; /* inode number */
mode_t st_mode; /* protection */
nlink_t st_nlink; /* number of hard links */
uid_t st_uid; /* user ID of owner */
gid_t st_gid; /* group ID of owner */
dev_t st_rdev; /* device ID (if special file) */
off_t st_size; /* total size, in bytes */
blksize_t st_blksize; /* blocksize for file system I/O */
blkcnt_t st_blocks; /* number of 512B blocks allocated */
time_t st_atime; /* time of last access */
time_t st_mtime; /* time of last modification */
time_t st_ctime; /* time of last status change */
};linux命令stat执行结果:
[root@centos linuxC]# stat stat.c
文件:"stat.c"
大小:1857 块:8 IO 块:4096 普通文件
设备:fd00h/64768d Inode:17763202 硬链接:1
权限:(0644/-rw-r--r--) Uid:( 0/ root) Gid:( 0/ root)
环境:unconfined_u:object_r:usr_t:s0
最近访问:2019-04-27 19:17:15.149083960 +0800
最近更改:2019-04-27 19:17:15.149083960 +0800
最近改动:2019-04-27 19:17:15.202084912 +0800注意三个时间的区别:
time_t st_atime; /* time of last access */ 文件被读,比如cat,open读等
time_t st_mtime; /* time of last modification */ 文件内容发生改变
time_t st_ctime; /* time of last status change */ 文件属性发生变化,比如大小,权限,硬连接数等
上图的解释:
0-2 其他用户权限
3-5 组用户权限
6-8 用户权限
9-11 特殊权限位
12-15 文件类型示例:
Linux自带示例(打印文件相关信息)
1 #include <sys/types.h>
2 #include <sys/stat.h>
3 #include <time.h>
4 #include <stdio.h>
5 #include <stdlib.h>
6
7 int
8 main(int argc, char *argv[])
9 {
10 struct stat sb;
11
12 if (argc != 2) {
13 fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s <pathname>\n", argv[0]);
14 exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
15 }
16
17 if (stat(argv[1], &sb) == -1) {
18 perror("stat");
19 exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
20 }
21
22 printf("File type: ");
23
24 switch (sb.st_mode & S_IFMT) {
25 case S_IFBLK: printf("block device\n"); break;
26 case S_IFCHR: printf("character device\n"); break;
27 case S_IFDIR: printf("directory\n"); break;
28 case S_IFIFO: printf("FIFO/pipe\n"); break;
29 case S_IFLNK: printf("symlink\n"); break;
30 case S_IFREG: printf("regular file\n"); break;
31 case S_IFSOCK: printf("socket\n"); break;
32 default: printf("unknown?\n"); break;
33 }
34 printf("I-node number: %ld\n", (long) sb.st_ino);
35
36 printf("Mode: %lo (octal)\n",
37 (unsigned long) sb.st_mode);
38
39 printf("Link count: %ld\n", (long) sb.st_nlink);
40 printf("Ownership: UID=%ld GID=%ld\n",
41 (long) sb.st_uid, (long) sb.st_gid);
42
43 printf("Preferred I/O block size: %ld bytes\n",
44 (long) sb.st_blksize);
45 printf("File size: %lld bytes\n",
46 (long long) sb.st_size);
47 printf("Blocks allocated: %lld\n",
48 (long long) sb.st_blocks);
49
50 printf("Last status change: %s", ctime(&sb.st_ctime));
51 printf("Last file access: %s", ctime(&sb.st_atime));
52 printf("Last file modification: %s", ctime(&sb.st_mtime));
53
54 exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
55 }
需求:使用stat实现实现 ls -l 的功能?如下所示
[root@centos linuxC]# ll -l xx.log
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 4月 27 23:25 xx.log在实现的过程中需要获取用户名及组名,因此先看两个函数:
1)getpwuid
- 作用:通过用户的uid获取用户名
- 头文件
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <pwd.h>- 函数原型
struct passwd *getpwuid(uid_t uid);- 参数说明:
uid用户的uid
- 返回值
失败:返回NULL
成功:返回 struct passwd * 结构体指针
其中:
struct passwd {
char *pw_name; /* username */ 用户名
char *pw_passwd; /* user password */
uid_t pw_uid; /* user ID */
gid_t pw_gid; /* group ID */
char *pw_gecos; /* user information */
char *pw_dir; /* home directory */
char *pw_shell; /* shell program */
};2)getgrgid- 作用:通过用户的gid获取用户组名
- 头文件
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <grp.h>- 函数原型
struct group *getgrgid(gid_t gid);- 参数说明:
gid用户组的gid
- 返回值
失败:返回NULL
成功:返回 struct group * 结构体指针
其中:
struct group {
char *gr_name; /* group name */
char *gr_passwd; /* group password */
gid_t gr_gid; /* group ID */
char **gr_mem; /* group members */
};3)localtime- 作用:获取本地时间
- 头文件
#include <time.h>- 函数原型
struct tm *localtime(const time_t *timep);- 参数说明:
timep:一个时间相关的结构体
- 返回值
失败:返回NULL
成功:返回 struct tm * 结构体指针
其中:
struct tm {
int tm_sec; /* seconds */
int tm_min; /* minutes */
int tm_hour; /* hours */
int tm_mday; /* day of the month */
int tm_mon; /* month */
int tm_year; /* year */
int tm_wday; /* day of the week */
int tm_yday; /* day in the year */
int tm_isdst; /* daylight saving time */
};传入参数 timep 对应stat函数得到的结构体的秒数(time_t类型)。
最终实现:
使用stat实现一个ls -l命令
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<unistd.h>
3 #include<sys/types.h>
4 #include<sys/stat.h>
5 #include<fcntl.h>
6 #include<string.h>
7 #include<time.h>
8 #include <grp.h>
9 #include <pwd.h>
10
11 int main(int argc, char *argv[])
12 {
13 if (argc != 2)
14 {
15 printf("./a.out filename\n");
16 return -1;
17 }
18 struct stat sb;
19 stat(argv[1], &sb);
20
21 char stmode[11] = {0};
22 memset(stmode, '-', sizeof(stmode)-1);
23
24 //解析文件属性
25 if (S_ISREG(sb.st_mode)) stmode[0] = '-'; //普通文件
26 if (S_ISDIR(sb.st_mode)) stmode[0] = 'd';
27 if (S_ISCHR(sb.st_mode)) stmode[0] = 'c';
28 if (S_ISBLK(sb.st_mode)) stmode[0] = 'b';
29 if (S_ISFIFO(sb.st_mode)) stmode[0] = 'p';
30 if (S_ISLNK(sb.st_mode)) stmode[0] = 'l';
31 if (S_ISSOCK(sb.st_mode)) stmode[0] = 's';
32
33 //解析权限
34 //user
35 if (sb.st_mode & S_IRUSR) stmode[1] = 'r';
36 if (sb.st_mode & S_IWUSR) stmode[2] = 'w';
37 if (sb.st_mode & S_IXUSR) stmode[3] = 'x';
38 //group
39 if (sb.st_mode & S_IRGRP) stmode[4] = 'r';
40 if (sb.st_mode & S_IWGRP) stmode[5] = 'w';
41 if (sb.st_mode & S_IXGRP) stmode[6] = 'x';
42 //other
43 if (sb.st_mode & S_IROTH) stmode[7] = 'r';
44 if (sb.st_mode & S_IWOTH) stmode[9] = 'w';
45 if (sb.st_mode & S_IXOTH) stmode[10] = 'x';
46
47 //分析 用户名,组名可以通过函数获得 getpwuid, getgrgid
48 //时间获取
49 struct tm *filetm = localtime(&sb.st_atim.tv_sec);
50 char timebuf[20] = {0};
51 sprintf(timebuf, "%d月 %d %02d:%02d", filetm->tm_mon+1, filetm->tm_mday, filetm->tm_hour, filetm->tm_min);
52
53 printf("%s %ld %s %s %ld %s %s\n", stmode, sb.st_nlink, getpwuid(sb.st_uid)->pw_name,
54 getgrgid(sb.st_gid)->gr_name, sb.st_size, timebuf, argv[1]);
55
56 return 0;
57 }
2. access
- 作用:测试指定文件是否有某种权限
- 头文件
#include <unistd.h>- 函数原型
int access(const char *pathname, int mode);- 参数说明:
pathname文件名
mode:
R_OK
W_OK
X_OK
F_OK
- 返回值
失败:返回-1,设置errno
成功:如果有权限或者文件存在,对应返回0
判断文件读写执行及文件是否存在
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include <unistd.h>
3
4 int main(int argc, char *argv[])
5 {
6 if (argc != 2)
7 {
8 printf("./a.out filename\n");
9 return -1;
10 }
11 if (access(argv[1], R_OK) == 0) printf("%s read ok!\n", argv[1]);
12 if (access(argv[1], W_OK) == 0) printf("%s write ok!\n", argv[1]);
13 if (access(argv[1], X_OK) == 0) printf("%s exe ok!\n", argv[1]);
14 if (access(argv[1], F_OK) == 0) printf("%s file exists!\n", argv[1]);
15
16 return 0;
17
18 }
3. chmod
#include <sys/stat.h>
int chmod(const char *path, mode_t mode);4. truncate
- 函数作用:截断文件
- 头文件
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>- 函数原型
int truncate(const char *path, off_t length);
int ftruncate(int fd, off_t length);- 参数说明:
path文件名
length长度,长度如果大于原文件,直接拓展,如果小于原文件,截断为length长度。
- 返回值
成功:返回0
失败:返回-1,设置errno
示例:
truncate示例
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<sys/types.h>
3 #include<stdio.h>
4
5 int main(int argc, char *argv[])
6 {
7 if (argc != 2)
8 {
9 printf("./a.out filename\n");
10 return -1;
11 }
12 truncate(argv[1], 1024);
13 return 0;
14 }
5. link
- 函数作用:创建硬连接
- 头文件
#include <unistd.h>- 函数原型
int link(const char *oldpath, const char *newpath);- 参数说明:
oldpath原文件
newpath硬连接文件
- 返回值
成功:返回0
失败:返回-1,设置errno
示例:
创建硬连接示例
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include <unistd.h>
3
4 int main(int argc, char *argv[])
5 {
6 if (argc != 2)
7 {
8 printf("./a.out filename\n");
9 return -1;
10 }
11
12 char filename[1024] = {0};
13 sprintf(filename, "%s_hard", argv[1]);
14
15 link(argv[1], filename);
16
17 return 0;
18 }
6. symlink
- 函数作用:创建软连接
- 头文件
#include <unistd.h>- 函数原型
int symlink(const char *oldpath, const char *newpath);- 参数解释:
oldpath原文件
newpath创建软连接文件
- 返回值
成功:返回0
失败:返回-1,设置errno
示例:
创建软连接
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include <unistd.h>
3
4 int main(int argc, char *argv[])
5 {
6 if (argc != 2)
7 {
8 printf("./a.out filename\n");
9 return -1;
10 }
11
12 char filename[1024] = {0};
13 sprintf(filename, "%s_soft", argv[1]);
14
15 symlink(argv[1], filename);
16
17 return 0;
18 }
6. readlink
- 函数作用:读取文件链接信息
- 头文件
#include <unistd.h>- 函数原型
ssize_t readlink(const char *path, char *buf, size_t bufsiz);- 参数解释:
path链接名
buf缓冲区
bufsiz缓冲区大小
- 返回值
成功:返回buf填充的大小
失败:返回-1,设置errno
示例:
readlink示例
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include <unistd.h>
3
4 int main(int argc, char *argv[])
5 {
6 if (argc != 2)
7 {
8 printf("./a.out filename\n");
9 return -1;
10 }
11
12 char buf[32] = {0};
13 readlink(argv[1], buf, sizeof(buf));
14 printf("buf is %s\n", buf);
15
16 unlink(argv[1]);
17
18 return 0;
19 }
7. unlink
- 函数作用:删除软硬链接
- 头文件
#include <unistd.h>- 函数原型
int unlink(const char *pathname);- 函数参数:
pathname 链接名,文件也可以
- 返回值
成功:返回0
失败:返回-1,设置errno
示例:
unlink示例
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include <unistd.h>
3 #include<stdlib.h>
4 #include<fcntl.h>
5 #include<string.h>
6 #include<sys/types.h>
7
8 int main(int argc, char *argv[])
9 {
10 if (argc != 2)
11 {
12 printf("./a.out filename\n");
13 return -1;
14 }
15
16 int fd = open(argv[1], O_WRONLY|O_CREAT, 0666);
17 //注意只要有进程在使用该文件,则unlink在该文件退出时删除该文件
18 unlink(argv[1]);
19
20 int ret = write(fd, "hello", 5);
21 if (ret > 0)
22 {
23 printf("write ok! %d\n", ret);
24 }
25 if (ret < 0)
26 {
27 perror("write err");
28 }
29
30 close(fd);
31
32 return 0;
33 }
8. chown
- 函数作用:修改文件属主及属组
- 头文件
#include <unistd.h>- 函数原型
int chown(const char *path, uid_t owner, gid_t group);- 函数参数:
path文件名
owner用户ID,/etc/passwd
owner组ID,/etc/group
- 返回值
成功:返回0
失败:返回-1,设置errno
9. rename
- 函数作用:文件或者目录重命名
- 头文件
#include <stdio.h>- 函数原型
int rename(const char *oldpath, const char *newpath);- 参数说明:
oldpath文件名
newpath文件新名
- 返回值
成功:返回0
失败:返回-1,设置errno
示例:
rename示例
1 #include<stdio.h>
2
3 int main(int argc, char *argv[])
4 {
5 if (argc != 2)
6 {
7 printf("./a.out filename\n");
8 return -1;
9 }
10
11 char buf[1024] = {0};
12 sprintf(buf, "%s_new", argv[1]);
13 rename(argv[1], buf);
14
15 return 0;
16 }
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)