初学Java常用设计模式之——装饰器模式
【摘要】
声明:转载请附上原文链接
提示:标题序号从8开始,是照应不同设计模式笔记发布的顺序而定的,比如,上一篇文章 初学Java常用设计模式之——桥接模式和组合模式 序号从7开始。
8. 装饰器设计模式(重点)
8.1 装饰器设计模式简介
装饰器设计模式(Decorator Pattern) 也叫包装设计模式,属于结构型模式,它是作为现有的 类的⼀个包装,允许...
声明:转载请附上原文链接
提示:标题序号从8开始,是照应不同设计模式笔记发布的顺序而定的,比如,上一篇文章 初学Java常用设计模式之——桥接模式和组合模式 序号从7开始。
8. 装饰器设计模式(重点)
8.1 装饰器设计模式简介
- 装饰器设计模式(Decorator Pattern)
- 也叫包装设计模式,属于结构型模式,它是作为现有的 类的⼀个包装,允许向⼀个现有的对象添加新的功能, 同时⼜不改变其结构
- 给对象增加功能,⼀般两种⽅式 继承或关联组合,将⼀ 个类的对象嵌⼊另⼀个对象中,由另⼀个对象来决定是 否调⽤嵌⼊对象的⾏为来增强功能,这个就是装饰器模 式,⽐继承模式更加灵活
- 应⽤场景
- 以动态、透明的⽅式给单个对象添加职责,但⼜能不改 变其结构
- JDK源码⾥⾯应⽤的最多的就是IO流,⼤量使⽤装饰设 计模式
-
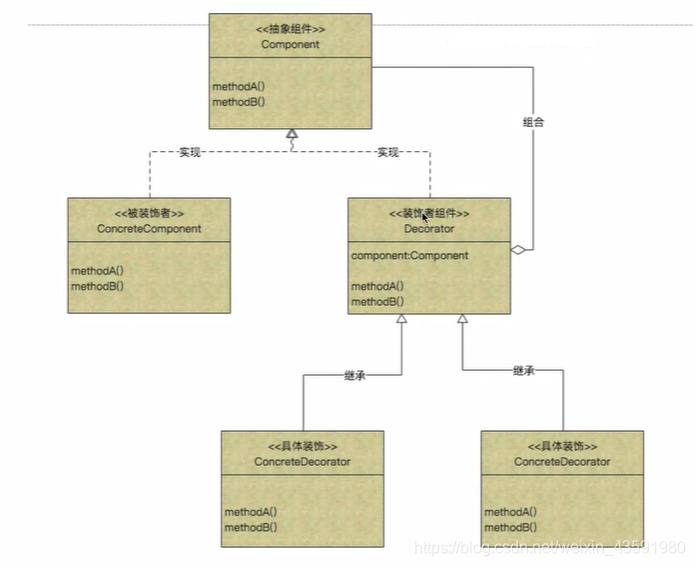
⻆⾊(装饰者和被装饰者有相同的超类(Component))
- 抽象组件(Component)
- 定义装饰⽅法的规范,比如,最初的⾃⾏⻋,仅仅定义了 ⾃⾏⻋的API;
- 被装饰者(ConcreteComponent)
- Component的具体实现,也就是我们要装饰的具体 对象
- 实现了核⼼⻆⾊的具体⾃⾏⻋
- 装饰者组件(Decorator)
- 定义具体装饰者的⾏为规范, 和Component⻆⾊有 相同的接⼝,持有组件(Component)对象的实例引⽤
- ⾃⾏⻋组件都有名称和价格
- 具体装饰物(ConcreteDecorator)
- 负责给构件对象装饰附加的功能
- ⽐如给自行车加喇叭,或者加防爆胎
- 抽象组件(Component)
8.2 案例
抽象组件(Component)——自行车抽象接口
/**
* @Auther: csp1999
* @Date: 2020/11/15/12:43
* @Description: 自行车抽象接口(抽象组件component)
*/
public interface Bike { /** * 自行车相关的描述 * @return */ String getDescription(); /** * 自行车价格 * @return */ int getPrice();
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
被装饰者(ConcreteComponent)——大/小号自行车
/**
* @Auther: csp1999
* @Date: 2020/11/15/12:45
* @Description: 大号自行车(具体的被装饰者ConcreteComponent)
*/
public class BigBike implements Bike{ private String description = "大号自行车"; @Override public String getDescription() { return description; } /** * 200元是大号自行车的价格 * @return */ @Override public int getPrice() { return 200; }
}
----------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* @Auther: csp1999
* @Date: 2020/11/15/12:45
* @Description: 小号自行车(具体的被装饰者ConcreteComponent)
*/
public class SmallBike implements Bike{ private String description = "小号自行车"; @Override public String getDescription() { return description; } /** * 100元是小号自行车的价格 * @return */ @Override public int getPrice() { return 100; }
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
装饰者组件(Decorator)
/**
* @Auther: csp1999
* @Date: 2020/11/15/12:50
* @Description: 装饰者组件Decorator
*/
public class BikeDecorator implements Bike{ private String description = "我只是装饰器,什么都不表示,子类帮我传递..."; @Override public String getDescription() { return description; } @Override public int getPrice() { return 0; }
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
具体装饰物(ConcreteDecorator)——防爆胎/喇叭
/**
* @Auther: csp1999
* @Date: 2020/11/15/12:53
* @Description: 防爆胎(具体装饰ConcreteDecorator)
*/
public class RSCBikeDecorator extends BikeDecorator {// 重写父类方法 private String description = "为自行车增加一个防爆胎..."; private Bike bike; public RSCBikeDecorator(Bike bike) { this.bike = bike; } @Override public String getDescription() { return bike.getDescription() + description; } /** * 50是防爆胎的价格 * @return */ @Override public int getPrice() { return bike.getPrice() + 50; }
}
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* @Auther: csp1999
* @Date: 2020/11/15/12:53
* @Description: 喇叭(具体装饰ConcreteDecorator)
*/
public class SuonaBikeDecorator extends BikeDecorator {// 重写父类方法 private String description = "为自行车增加一个喇叭..."; private Bike bike; public SuonaBikeDecorator(Bike bike) { this.bike = bike; } @Override public String getDescription() { return bike.getDescription() + description; } /** * 30是喇叭的价格 * @return */ @Override public int getPrice() { return bike.getPrice() + 30; }
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
测试
@Test
public void testDecorator() { /** * 大自行车200/小自行车100 * 防爆胎1 50 * 防爆胎2 50 * 喇叭 30 */ // 选一个自行车 Bike bike = new BigBike(); // 给自行车装2个RSC防爆胎 bike = new RSCBikeDecorator(bike); bike = new RSCBikeDecorator(bike); // 给自行车再装1个喇叭 bike = new SuonaBikeDecorator(bike); System.out.println(bike.getDescription()+" 价格: " + bike.getPrice());
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
测试结果:
大号自行车为自行车增加一个防爆胎...为自行车增加一个防爆胎...为自行车增加一个喇叭... 价格: 330
- 1
8.3 总结
- 装饰器设计模式优点
- 装饰模式与继承关系的⽬的都是要扩展对象的功能,但 装饰模式可以提供⽐继承更多的灵活性。
- 使⽤不同的具体装饰类以及这些装饰类的排列组合,可 以创造出很多不同⾏为的组合,原有代码⽆须改变,符 合“开闭原则”
- 装饰器设计模式缺点
- 装饰模式增加了许多⼦类,如果过度使⽤会使程序变得 很复杂 (多层包装)
- 增加系统的复杂度,加⼤学习与理解的难度
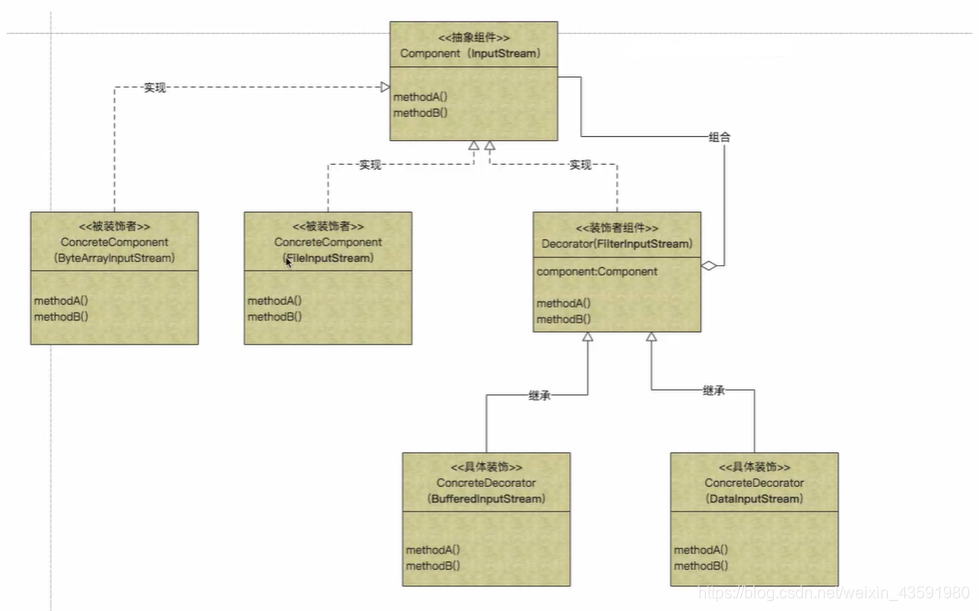
8.4 扩展:Stream IO流 中的装饰器设计模式
- 抽象组件(Component):InputStream
- 定义装饰⽅法的规范
- 被装饰者(ConcreteComponent) : FileInputStream 、 ByteArrayInputStream
- Component的具体实现,也就是我们要装饰的具体对 象
- 装饰者组件(Decorator):FilterInputStream
- 定义具体装饰者的⾏为规范, 和Component⻆⾊有相同 的接⼝,持有组件(Component)对象的实例引⽤
- ⾃⾏⻋组件 都有 名称和价格
- 具体装饰物 (ConcreteDecorator):BufferedInputStream、 DataInputStream
- 负责给构件对象装饰附加的功能
- ⽐如 喇叭,防爆胎
- 应⽤场景
//添加了Buffer缓冲功能
InputStream inputStream = new
BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(""));
- 1
- 2
- 3
如果文章对您有帮助希望点赞或者关注支持一下!
文章来源: csp1999.blog.csdn.net,作者:兴趣使然の草帽路飞,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:csp1999.blog.csdn.net/article/details/109702998
【版权声明】本文为华为云社区用户转载文章,如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)