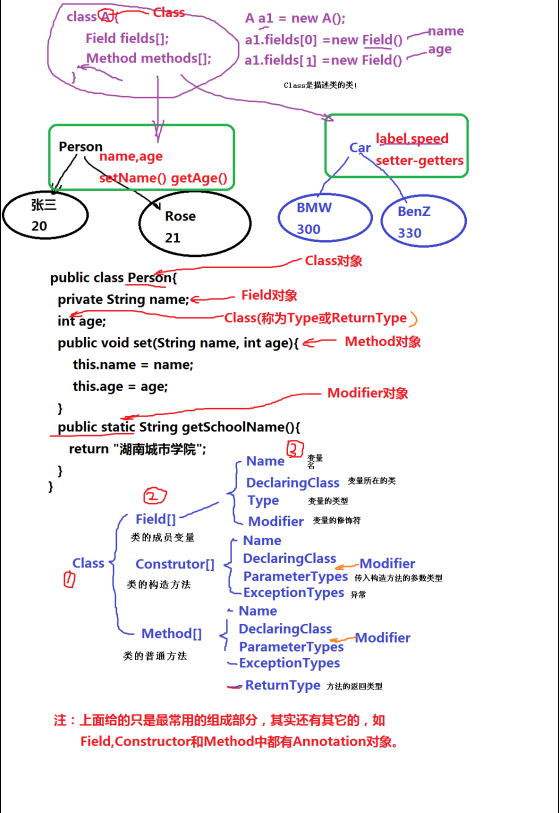
Java---类反射(1)---类反射入门和基础
什么是类反射
☆什么是反射
JAVA反射机制是在运行状态中,对于任意一个类,都能够知道这个类的所有属性和方法;对于任意一个对象,都能够调用它的任意一个方法和属性;这种动态获取的信息以及动态调用对象的方法的功能称为Java语言的反射机制。
反射(Reflection)是Java程序开发语言的特征之一,它允许运行中的Java程序对自身进行检查, 也称自审,并能直接操作程序的内部属性。例如,使用它能获得Java类中各成员的名称并显示出来。
Java的这一能力在实际应用中应用得很多,在其它的程序语言中根本就不存在这一特性。例如,Pascal、C或者C++中就没有办法在程序中获得函数定义相关的信息。
JavaBean是类反射的实际应用之一,它能让一些工具可视化的操作软件组件。这些工具通过类反射动态的载入并取得Java组件(类)的属性。后面学习的各种框架,基本上都会有反射的使用。
☆反射引例(HelloWorld、USB)
最简单的类反射:(相当于HelloWorld)
package cn.hncu.hello;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
/**
* 类反射的Helloworld版---入门
* 只演示了类方法的类反射---Method[]
* @author 陈浩翔
* @version 1.0 2016-5-1
*/
public class ReflectionHelloWold { public static void main(String[] args) { try { Class c = Class.forName("cn.hncu.introduce.Person"); System.out.println(c); Method mc[] = c.getDeclaredMethods();//获得 for(Method m:mc){ //获得整个方法 //包括修饰,返回类型,方法名字,方法参数 System.out.println(m); //解剖Method对象 System.out.println(Modifier.toString(m.getModifiers()));//修饰符 System.out.println(m.getReturnType());//返回类型 System.out.println(m.getName());//方法名字 Class pt[] = m.getParameterTypes(); for(Class p :pt){ System.out.println("parameter = "+p);//参数 } System.out.println(); System.out.println(m.getDeclaringClass());//这个方法所在的类 System.out.println(); System.out.println("------------------------------"); } } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
Person类:
package cn.hncu.introduce;
public class Person { private String name; int age; public final String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } private static final int sum(int age){ return 0; }
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
输出结果:
class cn.hncu.introduce.Person
private static final int cn.hncu.introduce.Person.sum(int)
private static final
int
sum
parameter = int
class cn.hncu.introduce.Person
------------------------------
public int cn.hncu.introduce.Person.getAge()
public
int
getAge
class cn.hncu.introduce.Person
------------------------------
public void cn.hncu.introduce.Person.setAge(int)
public
void
setAge
parameter = int
class cn.hncu.introduce.Person
------------------------------
public final java.lang.String cn.hncu.introduce.Person.getName()
public final
class java.lang.String
getName
class cn.hncu.introduce.Person
------------------------------
public void cn.hncu.introduce.Person.setName(java.lang.String)
public
void
setName
parameter = class java.lang.String
class cn.hncu.introduce.Person
------------------------------
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
USB实例:反射最大的好处是解耦
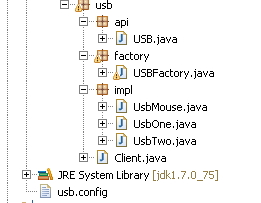
USB接口:
package cn.hncu.usb.api;
public interface USB { public abstract void work();
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
实现类:
package cn.hncu.usb.impl;
import cn.hncu.usb.api.USB;
public class UsbMouse implements USB{ @Override public void work() { System.out.println("UsbMouse...."); }
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
package cn.hncu.usb.impl;
import cn.hncu.usb.api.USB;
public class UsbOne implements USB{ @Override public void work() { System.out.println("UsbOne..."); }
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
package cn.hncu.usb.impl;
import cn.hncu.usb.api.USB;
public class UsbTwo implements USB{ @Override public void work() { System.out.println("UsbTwo...."); }
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
工厂方法:!!!读取配置文件的在这里
package cn.hncu.usb.factory;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Properties;
import cn.hncu.usb.api.USB;
public class USBFactory { public static USB getUSB(){ USB usb = null; Properties p = new Properties();//配置文件 FileInputStream in; try { in = new FileInputStream("usb.config");//读取配置文件 p.load(in); String className = p.getProperty("name"); //通过name获得name后面=号后面的字符串,这样就可以通过修改配置文件来new不同的类 Class c = Class.forName(className); usb = (USB) c.newInstance();//new 一个对象 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InstantiationException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return usb; }
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
main方法:
package cn.hncu.usb;
import cn.hncu.usb.api.USB;
import cn.hncu.usb.factory.USBFactory;
public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) { USB usb = USBFactory.getUSB(); usb.work(); }
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
配置文件:usb.config
你配置哪个,就是new哪个实现类的!!
‘#’号是配置文件的注释
#name = cn.hncu.usb.impl.UsbOne
#name = cn.hncu.usb.impl.UsbTwo
name = cn.hncu.usb.impl.UsbMouse
- 1
- 2
- 3
反射使用的三个步骤
用于反射的类,如Method,可以在java.lang.reflect包中找到。使用这些类的时候必须要遵循三个步骤:
第一步:获得你想操作的类的java.lang.Class对象。在运行中的Java程序中,用java.lang.Class类来描述类和接口等。
第二步:调用诸如getDeclaredMethods的方法,取得该类中定义的所有方法的列表。
第三步:使用反射的API来操作这些信息。
如下面这段代码:
Class c = Class.forName(“java.lang.String”);
Method ms[] = c.getDeclaredMethods();
System.out.println(ms[0].toString());
它将以文本方式打印出String中定义的第一个方法的原型。
☆反射示例(模拟instanceof的功能)
获取Class对象的三种方式
★ 方式一
通过对象的getClass方法进行获取。这种方式需要具体的类和该类的对象,以及调用getClass方法。
★ 方式二
任何数据类型(包括基本数据类型)都具备着一个静态的属性class,通过它可直接获取到该类型对应的Class对象。这种方式要使用具体的类,然后调用类中的静态属性class完成,无需调用方法,性能更好。
★ 方式三
通过Class.forName()方法获取。这种方式仅需使用类名,就可以获取该类的Class对象,更有利于扩展。
下面看怎么获取Class对象的代码:
package cn.hncu.reflect;
/**
* //获取Class对象的三种方式
* @author 陈浩翔
*
* @version 1.0 2016-5-1
*/
public class ReflectGetClass { public static void main(String[] args) { //getClassObj1(); //getClassObj2(); //getClassObj3(); test(); } private static void test() { Person p = new Person(); Object obj = (Object)p; Class c = obj.getClass();//运行时多态,new谁调谁 System.out.println(c);//输出为:class cn.hncu.reflect.Person System.out.println(int.class);//int System.out.println(Integer.class);//class java.lang.Integer System.out.println(Integer.TYPE);//int System.out.println((int.class)==(Integer.class));//false System.out.println((int.class)==(Integer.TYPE));//true } private static void getClassObj3() { try { String className = "cn.hncu.reflect.Person"; Class c = Class.forName(className);//3333用字符串(类名)---依赖于String类 System.out.println(c);//class cn.hncu.reflect.Person } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } private static void getClassObj2() { Class c = Person.class;//2222通过类名----依赖于Person类 System.out.println(c);//class cn.hncu.reflect.Person } private static void getClassObj1() { Person p1 = new Person(); Class c1 = p1.getClass();//1111通过对象 System.out.println(c1);//class cn.hncu.reflect.Person Person p2 = new Person(); Class c2 = p2.getClass(); System.out.println(p1==p2);//false-不同的对象 System.out.println(c1==c2);//true-同一个类模板,所有对象是共享同一个类模板的 }
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
运行结果在输出后面都注释了。。。
Class.isInstance(Object obj)判定指定的 Object 是否与此 Class 所表示的对象赋值兼容。
代码演示:
package cn.hncu.reflect;
/**
* @author 陈浩翔
* @version 1.0 2016-5-1
*/
public class SimulateInstanceof { /** * isInstance(Object obj)判定指定的 Object 是否与此 Class 所表示的对象赋值兼容。 * @param args * @throws Exception */ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Class c = Class.forName("cn.hncu.reflect.A"); boolean boo = c.isInstance(new Integer(100)); System.out.println(boo);//false boolean boo2 = c.isInstance( new A() ); System.out.println(boo2);//true boolean boo3 = c.isInstance(new B());//B和A兼容 //也就是说子类可以当父类用 System.out.println(boo3);//true }
}
class A{ private int age;
}
class B extends A{ private String name ;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
类的解剖(获取类的定义信息)
Person类:
package cn.hncu.reflect;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Person extends Parent{ String name; private int age; public int num; public static String schoolName; public Person(){ } private Person(String name, int age){ } protected Person(int age) throws IOException,NumberFormatException{ } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } protected void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } private int sum( int a){ return 0; } private int sum(){ return 0; } int aa(String a,int b) throws IOException,NumberFormatException{ return 0; }
}
class Parent{ public static final int N=100;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
★ 获取类的方法
找出一个类中定义了些什么方法,这是一个非常有价值也非常基础的反射用法。
代码演示:
package cn.hncu.reflect;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
/**
* 类的解剖(获取类的定义信息)
* @author 陈浩翔
*
* @version 1.0 2016-5-1
*/
public class ReflectDecompose { private static final String CLASS_FILE_NAME="cn.hncu.reflect.Person"; public static void main(String[] args) { try { fetchMethods(CLASS_FILE_NAME);//方法演示 } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 方法演示 * @param classFileName * @throws ClassNotFoundException */ private static void fetchMethods(String classFileName) throws ClassNotFoundException { Class c = Class.forName(CLASS_FILE_NAME); //1: 获取该类的能访问的所有public方法(包含当前类和父类的) Method methods[] = c.getMethods(); //2: 获取Person类中声明的所有方法,包括私有和其它权限的 //Method methods[] = c.getDeclaredMethods(); for(int i=0;i<methods.length;i++){ Method m = methods[i]; //System.out.println("modifiers:"+ m.getModifiers());//int,这个是数字。方法的修饰符 System.out.println("修饰符:"+ Modifier.toString( m.getModifiers() ) );//转换成字符串修饰符了。 System.out.println("方法返回类型:"+ m.getReturnType()); System.out.println("方法名称:"+ m.getName()); Class paramTypes[] = m.getParameterTypes();//方法需要传入的参数类型-为空就是没有 System.out.print("方法需要传入的参数类型: "); for(Class p:paramTypes){ System.out.print(p+" "); } System.out.println(); Class exceptionTypes[] = m.getExceptionTypes();//方法抛出的异常 System.out.print("方法抛出的异常: "); for(Class e:exceptionTypes){ System.out.print(e+" "); } System.out.println(); System.out.println("此方法属于的类: "+m.getDeclaringClass()); System.out.println(); System.out.println("--------------------------------"); } }
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
运行结果太长了,自己可以运行看看!
★ 获取类的构造器
找出一个类中定义的构造方法,构造器没有返回类型。
代码演示:
package cn.hncu.reflect;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
/**
* 类的解剖(获取类的定义信息)
* @author 陈浩翔
*
* @version 1.0 2016-5-1
*/
public class ReflectDecompose { private static final String CLASS_FILE_NAME="cn.hncu.reflect.Person"; public static void main(String[] args) { try { //fetchMethods(CLASS_FILE_NAME);//方法演示 fetchConstructors(CLASS_FILE_NAME);//类的构造方法演示 } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 类的构造方法演示 * @param classFileName * @throws ClassNotFoundException */ private static void fetchConstructors(String classFileName) throws ClassNotFoundException { Class c = Class.forName(CLASS_FILE_NAME); //构造方法不能继承父类的!!!!!!! //1: 该类中所有public的构造方法。 Constructor cons[] = c.getConstructors(); //2: 获取该类中声明的所有构造方法,包括私有和其它权限的 //Constructor cons[] = c.getDeclaredConstructors(); for(int i=0;i<cons.length;i++){ Constructor cs = cons[i]; //System.out.println("modifiers:"+ m.getModifiers());//int,这个是数字。方法的修饰符 System.out.println("修饰符:"+ Modifier.toString( cs.getModifiers() ) );//转换成字符串修饰符了。 System.out.println("构造方法名称:"+ cs.getName()); Class paramTypes[] = cs.getParameterTypes();//构造方法需要传入的参数类型-为空就是没有 System.out.print("构造方法需要传入的参数类型: "); for(Class p:paramTypes){ System.out.print(p+" "); } System.out.println(); Class exceptionTypes[] = cs.getExceptionTypes();//构造方法抛出的异常 System.out.print("构造方法抛出的异常: "); for(Class e:exceptionTypes){ System.out.print(e+" "); } System.out.println(); System.out.println("此构造方法属于的类: "+cs.getDeclaringClass());//全部是当前类!因为构造方法不能被继承 System.out.println(); System.out.println("--------------------------------"); } }
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
★ 获取类的属性字段
找出一个类中定义了哪些属性字段。
代码演示:
package cn.hncu.reflect;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
/**
* 类的解剖(获取类的定义信息)
* @author 陈浩翔
*
* @version 1.0 2016-5-1
*/
public class ReflectDecompose { private static final String CLASS_FILE_NAME="cn.hncu.reflect.Person"; public static void main(String[] args) { try { //fetchMethods(CLASS_FILE_NAME);//方法演示 //fetchConstructors(CLASS_FILE_NAME);//类的构造方法演示 fetchFields(CLASS_FILE_NAME);//类的成员变量演示 } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 类的成员变量演示 * @param classFileName * @throws ClassNotFoundException */ private static void fetchFields(String classFileName) throws ClassNotFoundException { Class c = Class.forName(CLASS_FILE_NAME); //获取该类及其父类中的所有public成员变量(属性) Field fields[] = c.getFields(); //获取该类声明的所有成员变量,包括私有及其它权限的 //Field fields[] = c.getDeclaredFields(); for(int i=0;i<fields.length;i++){ Field f = fields[i]; //System.out.println("modifiers:"+ m.getModifiers());//int,这个是数字。方法的修饰符 System.out.println("修饰符:"+ Modifier.toString( f.getModifiers() ) );//转换成字符串修饰符了。 System.out.println("方法名称:"+ f.getName()); System.out.println("此构造方法属于的类: "+f.getDeclaringClass());//全部是当前类!因为构造方法不能被继承 System.out.println(); System.out.println("--------------------------------"); } }
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
Class类真的很强大!
文章来源: chenhx.blog.csdn.net,作者:谙忆,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:chenhx.blog.csdn.net/article/details/51290566
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)