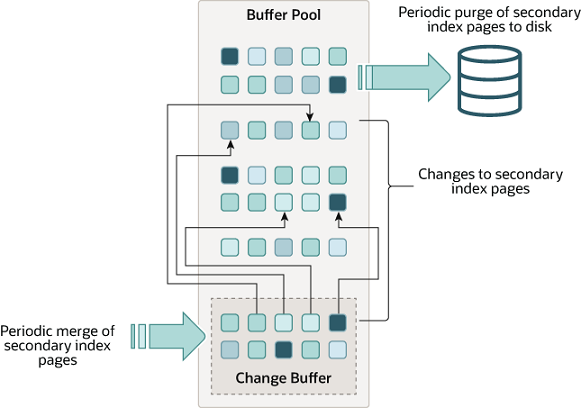
Change Buffer
The change buffer is a special data structure that caches changes to secondary index pages when those pages are not in the buffer pool. The buffered changes, which may result from INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE operations (DML), are merged later when the pages are loaded into the buffer pool by other read operations.
Unlike clustered indexes, secondary indexes are usually nonunique, and inserts into secondary indexes happen in a relatively random order. Similarly, deletes and updates may affect secondary index pages that are not adjacently located in an index tree. Merging cached changes at a later time, when affected pages are read into the buffer pool by other operations, avoids substantial random access I/O that would be required to read secondary index pages into the buffer pool from disk.
Periodically, the purge operation that runs when the system is mostly idle, or during a slow shutdown, writes the updated index pages to disk. The purge operation can write disk blocks for a series of index values more efficiently than if each value were written to disk immediately.
Change buffer merging may take several hours when there are many affected rows and numerous secondary indexes to update. During this time, disk I/O is increased, which can cause a significant slowdown for disk-bound queries. Change buffer merging may also continue to occur after a transaction is committed, and even after a server shutdown and restart (see Section 14.22.2, “Forcing InnoDB Recovery” for more information).
In memory, the change buffer occupies part of the buffer pool. On disk, the change buffer is part of the system tablespace, where index changes are buffered when the database server is shut down.
The type of data cached in the change buffer is governed by the innodb_change_buffering variable. For more information, see Configuring Change Buffering. You can also configure the maximum change buffer size. For more information, see Configuring the Change Buffer Maximum Size.
Change buffering is not supported for a secondary index if the index contains a descending index column or if the primary key includes a descending index column.
Configuring Change Buffering
When INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE operations are performed on a table, the values of indexed columns (particularly the values of secondary keys) are often in an unsorted order, requiring substantial I/O to bring secondary indexes up to date. The change buffer caches changes to secondary index entries when the relevant page is not in the buffer pool, thus avoiding expensive I/O operations by not immediately reading in the page from disk. The buffered changes are merged when the page is loaded into the buffer pool, and the updated page is later flushed to disk. The InnoDB main thread merges buffered changes when the server is nearly idle, and during a slow shutdown.
Because it can result in fewer disk reads and writes, change buffering is most valuable for workloads that are I/O-bound; for example, applications with a high volume of DML operations such as bulk inserts benefit from change buffering.
However, the change buffer occupies a part of the buffer pool, reducing the memory available to cache data pages. If the working set almost fits in the buffer pool, or if your tables have relatively few secondary indexes, it may be useful to disable change buffering. If the working data set fits entirely within the buffer pool, change buffering does not impose extra overhead, because it only applies to pages that are not in the buffer pool.
The innodb_change_buffering variable controls the extent to which InnoDB performs change buffering. You can enable or disable buffering for inserts, delete operations (when index records are initially marked for deletion) and purge operations (when index records are physically deleted). An update operation is a combination of an insert and a delete. The default innodb_change_buffering value is all.
Permitted innodb_change_buffering values include:
-
allThe default value: buffer inserts, delete-marking operations, and purges.
-
noneDo not buffer any operations.
-
insertsBuffer insert operations.
-
deletesBuffer delete-marking operations.
-
changesBuffer both inserts and delete-marking operations.
-
purgesBuffer physical deletion operations that happen in the background.
You can set the innodb_change_buffering variable in the MySQL option file (my.cnf or my.ini) or change it dynamically with the SET GLOBAL statement, which requires privileges sufficient to set global system variables. See Section 5.1.8.1, “System Variable Privileges”. Changing the setting affects the buffering of new operations; the merging of existing buffered entries is not affected.
The innodb_change_buffer_max_size variable permits configuring the maximum size of the change buffer as a percentage of the total size of the buffer pool. By default, innodb_change_buffer_max_size is set to 25. The maximum setting is 50.
Consider increasing innodb_change_buffer_max_size on a MySQL server with heavy insert, update, and delete activity, where change buffer merging does not keep pace with new change buffer entries, causing the change buffer to reach its maximum size limit.
Consider decreasing innodb_change_buffer_max_size on a MySQL server with static data used for reporting, or if the change buffer consumes too much of the memory space shared with the buffer pool, causing pages to age out of the buffer pool sooner than desired.
Test different settings with a representative workload to determine an optimal configuration. The innodb_change_buffer_max_size variable is dynamic, which permits modifying the setting without restarting the server.
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)