手写代码:KMP算法
【摘要】 Knuth-Morris-Pratt 字符串查找算法,简称为 KMP算法,常用于在一个文本串 S 内查找一个模式串 P 的出现位置。这个算法由 Donald Knuth、Vaughan Pratt、James H. Morris 三人于 1977 年联合发表,故取这 3 人的姓氏命名此算法。下面直接给出 KMP算法 的操作流程:1.假设现在文本串 S 匹配到 i 位置,模式串 P 匹配到 j...
Knuth-Morris-Pratt 字符串查找算法,简称为 KMP算法,常用于在一个文本串 S 内查找一个模式串 P 的出现位置。
这个算法由 Donald Knuth、Vaughan Pratt、James H. Morris 三人于 1977 年联合发表,故取这 3 人的姓氏命名此算法。
下面直接给出 KMP算法 的操作流程:
1.假设现在文本串 S 匹配到 i 位置,模式串 P 匹配到 j 位置。
2.如果 j = -1,或者当前字符匹配成功(即 S[i] == P[j] ),都令 i++,j++,继续匹配下一个字符。
3.如果 j != -1,且当前字符匹配失败(即 S[i] != P[j] ),则令 i 不变,j = next[j]。此举意味着失配时,模式串 P相对于文本串 S 向右移动了 j - next [j] 位。
4.换言之,将模式串 P 失配位置的 next 数组的值对应的模式串 P 的索引位置移动到失配处。
注意点:
1.字符串的位置一定是右移,不会左移。
2.匹配串的位置是一位一位的右移,左移是根据next数组。
3.字符串和匹配串的某个位置不等的时候,优先匹配串位置左移,左移不动的时候,字符串位置才右移。
代码用golang编写,代码如下:
func strStr(haystack string, needle string) int {
if len(needle)<=0{
return 0
}
return GetIndexOf(haystack,needle)
}
func GetNextArray(match string) []int {
matchLen := len(match)
if matchLen == 1 {
return []int{
-1}
}
next := make([]int, matchLen)
next[0] = -1
next[1] = 0
i := 2
// cn代表,cn位置的字符,是当前和i-1位置比较的字符
cn := 0
for i < matchLen {
if match[i-1] == match[cn] {
//匹配
cn++
next[i] = cn
i++
} else if cn > 0 {
cn = next[cn] //可回退指针
} else {
next[i] = 0
i++
}
}
fmt.Println("next = ", next)
return next
}
func GetIndexOf(s string, m string) int {
sLen := len(s)
mLen := len(m)
if sLen < len(m) {
return -1
}
next := GetNextArray(m)
x := 0 //从来不回退
y := 0 //根据next数组回退
for x < sLen && y < mLen {
if s[x] == m[y] {
x++
y++
} else if next[y] == -1 {
x++
} else {
y = next[y] //回退了
}
}
if y == mLen {
return x - y
} else {
return -1
}
}执行结果如下: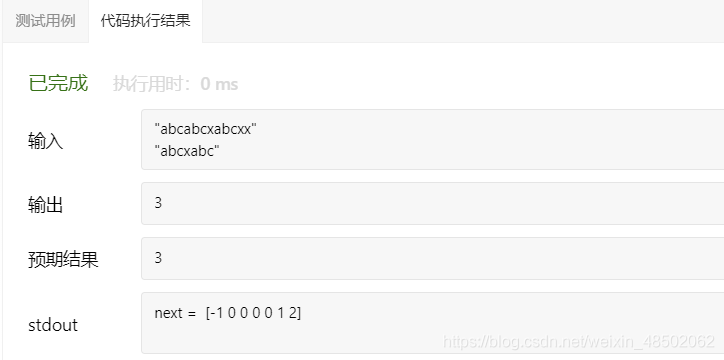
【版权声明】本文为华为云社区用户转载文章,如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)