vs2017\vs2019 VGG19处理cifar-10数据集的TensorFlow实现
这是针对于博客vs2017安装和使用教程(详细)和vs2019安装和使用教程(详细)的VGG19-CIFAR10项目新建示例
目录
一、代码(附有重要的注释)
1.博主提供的代码包含了很多重要的注释,都是博主精心查阅资料和debug的结果,对于新手了解tensorflow使用以及深度学习框架十分有用。
2.代码如下:
vgg19.py
-
import tensorflow as tf
-
import numpy as np
-
import time
-
import os
-
import sys
-
import pickle
-
import random
-
-
-
class_num = 10
-
image_size = 32
-
img_channels = 3
-
iterations = 200
-
batch_size = 250
-
total_epoch = 164
-
weight_decay = 0.0003
-
dropout_rate = 0.5
-
momentum_rate = 0.9
-
log_save_path = './vgg_logs'
-
model_save_path = './model/'
-
-
-
def download_data():
-
dirname = 'cifar-10-batches-py'
-
origin = 'http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar-10-python.tar.gz'
-
fname = './CAFIR-10_data/cifar-10-python.tar.gz'
-
fpath = './' + dirname
-
-
download = False
-
if os.path.exists(fpath) or os.path.isfile(fname):
-
download = False
-
print("DataSet already exist!")
-
else:
-
download = True
-
if download:
-
print('Downloading data from', origin)
-
import urllib.request
-
import tarfile
-
-
def reporthook(count, block_size, total_size):
-
global start_time
-
if count == 0:
-
start_time = time.time()
-
return
-
duration = time.time() - start_time
-
progress_size = int(count * block_size)
-
speed = int(progress_size / (1024 * duration))
-
percent = min(int(count*block_size*100/total_size),100)
-
sys.stdout.write("\r...%d%%, %d MB, %d KB/s, %d seconds passed" %
-
(percent, progress_size / (1024 * 1024), speed, duration))
-
sys.stdout.flush()
-
-
urllib.request.urlretrieve(origin, fname, reporthook)
-
print('Download finished. Start extract!', origin)
-
if fname.endswith("tar.gz"):
-
tar = tarfile.open(fname, "r:gz")
-
tar.extractall()
-
tar.close()
-
elif fname.endswith("tar"):
-
tar = tarfile.open(fname, "r:")
-
tar.extractall()
-
tar.close()
-
-
-
def unpickle(file):
-
with open(file, 'rb') as fo:
-
dict = pickle.load(fo, encoding='bytes')
-
return dict
-
-
-
def load_data_one(file):
-
batch = unpickle(file)#./cifar-10-batches-py/data_batch_1 ./cifar-10-batches-py/test_batch'
-
data = batch[b'data']#数据
-
labels = batch[b'labels']#标签
-
print("Loading %s : %d." % (file, len(data)))
-
return data, labels
-
-
-
def load_data(files, data_dir, label_count):
-
global image_size, img_channels
-
data, labels = load_data_one(data_dir + '/' + files[0])#./cifar-10-batches-py/data_batch_1 [0:10000]
-
for f in files[1:]:#test_batch时不经历该循环
-
data_n, labels_n = load_data_one(data_dir + '/' + f)#从./cifar-10-batches-py/data_batch_2
-
data = np.append(data, data_n, axis=0)#在行末尾追加,第一次循环变为[0:20000]
-
labels = np.append(labels, labels_n, axis=0)#最终[0:50000]
-
labels = np.array([[float(i == label) for i in range(label_count)] for label in labels])#labels重组,原数组第i个数字为k则第i行第k个位置位1,其它位置为0
-
#print(labels)
-
data = data.reshape([-1, img_channels, image_size, image_size])#-1缺省,函数自己计算,这里为train:50000 test:10000
-
data = data.transpose([0, 2, 3, 1])#train:[50000,3,32,32]变成[50000,32,32,3] test:[10000,3,32,32]变成[10000,32,32,3]
-
return data, labels
-
-
-
def prepare_data():
-
print("======Loading data======")
-
download_data()
-
data_dir = './cifar-10-batches-py'
-
image_dim = image_size * image_size * img_channels #32x32x3
-
meta = unpickle(data_dir + '/batches.meta')
-
-
label_names = meta[b'label_names']#[b'airplane', b'automobile', b'bird', b'cat', b'deer', b'dog', b'frog', b'horse', b'ship', b'truck']
-
label_count = len(label_names)#10
-
train_files = ['data_batch_%d' % d for d in range(1, 6)]#['data_batch_1', 'data_batch_2', 'data_batch_3', 'data_batch_4', 'data_batch_5']
-
train_data, train_labels = load_data(train_files, data_dir, label_count)#train_data[50000,32,32,3],train_labels[0,50000]
-
test_data, test_labels = load_data(['test_batch'], data_dir, label_count)
-
-
print("Train data:", np.shape(train_data), np.shape(train_labels))#Train data: (50000, 32, 32, 3) (50000, 10)
-
print("Test data :", np.shape(test_data), np.shape(test_labels))#Test data : (10000, 32, 32, 3) (10000, 10)
-
print("======Load finished======")#训练和测试数据读取完成
-
-
print("======Shuffling data======")
-
indices = np.random.permutation(len(train_data))#返回一个0-50000的随机排列
-
train_data = train_data[indices]#train重新排列
-
train_labels = train_labels[indices]#test重新排列
-
print("======Prepare Finished======")
-
-
return train_data, train_labels, test_data, test_labels
-
-
-
def bias_variable(shape):
-
initial = tf.constant(0.1, shape=shape, dtype=tf.float32)# <tf.Tensor 'Const:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32>
-
return tf.Variable(initial)
-
-
-
def conv2d(x, W):
-
#x:指需要做卷积的输入图像,它要求是一个Tensor,
-
#具有[batch, in_height, in_width, in_channels]这样的shape,
-
#具体含义是[训练时一个batch的图片数量, 图片高度, 图片宽度, 图像通道数],
-
#注意这是一个4维的Tensor,要求类型为float32和float64其中之一
-
#W:相当于CNN中的卷积核,它要求是一个Tensor,
-
#具有[filter_height, filter_width, in_channels, out_channels]这样的shape,
-
#具体含义是[卷积核的高度,卷积核的宽度,图像通道数,卷积核个数],
-
#要求类型与参数input相同,
-
#有一个地方需要注意,第三维in_channels,就是参数input的第四维
-
#strides:卷积时在图像每一维的步长,这是一个一维的向量,长度4
-
#padding:string类型的量,只能是"SAME","VALID"其中之一,这个值决定了不同的卷积方式
-
#padding = 'SAME':补0,受到strides大小影响
-
return tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
-
-
#
-
def max_pool(input, k_size=1, stride=1, name=None):
-
#input:需要池化的输入,一般池化层接在卷积层后面,所以输入通常是feature map,
-
#依然是[batch, height, width, channels]这样的shape
-
#ksize:池化窗口的大小,取一个四维向量,一般是[1, height, width, 1],
-
#因为我们不想在batch和channels上做池化,所以这两个维度设为了1
-
#strides:和卷积类似,窗口在每一个维度上滑动的步长,一般也是[1, stride,stride, 1]
-
#padding:和卷积类似,可以取'VALID' 或者'SAME'
-
#返回一个Tensor,类型不变,shape仍然是[batch, height, width, channels]这种形式
-
return tf.nn.max_pool(input, ksize=[1, k_size, k_size, 1], strides=[1, stride, stride, 1],
-
padding='SAME', name=name)
-
-
#公式如下:
-
#y=γ(x-μ)/σ+β
-
#其中:
-
#x是输入,
-
#y是输出,
-
#μ是均值,
-
#σ是方差,
-
#γ和β是缩放(scale)、偏移(offset)系数。
-
#一般来讲,这些参数都是基于channel来做的,比如输入x是一个16*32*32*128(NWHC格式)的feature map,
-
#那么上述参数都是128维的向量。其中γ和β是可有可无的,
-
#有的话,就是一个可以学习的参数(参与前向后向),
-
#没有的话,就简化成y=(x-μ)/σ。
-
#而μ和σ,在训练的时候,使用的是batch内的统计值,
-
#测试/预测的时候,采用的是训练时计算出的滑动平均值。
-
def batch_norm(input):
-
#decay:衰减系数。合适的衰减系数值接近1.0,特别是含多个9的值:0.999,0.99,0.9。
-
#如果训练集表现很好而验证/测试集表现得不好,选择小的系数(推荐使用0.9)。
-
#如果想要提高稳定性,zero_debias_moving_mean设为True
-
#center:如果为True,有beta偏移量;如果为False,无beta偏移量
-
#scale:如果为True,则乘以gamma。
-
#如果为False,gamma则不使用。
-
#当下一层是线性的时(例如nn.relu),由于缩放可以由下一层完成,所以可以禁用该层。
-
#epsilon:ε,避免被零除
-
#is_training:图层是否处于训练模式。
-
#在训练模式下,它将积累转入的统计量moving_mean并 moving_variance使用给定的指数移动平均值 decay。
-
#当它不是在训练模式,那么它将使用的数值moving_mean和moving_variance。
-
#updates_collections :Collections来收集计算的更新操作。
-
#updates_ops需要使用train_op来执行。
-
#如果为None,则会添加控件依赖项以确保更新已计算到位。
-
return tf.contrib.layers.batch_norm(input, decay=0.9, center=True, scale=True, epsilon=1e-3,
-
is_training=train_flag, updates_collections=None)
-
-
-
def _random_crop(batch, crop_shape, padding=None):
-
oshape = np.shape(batch[0])#(32, 32, 3)
-
-
if padding:
-
oshape = (oshape[0] + 2*padding, oshape[1] + 2*padding)#(40, 40)元组
-
new_batch = []
-
npad = ((padding, padding), (padding, padding), (0, 0))#((4, 4), (4, 4), (0, 0))
-
for i in range(len(batch)):#250
-
new_batch.append(batch[i])
-
if padding:
-
#pad(array,pad_width,mode,**kwars)
-
#其中array为要填补的数组(input)
-
#pad_width是在各维度的各个方向上想要填补的长度,如((2,3),(4,5)),
-
#如果直接输入一个整数,则说明各个维度和各个方向所填补的长度都一样。
-
#mode为填补类型,即怎样去填补,有“constant”,“edge”等模式,
-
#如果为constant模式,就得指定填补的值。
-
new_batch[i] = np.lib.pad(batch[i], pad_width=npad,
-
mode='constant', constant_values=0)#边缘填充,[0:32]变成[0,40]
-
#temp = oshape[0] - crop_shape[0]
-
nh = random.randint(0, oshape[0] - crop_shape[0])#返回[0,8]之间的整数
-
nw = random.randint(0, oshape[1] - crop_shape[1])
-
new_batch[i] = new_batch[i][nh:nh + crop_shape[0],
-
nw:nw + crop_shape[1]]#长度为32
-
return new_batch
-
-
-
def _random_flip_leftright(batch):
-
for i in range(len(batch)):
-
if bool(random.getrandbits(1)):#返回一个1位随机的integer
-
batch[i] = np.fliplr(batch[i])#左右翻转矩阵
-
return batch
-
-
-
def data_preprocessing(x_train,x_test):
-
-
x_train = x_train.astype('float32')#train数据转换为float32
-
x_test = x_test.astype('float32')#test数据转换为float32
-
#Z-score标准化(0-1标准化)方法,这种方法给予原始数据的均值(mean)和标准差(standard deviation)进行数据的标准化。
-
#经过处理的数据符合标准正态分布,即均值为0,标准差为1。
-
x_train[:, :, :, 0] = (x_train[:, :, :, 0] - np.mean(x_train[:, :, :, 0])) / np.std(x_train[:, :, :, 0])
-
x_train[:, :, :, 1] = (x_train[:, :, :, 1] - np.mean(x_train[:, :, :, 1])) / np.std(x_train[:, :, :, 1])
-
x_train[:, :, :, 2] = (x_train[:, :, :, 2] - np.mean(x_train[:, :, :, 2])) / np.std(x_train[:, :, :, 2])
-
-
x_test[:, :, :, 0] = (x_test[:, :, :, 0] - np.mean(x_test[:, :, :, 0])) / np.std(x_test[:, :, :, 0])
-
x_test[:, :, :, 1] = (x_test[:, :, :, 1] - np.mean(x_test[:, :, :, 1])) / np.std(x_test[:, :, :, 1])
-
x_test[:, :, :, 2] = (x_test[:, :, :, 2] - np.mean(x_test[:, :, :, 2])) / np.std(x_test[:, :, :, 2])
-
-
return x_train, x_test
-
-
-
def data_augmentation(batch):
-
batch = _random_flip_leftright(batch)#[0:250]
-
batch = _random_crop(batch, [32, 32], 4)#[250,32,32,3]
-
return batch
-
-
-
def learning_rate_schedule(epoch_num):
-
if epoch_num < 81:
-
return 0.1
-
elif epoch_num < 121:
-
return 0.01
-
else:
-
return 0.001
-
-
-
def run_testing(sess, ep):
-
acc = 0.0
-
loss = 0.0
-
pre_index = 0
-
add = 1000
-
for it in range(10):
-
batch_x = test_x[pre_index:pre_index+add]
-
batch_y = test_y[pre_index:pre_index+add]
-
pre_index = pre_index + add
-
loss_, acc_ = sess.run([cross_entropy, accuracy],
-
feed_dict={x: batch_x, y_: batch_y, keep_prob: 1.0, train_flag: False})
-
loss += loss_ / 10.0
-
acc += acc_ / 10.0
-
summary = tf.Summary(value=[tf.Summary.Value(tag="test_loss", simple_value=loss),
-
tf.Summary.Value(tag="test_accuracy", simple_value=acc)])
-
return acc, loss, summary
-
-
-
if __name__ == '__main__':
-
-
train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y = prepare_data()#准备数据,包括解压数据和打乱数据
-
train_x, test_x = data_preprocessing(train_x, test_x)#数据预处理,使其符合标准正态分布
-
-
# define placeholder x, y_ , keep_prob, learning_rate
-
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None, image_size, image_size, 3])#<tf.Tensor 'Placeholder:0' shape=(?, 32, 32, 3) dtype=float32>
-
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, class_num])#<tf.Tensor 'Placeholder_1:0' shape=(?, 10) dtype=float32>
-
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)#<tf.Tensor 'Placeholder_2:0' shape=<unknown> dtype=float32>
-
learning_rate = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)#<tf.Tensor 'Placeholder_4:0' shape=<unknown> dtype=float32>
-
train_flag = tf.placeholder(tf.bool)#<tf.Tensor 'Placeholder_5:0' shape=<unknown> dtype=bool>
-
-
# build_network
-
#He正态分布初始化方法,参数由0均值,标准差为sqrt(2 / fan_in) 的正态分布产生,其中fan_in权重张量的扇入
-
#W是卷积核
-
W_conv1_1 = tf.get_variable('conv1_1', shape=[3, 3, 3, 64], initializer=tf.contrib.keras.initializers.he_normal())#<tf.Variable 'conv1_1:0' shape=(3, 3, 3, 64) dtype=float32_ref>
-
b_conv1_1 = bias_variable([64])#<tf.Variable 'Variable:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref>
-
#这个函数的作用是计算激活函数 relu,即 max(features, 0)。即将矩阵中每行的非最大值置0。
-
output = tf.nn.relu(batch_norm(conv2d(x, W_conv1_1) + b_conv1_1))#<tf.Tensor 'Relu:0' shape=(?, 32, 32, 64) dtype=float32>
-
-
W_conv1_2 = tf.get_variable('conv1_2', shape=[3, 3, 64, 64], initializer=tf.contrib.keras.initializers.he_normal())#<tf.Variable 'conv1_2:0' shape=(3, 3, 64, 64) dtype=float32_ref>
-
b_conv1_2 = bias_variable([64])#<tf.Variable 'Variable_1:0' shape=(64,) dtype=float32_ref>
-
output = tf.nn.relu(batch_norm(conv2d(output, W_conv1_2) + b_conv1_2))#<tf.Tensor 'Relu_1:0' shape=(?, 32, 32, 64) dtype=float32>
-
output = max_pool(output, 2, 2, "pool1")#<tf.Tensor 'pool1_1:0' shape=(?, 16, 16, 64) dtype=float32>
-
-
W_conv2_1 = tf.get_variable('conv2_1', shape=[3, 3, 64, 128], initializer=tf.contrib.keras.initializers.he_normal())#<tf.Variable 'conv2_1:0' shape=(3, 3, 64, 128) dtype=float32_ref>
-
b_conv2_1 = bias_variable([128])#<tf.Variable 'Variable_2:0' shape=(128,) dtype=float32_ref>
-
output = tf.nn.relu(batch_norm(conv2d(output, W_conv2_1) + b_conv2_1))#<tf.Tensor 'Relu_2:0' shape=(?, 16, 16, 128) dtype=float32>
-
-
W_conv2_2 = tf.get_variable('conv2_2', shape=[3, 3, 128, 128], initializer=tf.contrib.keras.initializers.he_normal())
-
b_conv2_2 = bias_variable([128])
-
output = tf.nn.relu(batch_norm(conv2d(output, W_conv2_2) + b_conv2_2))
-
output = max_pool(output, 2, 2, "pool2")
-
-
W_conv3_1 = tf.get_variable('conv3_1', shape=[3, 3, 128, 256], initializer=tf.contrib.keras.initializers.he_normal())
-
b_conv3_1 = bias_variable([256])
-
output = tf.nn.relu( batch_norm(conv2d(output,W_conv3_1) + b_conv3_1))
-
-
W_conv3_2 = tf.get_variable('conv3_2', shape=[3, 3, 256, 256], initializer=tf.contrib.keras.initializers.he_normal())
-
b_conv3_2 = bias_variable([256])
-
output = tf.nn.relu(batch_norm(conv2d(output, W_conv3_2) + b_conv3_2))
-
-
W_conv3_3 = tf.get_variable('conv3_3', shape=[3, 3, 256, 256], initializer=tf.contrib.keras.initializers.he_normal())
-
b_conv3_3 = bias_variable([256])
-
output = tf.nn.relu( batch_norm(conv2d(output, W_conv3_3) + b_conv3_3))
-
-
W_conv3_4 = tf.get_variable('conv3_4', shape=[3, 3, 256, 256], initializer=tf.contrib.keras.initializers.he_normal())
-
b_conv3_4 = bias_variable([256])
-
output = tf.nn.relu(batch_norm(conv2d(output, W_conv3_4) + b_conv3_4))
-
output = max_pool(output, 2, 2, "pool3")
-
-
W_conv4_1 = tf.get_variable('conv4_1', shape=[3, 3, 256, 512], initializer=tf.contrib.keras.initializers.he_normal())
-
b_conv4_1 = bias_variable([512])
-
output = tf.nn.relu(batch_norm(conv2d(output, W_conv4_1) + b_conv4_1))
-
-
W_conv4_2 = tf.get_variable('conv4_2', shape=[3, 3, 512, 512], initializer=tf.contrib.keras.initializers.he_normal())
-
b_conv4_2 = bias_variable([512])
-
output = tf.nn.relu(batch_norm(conv2d(output, W_conv4_2) + b_conv4_2))
-
-
W_conv4_3 = tf.get_variable('conv4_3', shape=[3, 3, 512, 512], initializer=tf.contrib.keras.initializers.he_normal())
-
b_conv4_3 = bias_variable([512])
-
output = tf.nn.relu(batch_norm(conv2d(output, W_conv4_3) + b_conv4_3))
-
-
W_conv4_4 = tf.get_variable('conv4_4', shape=[3, 3, 512, 512], initializer=tf.contrib.keras.initializers.he_normal())
-
b_conv4_4 = bias_variable([512])
-
output = tf.nn.relu(batch_norm(conv2d(output, W_conv4_4)) + b_conv4_4)
-
output = max_pool(output, 2, 2)
-
-
W_conv5_1 = tf.get_variable('conv5_1', shape=[3, 3, 512, 512], initializer=tf.contrib.keras.initializers.he_normal())
-
b_conv5_1 = bias_variable([512])
-
output = tf.nn.relu(batch_norm(conv2d(output, W_conv5_1) + b_conv5_1))
-
-
W_conv5_2 = tf.get_variable('conv5_2', shape=[3, 3, 512, 512], initializer=tf.contrib.keras.initializers.he_normal())
-
b_conv5_2 = bias_variable([512])
-
output = tf.nn.relu(batch_norm(conv2d(output, W_conv5_2) + b_conv5_2))
-
-
W_conv5_3 = tf.get_variable('conv5_3', shape=[3, 3, 512, 512], initializer=tf.contrib.keras.initializers.he_normal())
-
b_conv5_3 = bias_variable([512])
-
output = tf.nn.relu(batch_norm(conv2d(output, W_conv5_3) + b_conv5_3))
-
-
W_conv5_4 = tf.get_variable('conv5_4', shape=[3, 3, 512, 512], initializer=tf.contrib.keras.initializers.he_normal())
-
b_conv5_4 = bias_variable([512])
-
output = tf.nn.relu(batch_norm(conv2d(output, W_conv5_4) + b_conv5_4))
-
-
# output = tf.contrib.layers.flatten(output)
-
output = tf.reshape(output, [-1, 2*2*512])#<tf.Tensor 'Reshape:0' shape=(?, 2048) dtype=float32>
-
-
W_fc1 = tf.get_variable('fc1', shape=[2048, 4096], initializer=tf.contrib.keras.initializers.he_normal())
-
b_fc1 = bias_variable([4096])
-
output = tf.nn.relu(batch_norm(tf.matmul(output, W_fc1) + b_fc1) )
-
#tf.nn.dropout是TensorFlow里面为了防止或减轻过拟合而使用的函数,它一般用在全连接层。
-
#Dropout就是在不同的训练过程中随机扔掉一部分神经元。也就是让某个神经元的激活值以一定的概率p,让其停止工作,
-
#这次训练过程中不更新权值,也不参加神经网络的计算。但是它的权重得保留下来(只是暂时不更新而已),因为下次样本输入时它可能又得工作了。
-
#第一个参数output:指输入
-
#第二个参数keep_prob: 设置神经元被选中的概率,在初始化时keep_prob是一个占位符, keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)。
-
#tensorflow在run时设置keep_prob具体的值,例如keep_prob: 0.5
-
output = tf.nn.dropout(output, keep_prob)
-
-
W_fc2 = tf.get_variable('fc7', shape=[4096, 4096], initializer=tf.contrib.keras.initializers.he_normal())
-
b_fc2 = bias_variable([4096])
-
output = tf.nn.relu(batch_norm(tf.matmul(output, W_fc2) + b_fc2))
-
output = tf.nn.dropout(output, keep_prob)
-
-
W_fc3 = tf.get_variable('fc3', shape=[4096, 10], initializer=tf.contrib.keras.initializers.he_normal())
-
b_fc3 = bias_variable([10])
-
output = tf.nn.relu(batch_norm(tf.matmul(output, W_fc3) + b_fc3))
-
# output = tf.reshape(output,[-1,10])
-
-
# loss function: cross_entropy
-
# train_step: training operation
-
-
#labels:一个分类标签,所不同的是,这个labels是分类的概率,
-
#比如说[0.2,0.3,0.5],labels的每一行必须是一个概率分布(即概率之合加起来为1)。
-
#logits:logit的值域范围[-inf,+inf](即正负无穷区间)。
-
#我们可以把logist理解为原生态的、未经缩放的,可视为一种未归一化的l“概率替代物”,
-
#如[4, 1, -2]。它可以是其他分类器(如逻辑回归等、SVM等)的输出。
-
#Softmax把一个系列的概率替代物(logits)从[-inf, +inf] 映射到[0,1]。
-
#经过softmax的加工,就变成“归一化”的概率(设为p1),这个新生成的概率p1,和labels所代表的概率分布(设为p2)一起作为参数,用来计算交叉熵。
-
#这个差异信息,作为我们网络调参的依据,理想情况下,这两个分布尽量趋近最好。
-
#如果有差异(也可以理解为误差信号),我们就调整参数,让其变得更小,这就是损失(误差)函数的作用。
-
cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y_, logits=output))#logit=log(odds)=log(P/(1-P))
-
#l2_loss:1/2Σvar2或者output = sum(t ** 2) / 2
-
#L1正则化是指权值向量w中各个元素的绝对值之和,通常表示为||w||1
-
#L2正则化是指权值向量w中各个元素的平方和然后再求平方根(可以看到Ridge回归的L2正则化项有平方符号),通常表示为||w||2
-
#也就是说Lx范数应用于优化的目标函数就叫做Lx正则化
-
#l2_loss一般用于优化目标函数中的正则项,防止参数太多复杂容易过拟合(所谓的过拟合问题是指当一个模型很复杂时,
-
#它可以很好的“记忆”每一个训练数据中的随机噪声的部分而忘记了要去“学习”训练数据中通用的趋势)
-
#多个l2(var向量)对应元素相加变为1行var
-
l2 = tf.add_n([tf.nn.l2_loss(var) for var in tf.trainable_variables()])
-
#动量梯度下降算法
-
#learning_rate: (学习率)张量或者浮点数
-
#momentum: (动量)张量或者浮点数
-
#use_locking: 为True时锁定更新
-
#name: 梯度下降名称,默认为 "Momentum".
-
#use_nesterov: 为True时,使用 Nesterov Momentum.
-
train_step = tf.train.MomentumOptimizer(learning_rate, momentum_rate, use_nesterov=True).\
-
minimize(cross_entropy + l2 * weight_decay)
-
#tf.argmax( , )中有两个参数,第一个参数是矩阵,第二个参数是0或者1。
-
#0表示的是按列比较返回最大值的索引,
-
#1表示按行比较返回最大值的索引。
-
#tf.equal(A, B)是对比这两个矩阵或者向量的相等的元素,
-
#如果是相等的那就返回True,否则返回False,
-
#返回的值的矩阵维度和A是一样的
-
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(output, 1), tf.argmax(y_, 1))
-
#将x的数据格式转化成dtype.例如,原来x的数据格式是bool,那么将其转化成float以后,就能够将其转化成0和1的序列。反之也可以
-
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
-
-
# initial an saver to save model
-
saver = tf.train.Saver()
-
-
with tf.Session() as sess:
-
-
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())#初始化全局变量
-
summary_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(log_save_path,sess.graph)#log是事件文件所在的目录,这里是工程目录下的log目录。第二个参数是事件文件要记录的图,也就是tensorflow默认的图。
-
if os.path.exists(model_save_path):
-
#模型的恢复用的是restore()函数,它需要两个参数restore(sess, save_path),
-
#save_path指的是保存的模型路径。
-
#我们可以使用tf.train.latest_checkpoint()来自动获取最后一次保存的模型。
-
saver.restore(sess,model_save_path+"vgg19.ckpt")
-
# epoch = 164
-
# make sure [bath_size * iteration = data_set_number]
-
-
for ep in range(1, total_epoch+1):#total_epoch = 164
-
lr = learning_rate_schedule(ep)#学习率变化时间表
-
pre_index = 0
-
train_acc = 0.0
-
train_loss = 0.0
-
start_time = time.time()
-
-
print("\n epoch %d/%d:" % (ep, total_epoch))
-
-
for it in range(1, iterations+1):#iterations = 200
-
batch_x = train_x[pre_index:pre_index+batch_size]#batch_size = 250
-
batch_y = train_y[pre_index:pre_index+batch_size]
-
-
batch_x = data_augmentation(batch_x)
-
-
_, batch_loss = sess.run([train_step, cross_entropy],
-
feed_dict={x: batch_x, y_: batch_y, keep_prob: dropout_rate,
-
learning_rate: lr, train_flag: True})
-
batch_acc = accuracy.eval(feed_dict={x: batch_x, y_: batch_y, keep_prob: 1.0, train_flag: True})
-
-
train_loss += batch_loss
-
train_acc += batch_acc
-
pre_index += batch_size
-
-
if it == iterations:
-
train_loss /= iterations
-
train_acc /= iterations
-
#第一个参数是要求的结果
-
#第二个参数feed_dict是给placeholder赋值
-
loss_, acc_ = sess.run([cross_entropy, accuracy],
-
feed_dict={x: batch_x, y_: batch_y, keep_prob: 1.0, train_flag: True})
-
train_summary = tf.Summary(value=[tf.Summary.Value(tag="train_loss", simple_value=train_loss),
-
tf.Summary.Value(tag="train_accuracy", simple_value=train_acc)])
-
-
val_acc, val_loss, test_summary = run_testing(sess, ep)
-
-
summary_writer.add_summary(train_summary, ep)
-
summary_writer.add_summary(test_summary, ep)
-
summary_writer.flush()
-
-
print("iteration: %d/%d, cost_time: %ds, train_loss: %.4f, "
-
"train_acc: %.4f, test_loss: %.4f, test_acc: %.4f"
-
% (it, iterations, int(time.time()-start_time), train_loss, train_acc, val_loss, val_acc))
-
else:
-
print("iteration: %d/%d, train_loss: %.4f, train_acc: %.4f"
-
% (it, iterations, train_loss / it, train_acc / it), end='\r')
-
save_path = saver.save(sess, model_save_path+"vgg19.ckpt")
-
print("Model saved in file: %s" % save_path)
二、项目结构
1.由于使用的是vs2017或vs2019,因此需要新建一个项目,可参考博主的博客:vs2017 开始自己的第一个Python程序或vs2019 开始自己的第一个Python程序
2.运行完该程序,你的项目结构应该是下图所示:

(1)vgg19.py就是你的代码文件
(2)项目名称是cifar,因此解决方案是cifar.sln或者是cifar.pyproj
(3)cifar-10-batches-py是程序下载的数据集,一开始是没有的,打开它,内容如下:

(4)model是你训练完成的模型文件夹,一开始是没有的,打开它,内容如下:

(5)vgg_logs是你运行代码的日志文件,可以用tensorboard打开,内容如下:
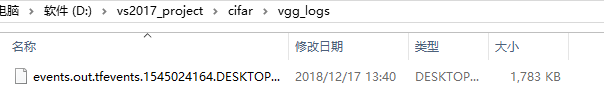
打开cmd或者Anaconda Prompt,指令是(以博主路径为例):
tensorboard --logdir D:\vs2017_project\cifar\vgg_logs
然后打开浏览器,输出命令最后一行提示的网址,打开tensorboard:http://desktop-xxxxxx:6006
三、VGG简介
1.概要
VGG模型是2014年ILSVRC竞赛的第二名,第一名是GoogLeNet。但是VGG模型在多个迁移学习任务中的表现要优于googLeNet。而且,从图像中提取CNN特征,VGG模型是首选算法。它的缺点在于,参数量有140M之多,需要更大的存储空间。但是这个模型很有研究价值。
2.用途和准确率
VGG Net由牛津大学的视觉几何组(Visual Geometry Group)和 Google DeepMind公司的研究员一起研发的的深度卷积神经网络,在 ILSVRC 2014 上取得了第二名的成绩,将 Top-5错误率降到7.3%。 它主要的贡献是展示出网络的深度(depth)是算法优良性能的关键部分。目前使用比较多的网络结构主要有ResNet(152-1000层),GooleNet(22层),VGGNet(19层),大多数模型都是基于这几个模型上改进,采用新的优化算法,多模型融合等。 到目前为止,VGG Net 依然经常被用来提取图像特征。
3.网络结构图


四、程序执行关键部分解析
1.数据预处理
Z-score标准化(0-1标准化)方法,这种方法给予原始数据的均值(mean)和标准差(standard deviation)进行数据的标准化。 经过处理的数据符合标准正态分布,即均值为0,标准差为1。
转化公式为:
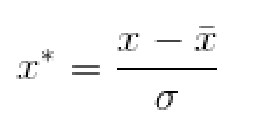
-
def data_preprocessing(x_train,x_test):
-
-
x_train = x_train.astype('float32')#train数据转换为float32
-
x_test = x_test.astype('float32')#test数据转换为float32
-
#Z-score标准化(0-1标准化)方法,这种方法给予原始数据的均值(mean)和标准差(standard deviation)进行数据的标准化。
-
#经过处理的数据符合标准正态分布,即均值为0,标准差为1。
-
x_train[:, :, :, 0] = (x_train[:, :, :, 0] - np.mean(x_train[:, :, :, 0])) / np.std(x_train[:, :, :, 0])
-
x_train[:, :, :, 1] = (x_train[:, :, :, 1] - np.mean(x_train[:, :, :, 1])) / np.std(x_train[:, :, :, 1])
-
x_train[:, :, :, 2] = (x_train[:, :, :, 2] - np.mean(x_train[:, :, :, 2])) / np.std(x_train[:, :, :, 2])
-
-
x_test[:, :, :, 0] = (x_test[:, :, :, 0] - np.mean(x_test[:, :, :, 0])) / np.std(x_test[:, :, :, 0])
-
x_test[:, :, :, 1] = (x_test[:, :, :, 1] - np.mean(x_test[:, :, :, 1])) / np.std(x_test[:, :, :, 1])
-
x_test[:, :, :, 2] = (x_test[:, :, :, 2] - np.mean(x_test[:, :, :, 2])) / np.std(x_test[:, :, :, 2])
-
-
return x_train, x_test
2. 网络部分
(1)initializer=tf.contrib.keras.initializers.he_normal()
其中he_normal()指的是He正态分布初始化方法
-
#He正态分布初始化方法,参数由0均值,标准差为sqrt(2 / fan_in) 的正态分布产生,其中fan_in权重张量的扇入
-
#W是卷积核
-
W_conv1_1 = tf.get_variable('conv1_1', shape=[3, 3, 3, 64], initializer=tf.contrib.keras.initializers.he_normal())b_conv1_1 = bias_variable([64])
-
#这个函数的作用是计算激活函数 relu,即 max(features, 0)。即将矩阵中每行的非最大值置0。
-
output = tf.nn.relu(batch_norm(conv2d(x, W_conv1_1) + b_conv1_1))
然后,我们分析一下tf.nn.relu(batch_norm(conv2d(x, W_conv1_1) + b_conv1_1))这句话
(2)tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
-
def conv2d(x, W):
-
#x:指需要做卷积的输入图像,它要求是一个Tensor,
-
#具有[batch, in_height, in_width, in_channels]这样的shape,
-
#具体含义是[训练时一个batch的图片数量, 图片高度, 图片宽度, 图像通道数],
-
#注意这是一个4维的Tensor,要求类型为float32和float64其中之一
-
#W:相当于CNN中的卷积核,它要求是一个Tensor,
-
#具有[filter_height, filter_width, in_channels, out_channels]这样的shape,
-
#具体含义是[卷积核的高度,卷积核的宽度,图像通道数,卷积核个数],
-
#要求类型与参数input相同,
-
#有一个地方需要注意,第三维in_channels,就是参数x的第四维
-
#strides:卷积时在图像每一维的步长,这是一个一维的向量,长度4
-
#padding:string类型的量,只能是"SAME","VALID"其中之一,这个值决定了不同的卷积方式
-
#padding = 'SAME':补0,受到strides大小影响
-
return tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
参数解析:
x:指需要做卷积的输入图像,它要求是一个Tensor,具有[batch, in_height, in_width, in_channels]这样的shape,具体含义是[训练时一个batch的图片数量, 图片高度, 图片宽度, 图像通道数],注意这是一个4维的Tensor,要求类型为float32和float64其中之一
W:相当于CNN中的卷积核,它要求是一个Tensor,具有[filter_height, filter_width, in_channels, out_channels]这样的shape,具体含义是[卷积核的高度,卷积核的宽度,图像通道数,卷积核个数],要求类型与参数input相同,有一个地方需要注意,第三维in_channels,就是参数x的第四维
strides:卷积时在图像每一维的步长,这是一个一维的向量,长度4
padding:string类型的量,只能是"SAME","VALID"其中之一,这个值决定了不同的卷积方式,padding = 'SAME':补0,受到strides大小影响
这里conv2d(x, W_conv1_1)指的是x是卷积输入图像,W_conv1_1是卷积核,而且这个卷积核大小为3x3,输入通道为3,输出通道为64
(3)tf.contrib.layers.batch_norm()
-
def batch_norm(input):
-
#decay:衰减系数。合适的衰减系数值接近1.0,特别是含多个9的值:0.999,0.99,0.9。
-
#如果训练集表现很好而验证/测试集表现得不好,选择小的系数(推荐使用0.9)。
-
#如果想要提高稳定性,zero_debias_moving_mean设为True
-
#center:如果为True,有beta偏移量;如果为False,无beta偏移量
-
#scale:如果为True,则乘以gamma。
-
#如果为False,gamma则不使用。
-
#当下一层是线性的时(例如nn.relu),由于缩放可以由下一层完成,所以可以禁用该层。
-
#epsilon:ε,避免被零除
-
#is_training:图层是否处于训练模式。
-
#在训练模式下,它将积累转入的统计量moving_mean并 moving_variance使用给定的指数移动平均值 decay。
-
#当它不是在训练模式,那么它将使用的数值moving_mean和moving_variance。
-
#updates_collections :Collections来收集计算的更新操作。
-
#updates_ops需要使用train_op来执行。
-
#如果为None,则会添加控件依赖项以确保更新已计算到位。
-
return tf.contrib.layers.batch_norm(input, decay=0.9, center=True, scale=True, epsilon=1e-3,
-
is_training=train_flag, updates_collections=None)
公式如下:
y=γ(x-μ)/σ+β
其中:x是输入,y是输出,μ是均值,σ是方差,γ和β是缩放(scale)、偏移(offset)系数。
一般来讲,这些参数都是基于channel来做的,比如输入x是一个16*32*32*128(NWHC格式)的feature map,那么上述参数都是128维的向量。
其中γ和β是可有可无的,有的话,就是一个可以学习的参数(参与前向后向),没有的话,就简化成y=(x-μ)/σ。
而μ和σ,在训练的时候,使用的是batch内的统计值,测试/预测的时候,采用的是训练时计算出的滑动平均值。
参数解析:
decay:衰减系数。合适的衰减系数值接近1.0,特别是含多个9的值:0.999,0.99,0.9。如果训练集表现很好而验证/测试集表现得不好,选择小的系数(推荐使用0.9)。如果想要提高稳定性,zero_debias_moving_mean设为True
center:如果为True,有beta偏移量;如果为False,无beta偏移量
scale:如果为True,则乘以gamma。如果为False,gamma则不使用。当下一层是线性的时(例如nn.relu),由于缩放可以由下一层完成,所以可以禁用该层。
epsilon:ε,避免被零除
is_training:图层是否处于训练模式。在训练模式下,它将积累转入的统计量moving_mean并 moving_variance使用给定的指数移动平均值 decay。当它不是在训练模式,那么它将使用的数值moving_mean和moving_variance。
updates_collections :Collections来收集计算的更新操作。updates_ops需要使用train_op来执行。如果为None,则会添加控件依赖项以确保更新已计算到位。
(4)tf.nn.dropout(output, keep_prob)
-
W_fc1 = tf.get_variable('fc1', shape=[2048, 4096], initializer=tf.contrib.keras.initializers.he_normal())
-
b_fc1 = bias_variable([4096])
-
output = tf.nn.relu(batch_norm(tf.matmul(output, W_fc1) + b_fc1) )
-
#tf.nn.dropout是TensorFlow里面为了防止或减轻过拟合而使用的函数,它一般用在全连接层。
-
#Dropout就是在不同的训练过程中随机扔掉一部分神经元。也就是让某个神经元的激活值以一定的概率p,让其停止工作,
-
#这次训练过程中不更新权值,也不参加神经网络的计算。但是它的权重得保留下来(只是暂时不更新而已),因为下次样本输入时它可能又得工作了。
-
#第一个参数output:指输入
-
#第二个参数keep_prob: 设置神经元被选中的概率,在初始化时keep_prob是一个占位符, keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)。
-
#tensorflow在run时设置keep_prob具体的值,例如keep_prob: 0.5
-
output = tf.nn.dropout(output, keep_prob)
该函数是TensorFlow里面为了防止或减轻过拟合而使用的函数,它一般用在全连接层。
Dropout就是在不同的训练过程中随机扔掉一部分神经元。也就是让某个神经元的激活值以一定的概率p,让其停止工作,这次训练过程中不更新权值,也不参加神经网络的计算。
但是它的权重得保留下来(只是暂时不更新而已),因为下次样本输入时它可能又得工作了。
参数解析:
output:指输入
keep_prob: 设置神经元被选中的概率,在初始化时keep_prob是一个占位符, keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)。tensorflow在run时设置keep_prob具体的值,例如keep_prob: 0.5
FC层
左边的图为一个完全的全连接层,右边为应用dropout后的全连接层。

3. 损失函数
(1)交叉熵
cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y_, logits=output))#logit=log(odds)=log(P/(1-P))
参数解析:
labels:一个分类标签,所不同的是,这个labels是分类的概率,比如说[0.2,0.3,0.5],labels的每一行必须是一个概率分布(即概率之合加起来为1)。
logits:logit的值域范围[-inf,+inf](即正负无穷区间)。我们可以把logist理解为原生态的、未经缩放的,可视为一种未归一化的l“概率替代物”,如[4, 1, -2]。它可以是其他分类器(如逻辑回归等、SVM等)的输出。
logit公式如下:
![]()
Odds(A)= 发生事件A次数 / 其他事件的次数(即不发生A的次数)
概率P(A)和Odds(A)的值域是不同的。前者被锁定在[0,1]之间,而后者则是[0,∞)
softmax对于logits的用处:
Softmax把一个系列的概率替代物(logits)从[-inf, +inf] 映射到[0,1]
(2)L2损失
l2 = tf.add_n([tf.nn.l2_loss(var) for var in tf.trainable_variables()])
参数解析:
l2_loss:1/2Σvar^2或者output = sum(t ** 2) / 2
L1正则化是指权值向量w中各个元素的绝对值之和,通常表示为||w||1
L2正则化是指权值向量w中各个元素的平方和然后再求平方根(可以看到Ridge回归的L2正则化项有平方符号),通常表示为||w||2
也就是说Lx范数应用于优化的目标函数就叫做Lx正则化
l2_loss一般用于优化目标函数中的正则项,防止参数太多复杂容易过拟合(所谓的过拟合问题是指当一个模型很复杂时,它可以很好的“记忆”每一个训练数据中的随机噪声的部分而忘记了要去“学习”训练数据中通用的趋势)
tf.add_n:多个l2(var向量)对应元素相加变为1行var
(3)动量梯度下降算法
-
train_step = tf.train.MomentumOptimizer(learning_rate, momentum_rate, use_nesterov=True).\
-
minimize(cross_entropy + l2 * weight_decay)
参数解析:
learning_rate: (学习率)张量或者浮点数
momentum: (动量)张量或者浮点数
use_locking: 为True时锁定更新
name: 梯度下降名称,默认为 "Momentum".
use_nesterov: 为True时,使用 Nesterov Momentum
梯度下降法参数更新公式:
W:=W−α∇W
b:=b−α∇b
可以看到,每次更新仅与当前梯度值相关,并不涉及之前的梯度。
而动量梯度下降法则对各个mini-batch求得的梯度∇W,∇b 使用指数加权平均得到 V∇w,V∇b 并使用新的参数更新之前的参数。
例如,在100次梯度下降中求得的梯度序列为:
{∇W1,∇W2,∇W3.........∇W99 ,∇W100}
则其对应的动量梯度分别为:
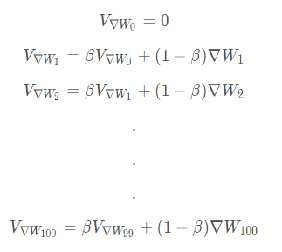
使用指数加权平均之后梯度代替原梯度进行参数更新。
因为每个指数加权平均后的梯度含有之前梯度的信息。
4.准确率
-
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(output, 1), tf.argmax(y_, 1))
-
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
tf.argmax( , )参数解析:
第一个参数是矩阵,第二个参数是0或者1。 0表示的是按列比较返回最大值的索引, 1表示按行比较返回最大值的索引。 tf.equal(A, B)参数解析:
对比这A和B两个矩阵或者向量的相等的元素, 如果是相等的那就返回True,否则返回False, 返回的值的矩阵维度和A是一样的。
tf.cast(x,dtype)参数解析:
将x的数据格式转化成dtype
例如,原来x的数据格式是bool,那么将其转化成float以后,就能够将其转化成0和1的序列。反之也可以。
五、训练过程和结果
由于一个epoch耗时34s,因此164个epoch需要大约1.5小时训练完成
1.训练过程

2.结果

其中学习率在epoch为82和122时会有转变,代码部分如下:
-
def learning_rate_schedule(epoch_num):
-
if epoch_num < 81:
-
return 0.1
-
elif epoch_num < 121:
-
return 0.01
-
else:
-
return 0.001
tensorboard结果:
我们也可以从图表中看到在82和121的剧烈变化



最终训练准确率在89%左右,测试准确率在84.5%左右~
六、参考博客和文献
1.2014-VGG-《Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition》
4.tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits中的“logits”到底是个什么意思?
5.tf.nn.l2_loss和 tf.nn.l2_normalize
7.动量梯度下降法(gradient descent with momentum)
返回至原博客:
文章来源: nickhuang1996.blog.csdn.net,作者:悲恋花丶无心之人,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:nickhuang1996.blog.csdn.net/article/details/85046067
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)