【SpringBoot】快速入门
一、SpringBoot快速入门
(1)新建模块,选择Spring Initializer,一定要记得选择SpringBoot的版本为2.7.7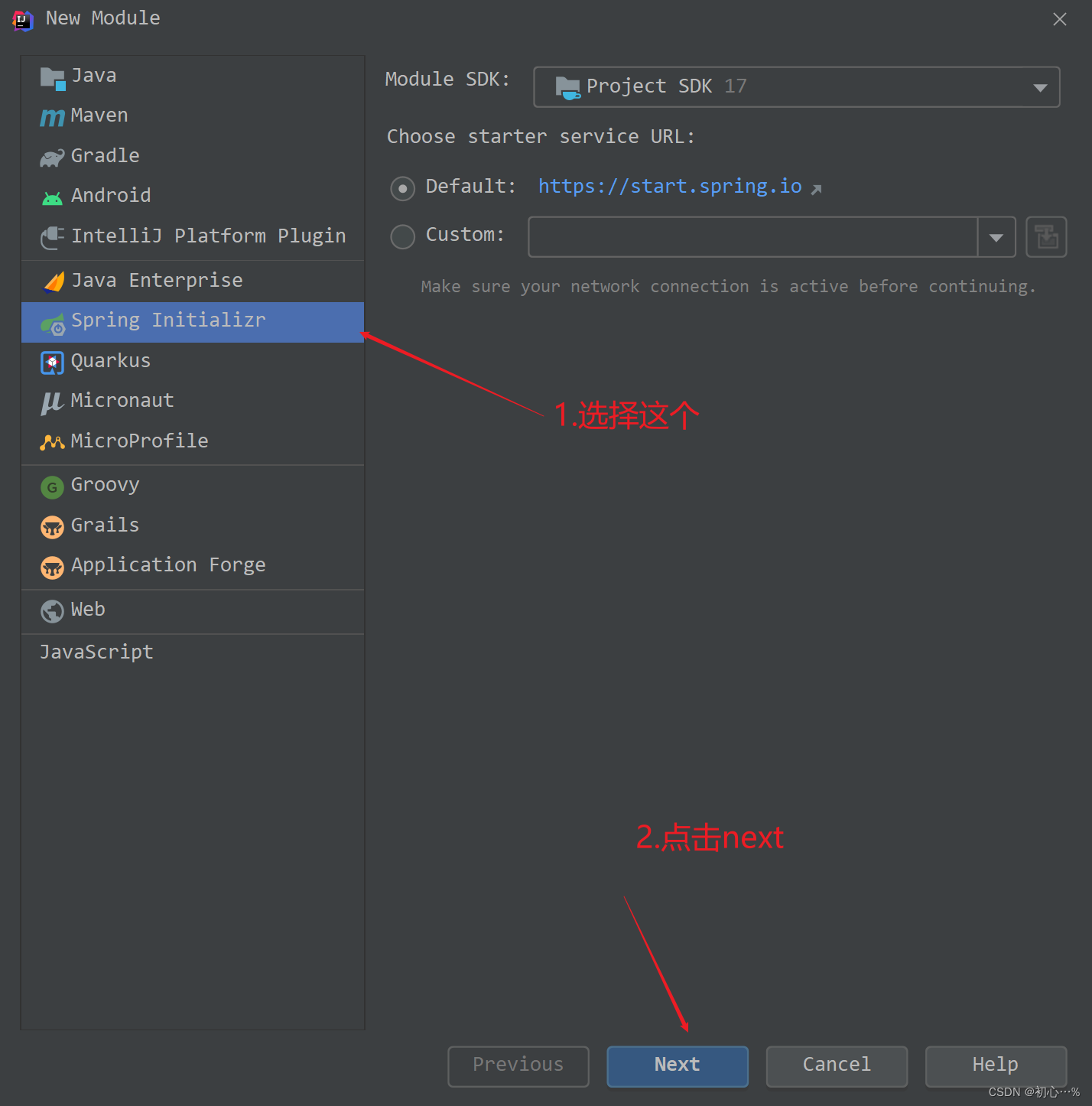
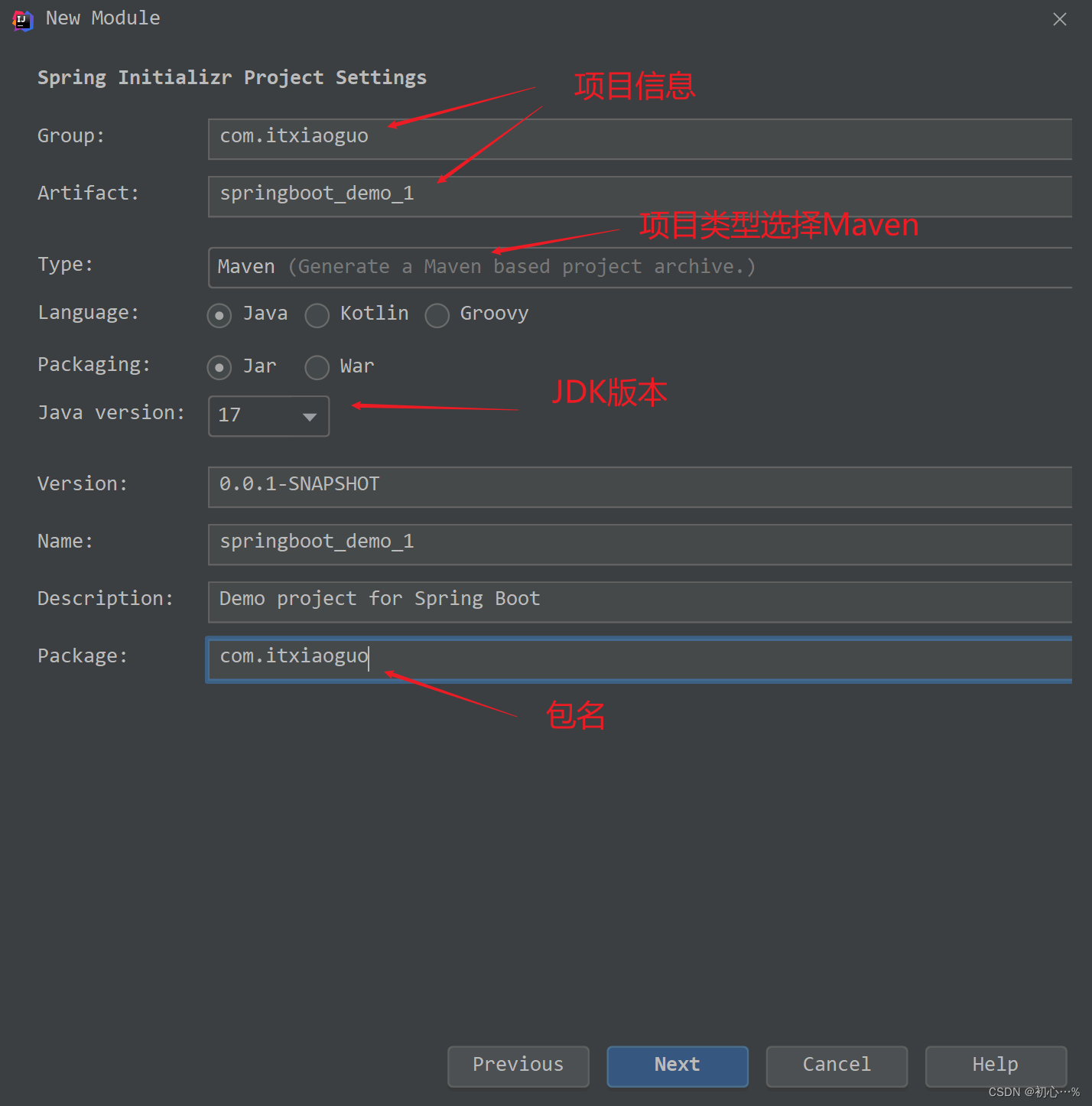

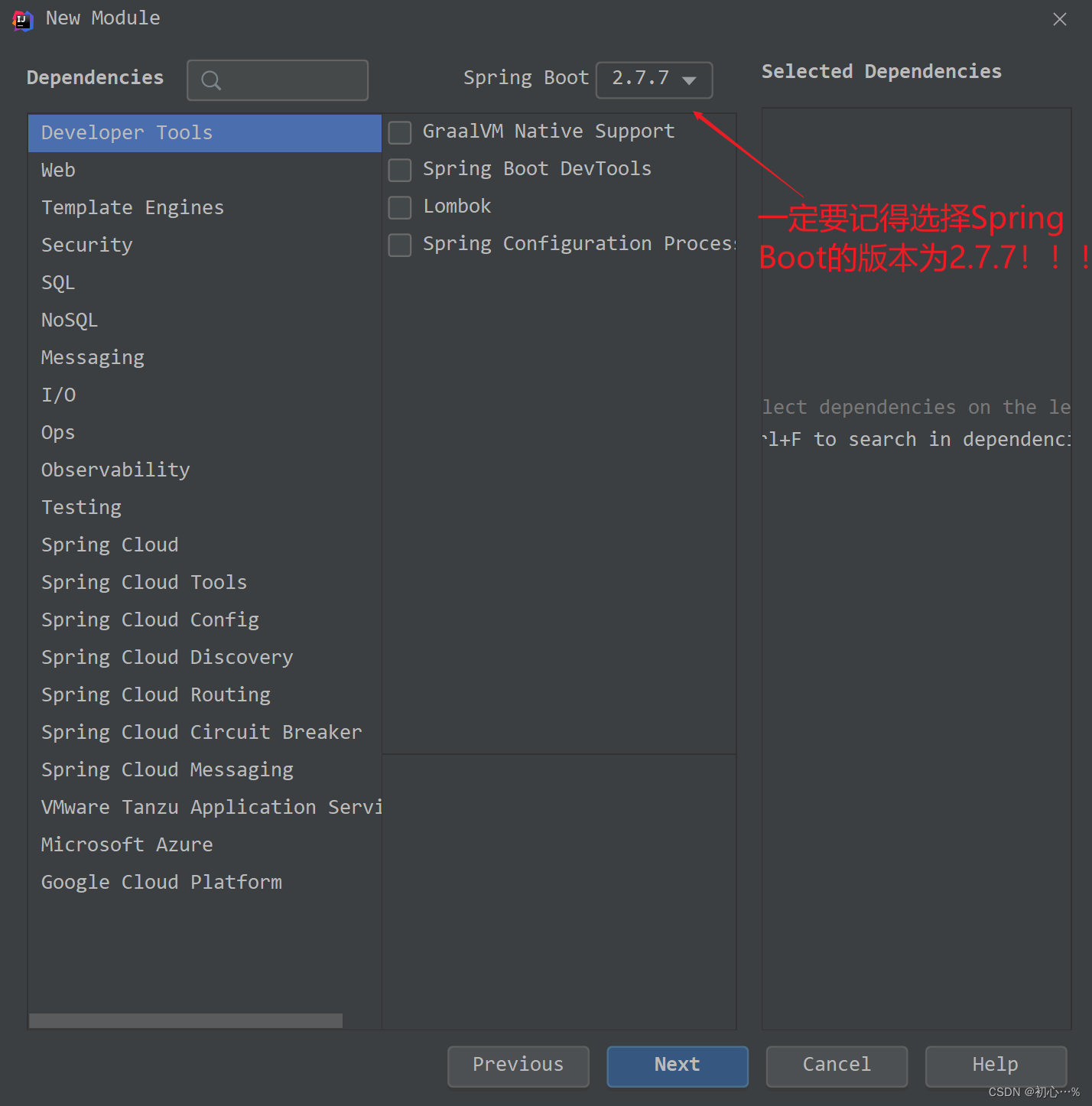

注意上面的两个目录一定要是空目录,然后点击apply,OK即可,之后进入到主界面。
(2)编写UserController类
package com.itxiaoguo.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/users")
public class UserController {
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public String selectById(@PathVariable Integer id) {
System.out.println("id --> "+ id);
return "id --> "+id;
}
}
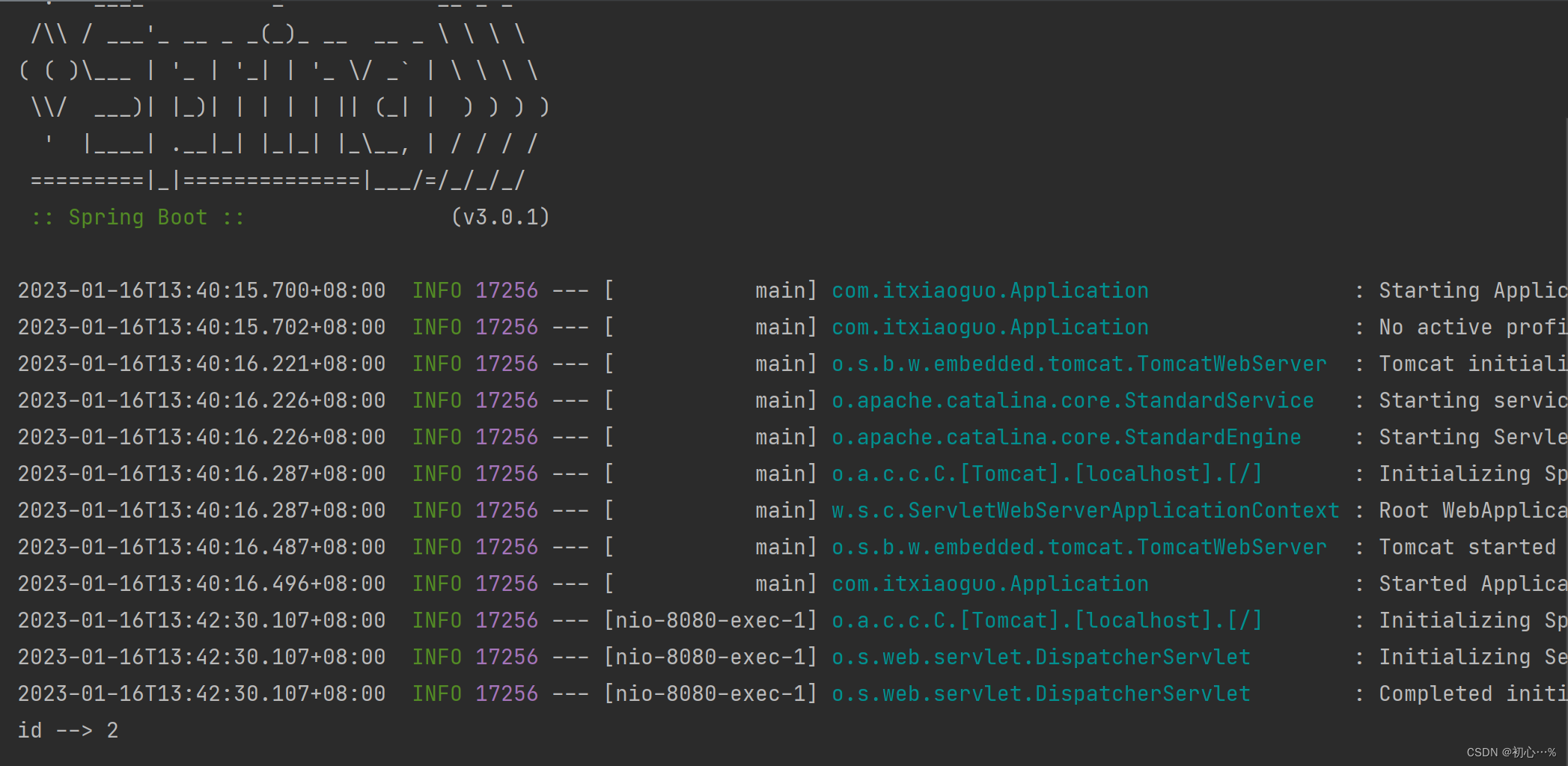
(3)运行Application并使用Postman测试

| 遇到的问题 | 无法使用RestController注解 | 运行主类报错无法运行主类 | JVM热重载 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 原因 | 新建SpringBoot项目时没有勾选Spring Web | 找不到主类 | 虚拟机创建时分配的内存不足 |
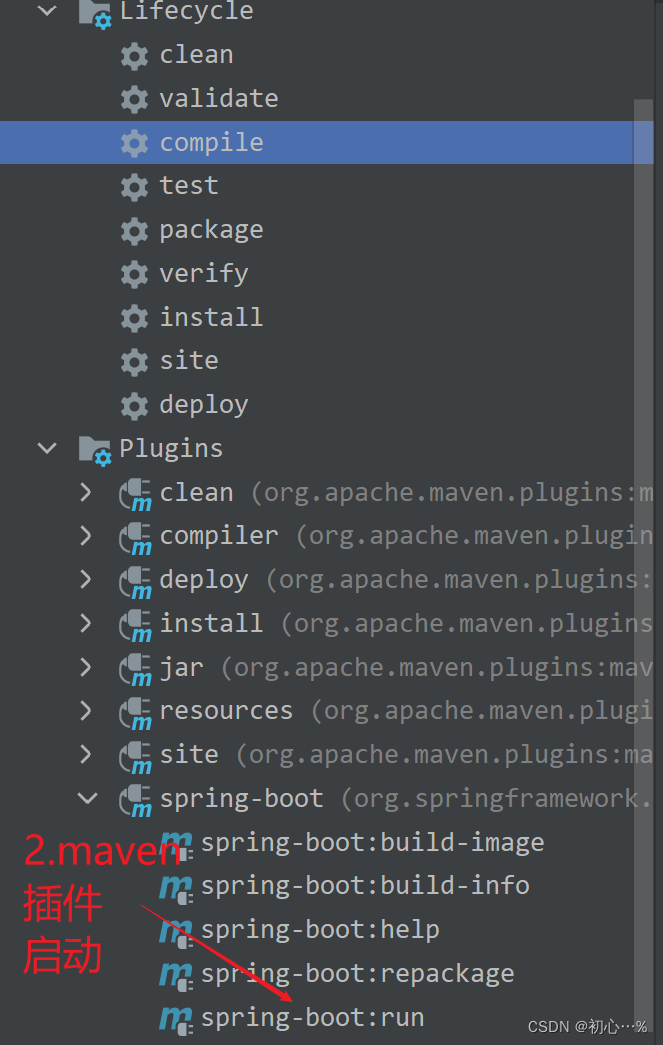
| 解决方案 | 删掉当前项目新建(不建议);在pom文件中添加如下依赖 | 执行mvn clean、mvn compile、mvn install、mvn spring-boot run | 暂不理会 |
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
点击Spring Initializer官网,选择要生成的项目骨架,下载解压下来。

| 启动方式 | 主类启动 | maven指令启动 | 命令行启动 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 具体步骤 |  |
 |
 |
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
pom文件中这些原本存在的、带有starter前缀的依赖称为起步依赖,通过起步依赖,SpringBoot项目一开始就导入了大量的依赖,定义了大量的依赖版本号,官方的starter一般都是spring-boot-starter-xxx的格式。
这里举例不使用默认的tomcat服务器,使用jetty服务器。
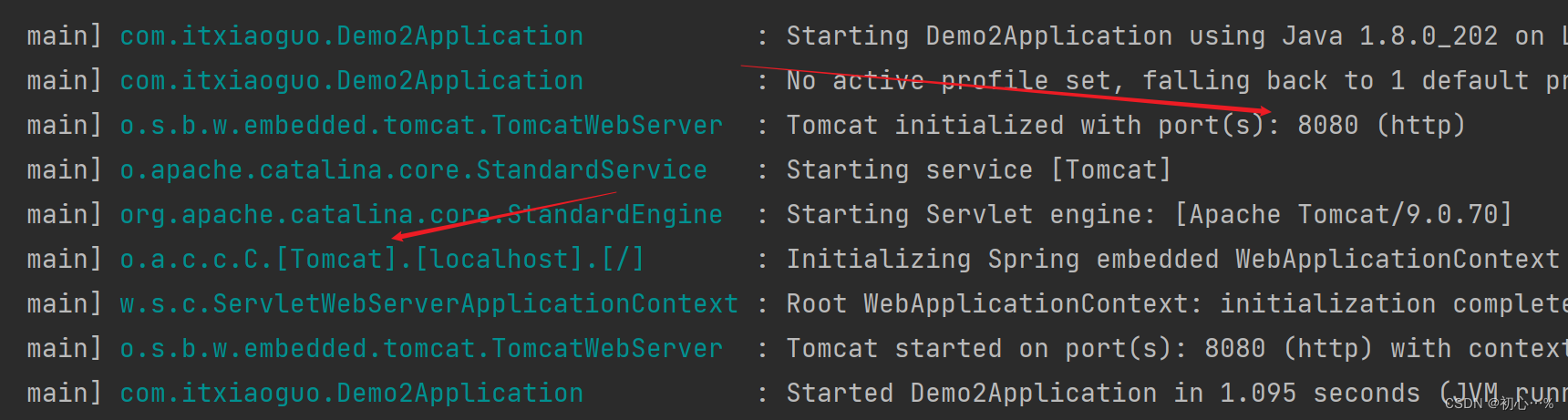
(1)启动tomcat时的日志信息
(2)排除默认的tomcat,添加jetty起步依赖,之后刷新pom文件
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<!-- 排除默认的tomcat -->
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<!-- 添加jetty起步依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jetty</artifactId>
</dependency>
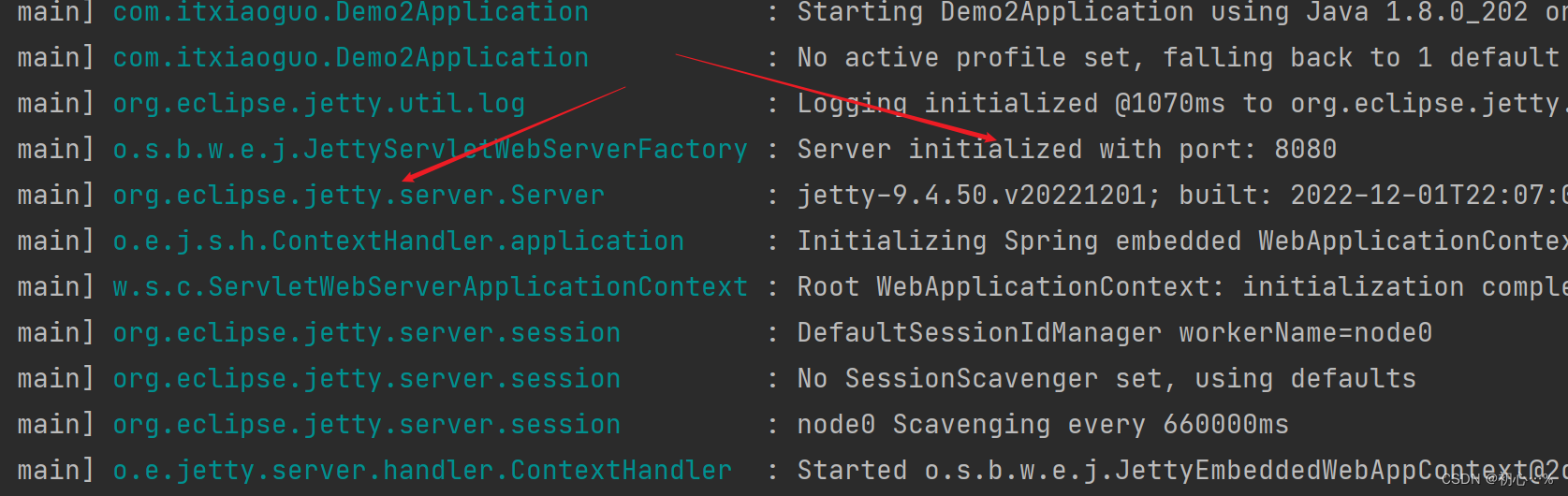
(3) 启动jetty时的日志信息
SpringBoot项目默认的配置文件是application.properties,并且所有的配置文件都要以application-开头。 下面通过修改tomcat服务器端口的例子介绍三种配置文件的格式。
| 配置文件格式 | .properties | .yml(后续主要写) | .yaml |
|---|---|---|---|
| 优先级 | 1 | 2 | 3 |



(1)查看tomcat使用的端口:

(2)注释掉application.properties文件,查看端口:

由此可以得出优先级,properties文件大于yml文件大于yaml文件。
修改了配置文件后不生效,先更改下面的内容,再重启。
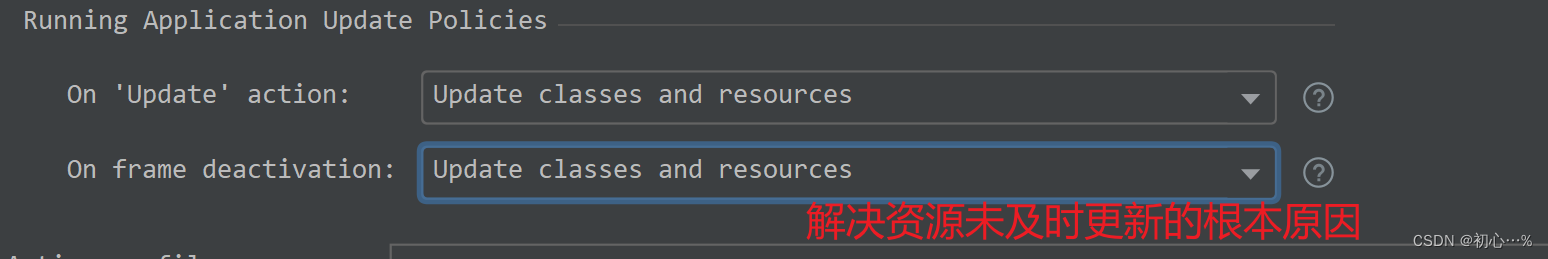
YAML 是 “YAML Ain’t a Markup Language”(YAML 不是一种标记语言)的递归缩写。在开发的这种语言时,YAML 的意思其实是:“Yet Another Markup Language”(仍是一种标记语言)。

下面看使用yaml语法的例子
| 方式 | @Value读取 | 使用Environment对象+@AutoWired读取 | 定义一个Enterprise实体类 |
|---|
下面介绍三种方式的代码,再省略再Postman发送请求的过程。
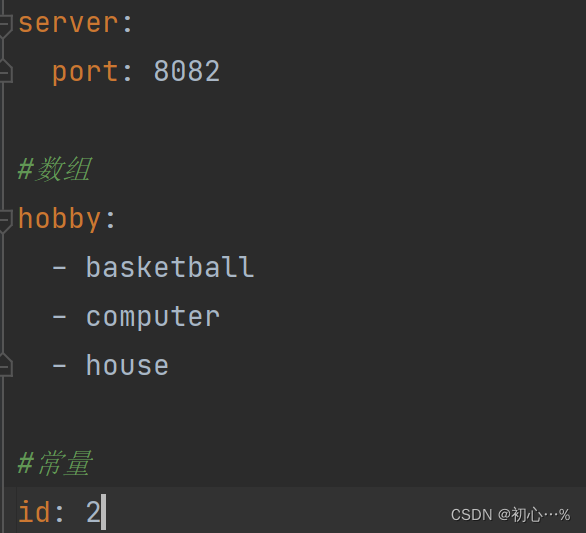
server:
port: 8080
#数组
test:
hobby:
- basketball
- computer
- house
#常量
id: 2
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "test")
public class Enterprise {
private String[] hobby;
// 省略getter、setter、有参、空参、toString()方法
}
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/users")
public class UserController {
// 1.直接获取yml文件的数据
@Value("${id}")
private Integer id;
@Value("${server.port}")
private String port;
// 2.通过Environment对象获取
@Autowired
private Environment environment;
// 3.通过实体类获取
@Autowired
private Enterprise enterprise;
@GetMapping
public String selectAll() {
System.out.println("--------1------");
System.out.println("id --> " + id + ",port --> " + port);
System.out.println("-------2-------");
System.out.println("id --> " + environment.getProperty("id") + ",port --> " + environment.getProperty("server.port"));
System.out.println("--------3------");
System.out.println(enterprise);
return "id --> " + id;
}
}

| 环境配置方式 | yaml文件配置多环境(推荐) | properties文件设置多环境 |
|---|---|---|
| 使用方式 | 在yml文件中选择环境 | 每一个环境是独立的properties文件,根据文件名识别 |
# yml文件多环境开发配置(使用---将多个环境分开)
---
server:
port: 81
spring:
config:
activate:
on-profile: dev # 开发环境
---
server:
port: 82
spring:
config:
activate:
on-profile: pro # 生产环境
---
server:
port: 83
spring:
config:
activate:
on-profile: test # 测试环境
---
# 选择环境
spring:
profiles:
active: pro
根据上面的配置,选择的是生产环境,端口应该是82,启动服务器查看端口:

验证成功!下面看使用properties文件配置多环境:

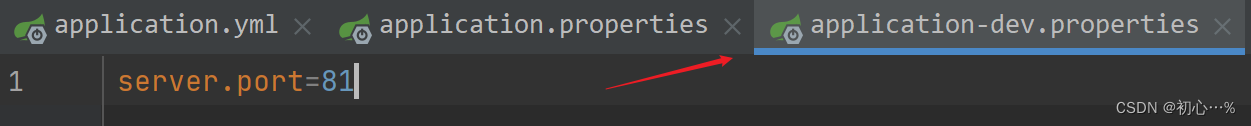

验证成功!

上面的环境在项目打包好之后就不能改变了,显然不够灵活,通过命令行带参数启动springboot的形式,达到临时切换环境的目的。
注意事项:
打包(package)之前先清除target目录(clean)

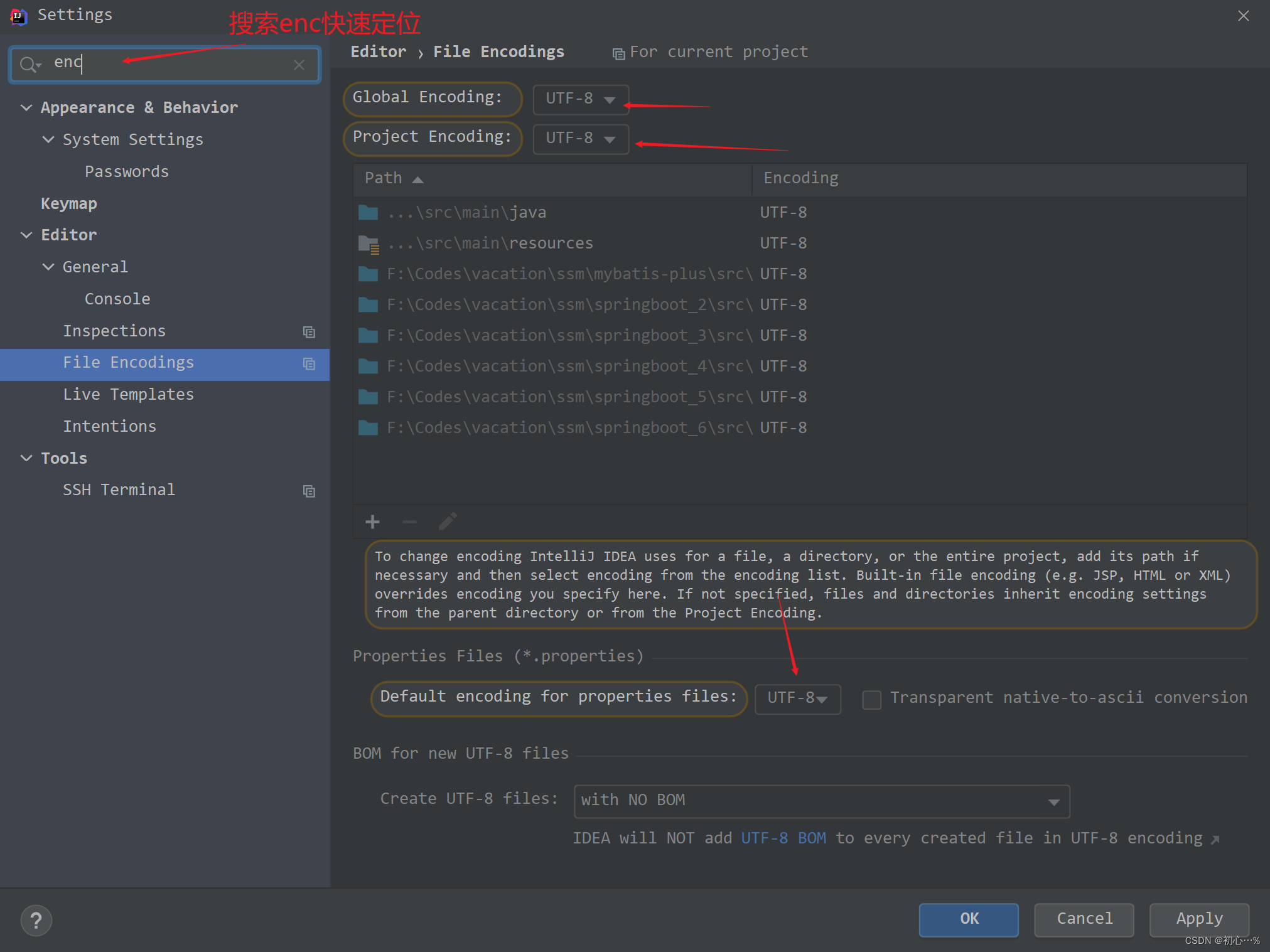
将IDEA文件编码设置为UTF-8

| 命令行切换环境 | 命令行切换端口 |
|---|---|
| java -jar **.jar --spring.profiles.active=环境名 | java -jar **.jar --server.port=85 |
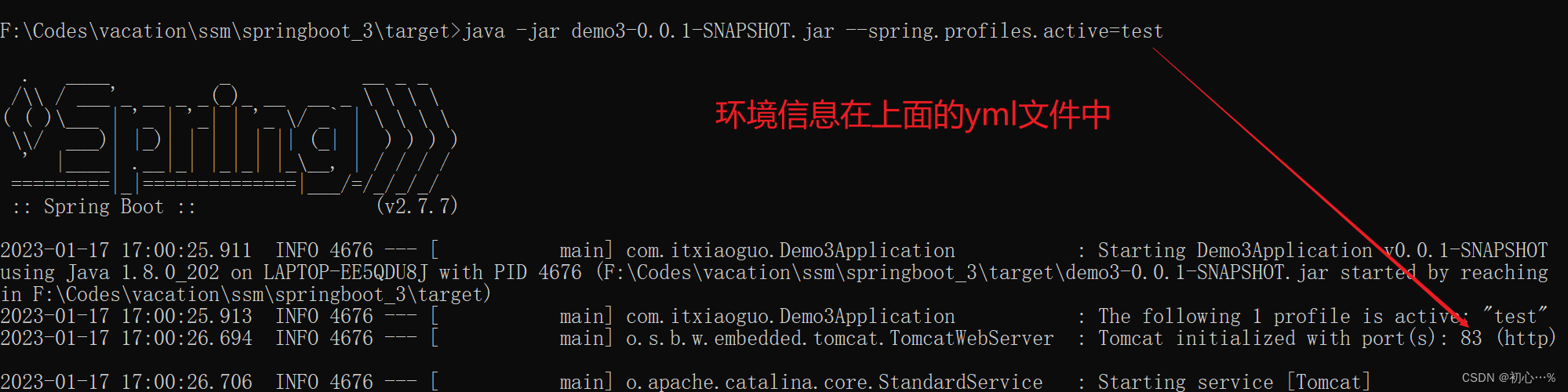
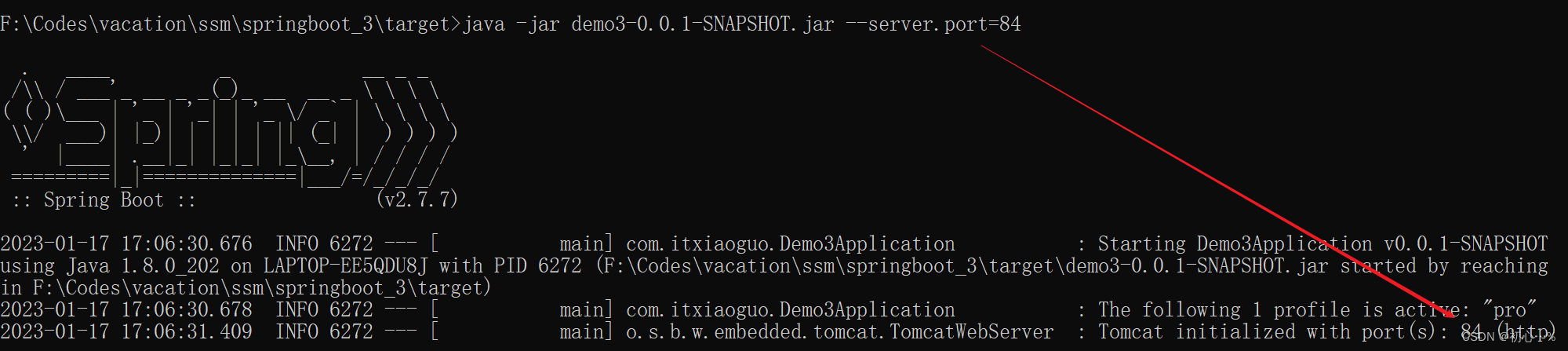
Maven和SpringBoot都有多环境,当都配置了多环境时,SpringBoot使用Maven的环境,便于项目管理。
(1)Maven的pom文件设置多环境
<build>
<plugins>
<!-- 让非pom文件也能识别${},从而获取到Maven中的环境-->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-resources-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<encoding>UTF-8</encoding>
<useDefaultDelimiters>true</useDefaultDelimiters>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
<!-- Maven配置多环境-->
<profiles>
<!-- 生产环境-->
<profile>
<id>pro</id>
<properties>
<profile.active>pro</profile.active>
</properties>
<!-- 默认使用这个环境-->
<activation>
<activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault>
</activation>
</profile>
<!-- 开发环境-->
<profile>
<id>dev</id>
<properties>
<profile.active>dev</profile.active>
</properties>
</profile>
<!-- 测试环境-->
<profile>
<id>test</id>
<properties>
<profile.active>test</profile.active>
</properties>
</profile>
</profiles>
(2)yml文件中引用Maven属性,从而获取环境
# 选择环境
spring:
profiles:
active: ${profile.active}
(3)执行打包命令查看端口
当不要用命令行启动时要及时关闭,不能双击jar包,否则会导致IO异常,clean,package报错。
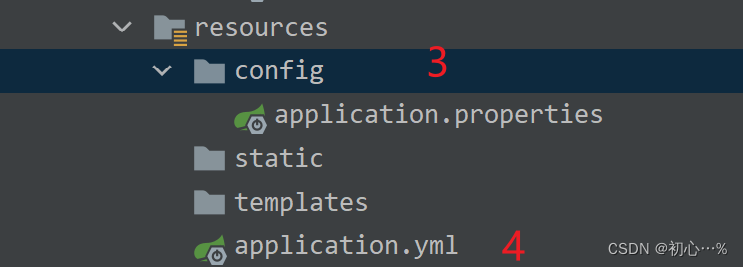
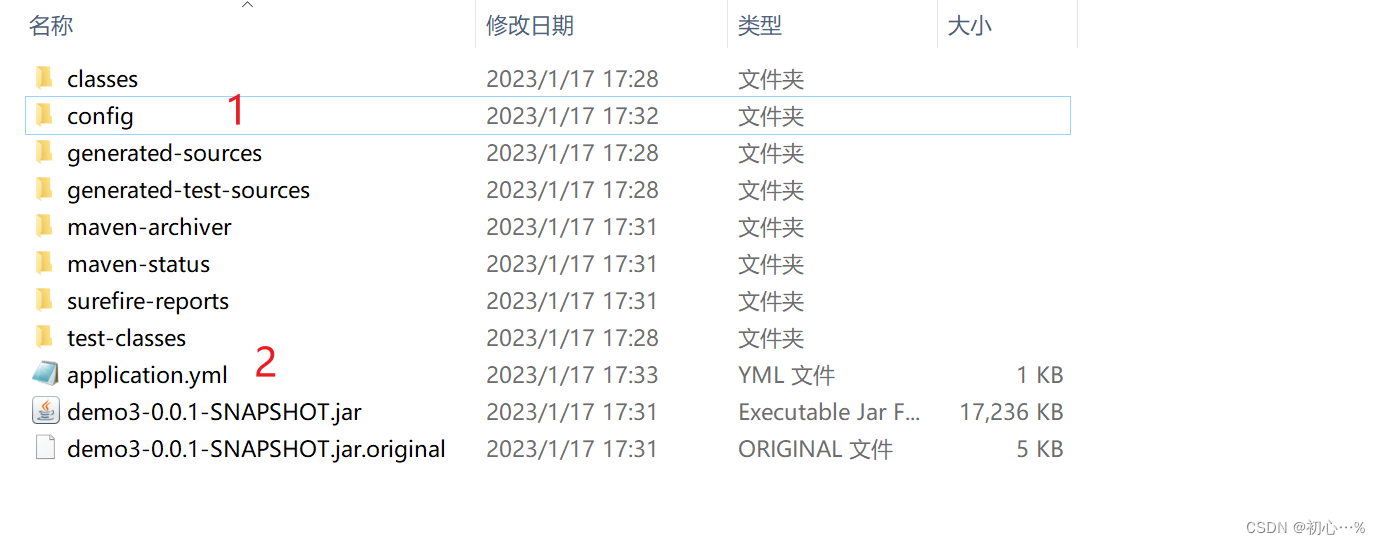
| 配置文件类别 | resources下的配置文件 | config目录下的配置文件 | target目录下的application.yml文件 | target目录下的config文件夹下的application.yml文件 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 优先级 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)