Python中的变量和数据类型是什么?
Python编程语言是当今最受欢迎的编程语言之一。开发人员希望专注于实现部分,而不是花时间编写复杂的程序。这是python实际交付的地方,具有易于访问和可读性的特点。基本概念是任何编程语言的基础,因此在本博客中,我们将学习python中的变量和数据类型的概念。以下是此博客涵盖的主题:
Python中的变量是什么?
顾名思义,python中的变量和数据类型是变化的值。在编程语言中,变量是您存储值的存储位置。您存储的值将来可能会根据规格更改。
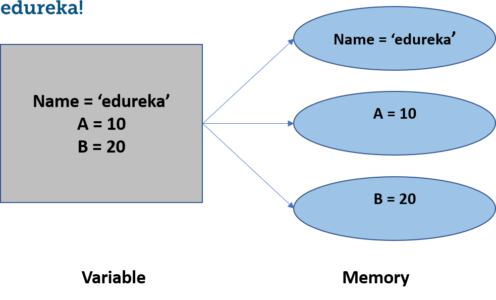
一旦为它分配了值,就会在python中创建一个Variable。它不需要任何其他命令即可在python中声明变量。
编写变量时必须遵循某些规则和规定,让我们看一下变量定义和声明,以了解我们如何在python中声明变量。
变量定义和声明
Python没有其他命令来声明变量。为其分配值后,立即声明该变量。
|
1
2
|
x = 10
#variable is declared as the value 10 is assigned to it.
|
声明变量时,我们必须牢记某些规则:
- 变量名称不能以数字开头。它只能以字符或下划线开头。
- python中的变量区分大小写。
- 它们只能包含字母数字字符和下划线。
- 不允许使用特殊字符。
python中有几种数据类型。让我们看一下python中的数据类型。
我们在python中声明的每个值都有一个数据类型。数据类型是类,变量是这些类的实例。
Python中的数据类型
根据它们拥有的属性,python中主要有六种数据类型。虽然还有一个数据类型范围,但在python中使用循环时经常使用。
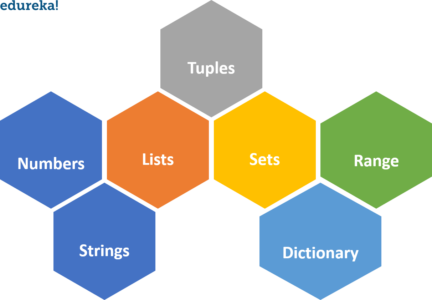
数值数据类型
数值数据类型保存数值。在数字数据中,也有4个子类型。以下是数值数据类型的子类型:
- 整数
- 浮点数
- 复数
- 布尔型
整数(Integers) 用于表示整数值。
|
1
2
3
|
x = 100
y = 124
# it will be the integer as long as the value is a whole number.
|
要检查任何变量数据类型的类型,我们可以使用type()函数。它将返回所提到的变量数据类型的类型。
浮点数(Float) 数据类型用于表示小数点值。
x = 10.25
y = 12.30复数(Complex) 用于表示虚数值。虚数值在数字末尾用“ j”表示。
x = 10 + 5j布尔(Boolean) 值用于分类输出,因为布尔值的输出为true或false。
num = 5 > 4
#num is the boolean variable
type(num)
#the output will be bool
print(num)
#this will print true.字符串(Strings)
python中的字符串用于表示unicode字符值。Python没有字符数据类型,单个字符也被视为字符串。
我们用单引号或双引号表示或声明字符串值。要访问字符串中的值,我们使用索引和方括号。
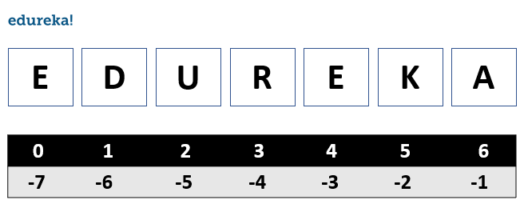
name = 'edureka'
name[2]
#this will give you the output as 'u'字符串本质上是不可变的,这意味着一旦替换,您将无法更改字符串。
字符串的命令行输入
x = input()
print( 'hello' , x)使用字符串的操作
name = 'edureka'
name.upper()
#this will make the letters to uppercase
name.lower()
#this will make the letters to lowercase
name.replace('e') = 'E'
#this will replace the letter 'e' with 'E'
name[1: 4]
#this will return the strings starting at index 1 until the index 4.现在我们已经了解了数字和字符串,让我们了解相对复杂的数据类型。
列表(Lists)
List是我们在python中拥有的四种收集数据类型之一。选择集合类型时,了解集合的功能和局限性很重要。元组,集合和字典是另一个集合数据类型,是python。
与字符串不同,列表是有序的并且可以更改。我们也可以添加重复值。为了声明列表,我们使用方括号。
mylist = [10,20,30,40,20,30, 'edureka']从列表访问值
我们使用索引来访问字符串中的值。
mylist[2:6]
#this will get the values from index 2 until index 6.在列表中添加/替换值
mylist[6] = 'python'
#this will replace the value at the index 6.
mylist.append('edureka')
#this will add the value at the end of the list.
mylist.insert(5, 'data science')
#this will add the value at the index 5.我们可以对列表执行的其他操作如下:
| Method Name | Property | 备注 |
| clear() | removes all the elements from the list | 从列表中删除所有元素 |
| copy() | returns a copy of the list | 返回列表的副本 |
| extend() | add the elements of the list to the end of the current list | 将列表的元素添加到当前列表的末尾 |
| count() | returns the number of elements of the specified value | 返回指定值的元素数 |
| index() | returns the index of the element | 返回元素的索引 |
| pop() | removes the element from the specified position | 从指定位置移除元素 |
| remove() | removes the item with the specified value | 删除具有指定值的项目 |
| sort() | sorts the list | 排序列表 |
| reverse() | returns the reversed list | 返回反向列表 |
列表可以将任何数据类型存储为项目。无论是数字,字符串还是任何其他数据类型。
a = [10,20,30]
b = [60 , 50 , 40, a]
#to access a value from the list a we can write
b[3][2]
#this will return 30 as output.让我们了解python中的下一个集合数据类型,即元组。
元组(Tuples)
元组是不可更改或不可变的集合。它是有序的,可以使用索引值访问值。元组也可以具有重复的值。要声明一个元组,我们使用圆括号。
mytuple = (10,10,20,30,40,50)
#to count the number of elements
mytuple.count(10)
#the output will be 2
#to find the index
mytuple.index(50)
#the output will be 5. since the index number at 50 is 5.由于元组一旦声明就不可更改,因此对元组执行的操作并不多。但是使用元组有一个光明的一面,您可以将值存储在您在项目中工作时不希望更改的元组中。尽管您将能够访问这些值,但是不会进行任何更改。
集合(Sets)
集合是无序的集合,也没有任何索引。为了在python中声明一个集合,我们使用大括号。
myset = {10, 20 , 30 ,40, 50, 50}一个集合没有任何重复的值,即使在声明该集合时不会显示任何错误,输出也将仅具有不同的值。
要访问集合中的值,我们可以遍历集合,也可以使用成员运算符查找特定值
for x in myset:
print(x)
#this will get all the values.
20 in myset
#this will return true if the value is in the set.
#to add a value in a set
myset.add('edureka')
#to add multiple values in a list
myset.update([ 10, 20, 30, 40, 50])
#to remove an item from a set
myset.remove('edureka')
#we can use the discard or pop method to remove an item from a set as well.
myset = {10, 20, 30}
myset1 = {10,30,50}
myset.issubset(myset1)
#this will return false
myset.union(myset1)
#this will return a set with the union of the two sets.| Method Name | Property | 备注 |
| clear() | clears the items from a set | 从集合中清除项目 |
| copy() | returns the copy of the set | 返回集合的副本 |
| difference() | returns a set with the difference of the two sets | 返回具有两个集合之差的集合 |
| isdisjoint() | returns if the sets have intersection | 如果集合有交集,则返回 |
| issubset() | returns if the set is a subset | 如果集合是子集,则返回 |
| symmetricdifference() | returns a set with the symmetric difference | 返回具有对称差异的集合 |
| update() | update the sets with union of the set | 用集合的并集更新集合 |
让我们看一下另一个具有键值对的集合数据类型。
字典(Dictionary)
字典就像python中的任何其他集合数组一样。但是它们具有键值对。字典是无序且可变的。我们使用键来访问字典中的项目。要声明字典,请使用大括号。
mydictionary = { 'python': 'data science', 'machine learning' : 'tensorflow' , 'artificial intelligence': 'keras'}
mydictionary['machine learning']
#this will give the output as 'tensorflow'
mydictionary.get('python')
#this serves the same purpose to access the value.由于我们使用键来访问项目,因此它们不能重复。值可以具有重复的项目。
字典中的数据处理
#adding a new value
mydictionary['analysis'] = 'matplotlib'
#replacing a value
mydictionary['analysis'] = 'pandas'
#deleting a value
mydictionary.pop('analysis')
#remove() , del also serves the same purpose for deleting a value.词典中的其他操作包括以下内容。
| Method Name | Property | 备注 |
| copy() | returns a copy of the dictionary | 返回字典的副本 |
| clear() | clears the dictionary | 清除字典 |
| items() | returns a list containing tuple of key value pairs | 返回包含键值对的元组的列表 |
| keys() | returns a list containing all the keys | 返回包含所有键的列表 |
| update() | updates the dictionary with all the key-value pairs | 使用所有键值对更新字典 |
| values() | returns a list of all the values in a dictionary | 返回字典中所有值的列表 |
| setdefault() | returns the value of a specified key | 返回指定键的值 |
范围(Range)
范围是一种数据类型,主要在我们使用循环时使用。让我们举个例子来理解这一点。
for x in range(10):
print(x)
#this will print the numbers from 0-10. Range will have the numbers from 0-10既然我们已经了解了python中具有的不同数据类型,那么还有一个重要的类型转换概念,当我们从一种数据类型转换为另一种数据类型时,这很有用。让我们了解类型转换的概念。
- list()
- set()
- tuple()
- dict()
- str()
- int()
- float()
我们可以简单地使用这些构造函数来使用指定的数据类型,也可以使用这些构造函数将数据类型更改为另一种。让我们用一个例子来理解这一点。
a = [ 10 , 20 ,30,40]
#to change this list into a tuple i can simply write
tuple(a)
#now the list will change to a tuple.现在,我们已经讨论了python中的变量和数据类型。我希望每种数据类型的属性和操作对您来说都是清楚的。
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)