Android四大组件之Service
作用:
是在后台长期运行某些服务,如复杂的计算 、音乐播放、下载等等。
分类:
- Service按运行的位置划分有:本地服务、远程服务
- Service按运行的类型划分有:前台服务、后台服务
- Service按运行的功能划分有:可通信服务、不可通信服务
下面逐一讲解。
本地服务与远程服务
| 类型 | 说明 | 优缺点 | 应用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 本地服务(最常用) | 运行在主线程,当主线程终止后,服务也会跟着终止 | 优点:通信方便,因为是在同一进程中。不需要为创建新的进程而消耗资源。缺点:限制性较大,主线程终止,它执行的任务也会被终止。 | 常用于需要依赖某个进程的任务:如音乐播放 |
| 远程服务 (独立进程) | 运行在独立进程中,常驻后台,不受Activity影响 | 优点 :1.远程服务有自己的独立进程,不会受到其它进程的影响;2.可以被其它进程复用,提供公共服务;3.具有很高的灵活性。缺点 :相对普通服务,占用系统资源较多,进程前通信麻烦,要使用AIDL进行IPC通信。 | 为其它应用程序提供公共服务的Service,这种Service为系统常驻的Service。多个应用程序共享同一个后台服务 |
本地服务使用步骤
本地服务使用步骤1: 新建子类继承Service类,重写父类的onCreate()、onStartCommand()、onDestroy()和onBind()方法。
package com.ti.myservice;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.util.Log;
// 本地Service这是最常用的
public class LocalService extends Service { public LocalService() { } @Override public void onCreate() { super.onCreate(); Log.d("本地Service#","onCreate创建服务"); } @Override public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) { Log.d("本地Service#","onStartCommand开始服务"); return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId); } @Override public void onDestroy() { super.onDestroy(); Log.d("本地Service#","onDestroy销毁服务"); } @Override public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) { Log.d("本地Service#","onBind绑定服务"); return null; }
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
本地服务使用步骤2: 在AndroidManifest.xml里注册Service
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.ti.myservice">
... <application ...> <service android:name=".LocalService" android:enabled="true" android:exported="true"></service> ... </application>
</manifest>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
AndroidManifest.xml里Service标签的常见属性:
| 属性 | 说明 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| android:name | Service的类名 | 必要的 |
| android:label | Service的名字 | 若不设置,默认为Service类名 |
| android:icon | Service的图标 | |
| android:permission | 申明此Service的权限 | 提供该权限的应用才能控制或连接此服务 |
| android:process | 表示该服务是否在另一个进程中运行(远程服务) | 不设置默认为本地服务;设置为:remote则成远程服务 |
| android:enabled | 系统默认启动 | true:Service 将会默认被系统启动;不设置则默认为false |
| android:exported | 该服务是否能够被其他应用程序所控制或连接 | 不设置此项默认为 false |
本地服务使用步骤3: 构建用于启动Service的Intent对象
启动Service Intent
Intent startLocalServiceIntent = new Intent(MainActivity.this,LocalService.class);
- 1
终止Service Intent
Intent stopLocalServiceIntent = new Intent(MainActivity.this,LocalService.class);
- 1
本地服务使用步骤4:
调用startService()启动Service
Intent startLocalServiceIntent = new Intent(MainActivity.this,LocalService.class);
startService(startLocalServiceIntent);
- 1
- 2
调用stopService()停止服务
Intent stopLocalServiceIntent = new Intent(MainActivity.this,LocalService.class);
stopService(stopLocalServiceIntent);
- 1
- 2
本地服务运行结果:
2019-07-22 18:27:59.377 17266-17266/com.ti.myservice D/本地Service#: onCreate创建服务
2019-07-22 18:27:59.378 17266-17266/com.ti.myservice D/本地Service#: onStartCommand开始服务
2019-07-22 18:28:09.813 17266-17266/com.ti.myservice D/本地Service#: onDestroy销毁服务
- 1
- 2
- 3
远程服务使用
远程服务(Remote Service)也被称之为独立进程,它不受其它进程影响,可以为其它应用程序提供调用的接口——实际上就是进程间通信IPC(Inter-Process Communication),Android提供了AIDL(Android Interface Definition Language,接口描述语言)工具来帮助进程间接口的建立。
在Android中,不同的应用属于不同的进程(Process),一个进程不能访问其它进程的存储,但是可以通过ContentProvider实现,如:通讯录的读取。
远程服务与本地服务最大的区别是:远程Service与调用者不在同一个进程里(即远程Service是运行在另外一个进程);而本地服务则是与调用者运行在同一个进程里。
将一个Service变成远程服务,加上android:process=":remote"就可以了,然后它就在另一个进程里自己运行了,你要和它通信就要用AIDL的方式了。
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.ti.myapplication">
... <application ...> <service android:name=".LocalService" android:enabled="true" android:exported="true" android:process=":remote"></service> ... </application>
</manifest>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
远程服务的讲解,独立成一章《远程服务Service & AIDL & IPC》
前台服务与后台服务
| 类型 | 说明 | 应用场景 |
|---|---|---|
| 前台服务 | 在通知栏显示(用户可见) | 服务使用时,需要让用户知道、并进行相关操作,如音乐播放 |
| 后台服务 | 处于后台服务(用户看不见) | 服务使用时,不需要让用户知道,如天气更新、日期同步等 |
前台服务使用步骤
创建前台服务步骤1:
编写继承Service的子类,重写onCreate()方法,在其中开启前台线程。这样既可以使用startService(),也可以使用bindService()开启前台服务,因为它们都会执行onCreate方法。
如果把开启前台线程写到onStartCommand(),那么只能用startService()开启前台服务,bindService()就开启不了,因为用bindService开启,onStartCommand不会被执行。
如果把开启前台线程写到onBind,那么只能用用bindService开启,因为startService调用时,onBind不会被执行。而只有onCreate是两种开启方法时都会被调用的。
@Override public void onCreate() { super.onCreate(); String id = "channel_01"; String name="我是渠道名字"; // 添加下列代码将后台Service变成前台Service // 构建点击通知后打开MainActivity的Intent对象 Intent notificationIntent = new Intent(this,MainActivity.class); PendingIntent pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity(this, 1, notificationIntent, PendingIntent.FLAG_CANCEL_CURRENT); //获取系统通知服务 NotificationManager notificationManager = (NotificationManager) getSystemService(Context.NOTIFICATION_SERVICE); Notification notification = null; if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.O) { NotificationChannel mChannel = new NotificationChannel(id, name, NotificationManager.IMPORTANCE_LOW); notificationManager.createNotificationChannel(mChannel); notification = new Notification.Builder(this,id) .setContentTitle("前台服务通知的标题")// 设置通知的标题 .setContentText("前台服务通知的内容")// 设置通知的内容 .setSmallIcon(R.mipmap.ic_launcher)// 设置通知的图标 .setContentIntent(pendingIntent)// 设置点击通知后的操作 .build(); } else { notification = new NotificationCompat.Builder(this) .setContentTitle("前台服务通知的标题") .setContentText("前台服务通知的内容") .setSmallIcon(R.mipmap.ic_launcher) .setOngoing(true) .setChannelId(id) .setContentIntent(pendingIntent) //设置pendingIntent,点击通知时就会用到 .build(); } startForeground(1, notification);// 让Service变成前台Service,并在系统的状态栏显示出来 Log.d("前台Service#","onCreate创建服务"); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
创建前台服务步骤2:
在AndroidManifest.xml中注册服务。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.ti.myapplication">
... <application ...> ... <service android:name=".FrontService" android:enabled="true" android:exported="true"></service> ... </application>
</manifest>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
创建前台服务步骤3:开启服务。
用startService开启
Intent startFrontServiceIntent = new Intent(MainActivity.this,FrontService.class);
startService(startFrontServiceIntent);
- 1
- 2
关闭
Intent stopFrontServiceIntent = new Intent(MainActivity.this,FrontService.class);
stopService(stopFrontServiceIntent);
- 1
- 2
用bindService绑定服务:
private ServiceConnection testServiceConnection = new ServiceConnection() { @Override public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) { } @Override public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) { } };
bindService(startFrontServiceIntent,testServiceConnection,BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
解绑:
unbindService(testServiceConnection);
- 1
可通信服务与不可通信服务
| 类型 | 说明 | 应用场景 |
|---|---|---|
| 可通信服务 | bindService()启动。当调用者退出后,服务也跟着销毁 | 服务要与Activity通信,需要控制好服务开始时间,第一次bindService时才会创建服务的实例并运行。BroadcastReceiver可实现与此Service相同的功能,但若操作太频繁,将会造成性能问题。 |
| 不可通信服务 | startService()启动。当调用者退出后,服务仍然存在 | 服务不需要与Activity通信 |
可通信服务使用步骤
可通信服务使用步骤1: 新建子类继承Service类和定义一个Binder。
package com.ti.myapplication;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Binder;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.util.Log;
public class CommunicationService extends Service { private CommunicationBinder mBinder = new CommunicationBinder("可通信Service"); public CommunicationService() { } @Override public void onCreate() { super.onCreate(); Log.d("可通信Service#","onCreate创建服务"); } // 可通信Service在绑定服务时,不会执行onStartCommand方法 @Override public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) { Log.d("可通信Service#","onStartCommand开始服务"); return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId); } @Override public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) { Log.d("可通信Service#","onBind绑定服务"); return mBinder; } @Override public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) { Log.d("可通信Service#","onUnbind解绑服务"); return super.onUnbind(intent); } @Override public void onDestroy() { super.onDestroy(); Log.d("可通信Service#","onDestroy销毁服务"); } //新建一个子类继承自Binder类 class CommunicationBinder extends Binder { private String name; public CommunicationBinder(String name){ this.name = name; } public void service_connect_Activity() { Log.d("","Service关联了Activity,并在Activity执行了Service的方法"); } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
可通信服务使用步骤2: 在AndroidManifest.xml中注册服务
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.ti.myapplication">
... <application ....> <service android:name=".CommunicationService" android:enabled="true" android:exported="true"></service>
... </application>
</manifest>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
可通信服务使用步骤3: 准备好ServiceConnection
private CommunicationService.CommunicationBinder myBinder; // 创建ServiceConnection的匿名类 private ServiceConnection connection = new ServiceConnection() { // 重写onServiceConnected()方法和onServiceDisconnected()方法 // 在Activity与Service建立关联和解除关联的时候调用 @Override public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) { } //在Activity与Service解除关联的时候调用 @Override public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) { // 实例化Service的内部类myBinder // 通过向下转型得到了MyBinder的实例 myBinder = (CommunicationService.CommunicationBinder) service; // 在Activity调用Service类的方法 myBinder.service_connect_Activity(); } };
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
可通信服务使用步骤4: 绑定服务
package com.ti.myapplication;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private CommunicationService.CommunicationBinder myBinder; // 创建ServiceConnection的匿名类 private ServiceConnection connection = new ServiceConnection() { // 重写onServiceConnected()方法和onServiceDisconnected()方法 // 在Activity与Service建立关联和解除关联的时候调用 @Override public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) { } //在Activity与Service解除关联的时候调用 @Override public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) { // 实例化Service的内部类myBinder // 通过向下转型得到了MyBinder的实例 myBinder = (CommunicationService.CommunicationBinder) service; // 在Activity调用Service类的方法 myBinder.service_connect_Activity(); } }; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); findViewById(R.id.bind_service).setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { // 构建绑定服务的Intent对象 Intent bindServiceIntent = new Intent(MainActivity.this,CommunicationService.class); // 第一个参数:Intent对象 // 第二个参数:上面创建的ServiceConnection实例 // 第三个参数:标志位 // 这里传入BIND_AUTO_CREATE表示在Activity和Service建立关联后自动创建Service // 这会使得MyService中的onCreate()方法得到执行,但onStartCommand()方法不会执行 bindService(bindServiceIntent,connection,BIND_AUTO_CREATE); } }); findViewById(R.id.unbind_service).setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { // 调用unbindService()解绑服务 // 参数是上面创建的Serviceconnection实例 unbindService(connection); } }); }
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
测试结果:
2019-07-22 20:09:59.662 17540-17540/com.ti.myapplication D/可通信Service#: onCreate创建服务
2019-07-22 20:09:59.663 17540-17540/com.ti.myapplication D/可通信Service#: onBind绑定服务
2019-07-22 20:10:01.067 17540-17540/com.ti.myapplication D/可通信Service#: onUnbind解绑服务
2019-07-22 20:10:01.068 17540-17540/com.ti.myapplication D/可通信Service#: onDestroy销毁服务
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Service与Thread
它们没有任何的关系,但它们常常在一起组合着使用。
Service与Thread的相同点:都是用于执行异步操作的。
Service与Thread的不同点:
- Service运行在主线程,Thread运行在工作线程
- Servcie运行在主线程,不依赖UI/Activity,Thread则要依赖在某个Activity上。
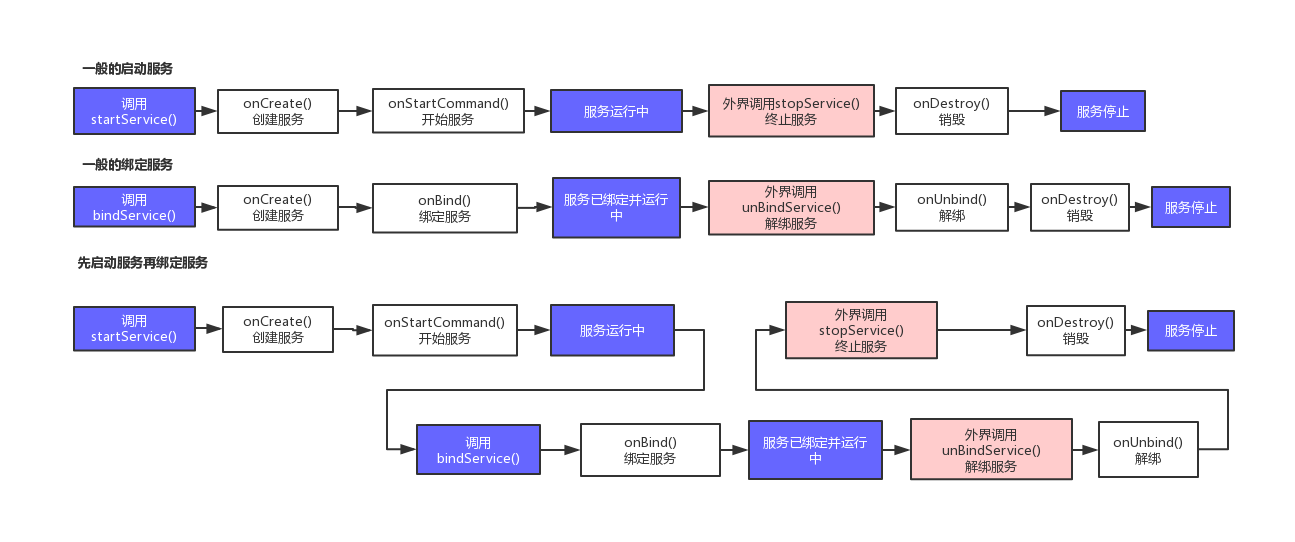
Service的生命周期
远程服务的讲解,独立成一章《远程服务Service & AIDL & IPC》
关于本地服务、可通信服务、前台服务的使用的demo已上传Github。欢迎下载学习!
文章来源: blog.csdn.net,作者:WongKyunban,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:blog.csdn.net/weixin_40763897/article/details/96863519
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)