java 并发编程学习笔记(一)之 并发基础
【摘要】 并发基础
并发小测试
java.util.concurrent.Semaphore 类
public class SemTest { /** * Semaphore 通常用来控制同时有多少个线程在运行 */ private static Semaphore semap...
并发基础
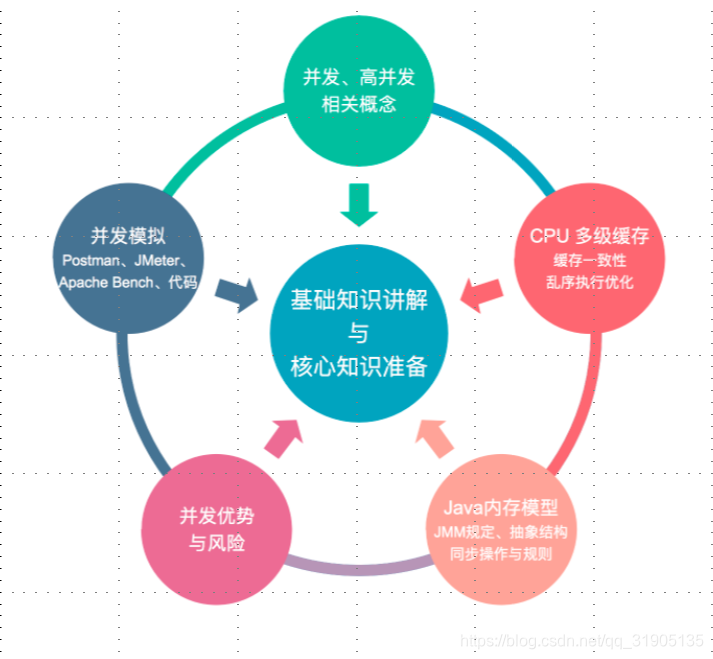
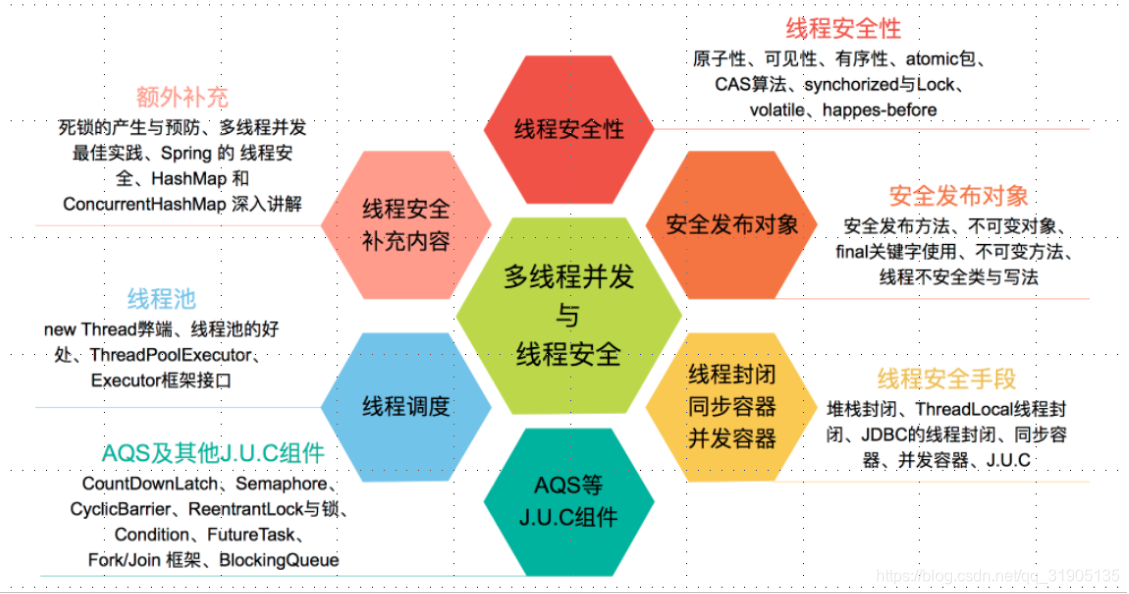
- 并发小测试
java.util.concurrent.Semaphore 类
-
public class SemTest {
-
/**
-
* Semaphore 通常用来控制同时有多少个线程在运行
-
*/
-
private static Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(1);
-
// private static Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(3);
-
static class car implements Runnable {
-
-
-
@Override
-
public void run() {
-
try {
-
semaphore.acquire();
-
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "start ");
-
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "end");
-
semaphore.release();
-
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}
-
}
-
}
-
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
ExecutorService service = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
-
Thread thread = new Thread(new car(), "小汽车1");
-
Thread thread2 = new Thread(new car(), "小汽车2");
-
Thread thread3 = new Thread(new car(), "小汽车3");
-
List<Thread> list = new ArrayList<Thread>();
-
list.add(thread);
-
list.add(thread2);
-
list.add(thread3);
-
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
-
service.execute(list.get(i));
-
}
-
}
-
}
-
@Slf4j
-
public class CountExample {
-
-
private static int threadTotal = 1;
-
private static int clientTotal = 5000;
-
-
private static long count = 0;
-
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
ExecutorService exec = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
-
final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(threadTotal);
-
for (int index = 0; index < clientTotal; index++) {
-
exec.execute(() -> {
-
-
try {
-
semaphore.acquire();
-
add();
-
semaphore.release();
-
} catch (Exception e) {
-
log.error("exception", e);
-
}
-
});
-
}
-
exec.shutdown();
-
log.info("count:{}", count);
-
}
-
-
private static void add() {
-
count++;
-
}
-
}
并发: 多个线程操作相同的资源,保证线程安全,合理使用资源
高并发: 服务器同时处理很多请求,提高程序性能


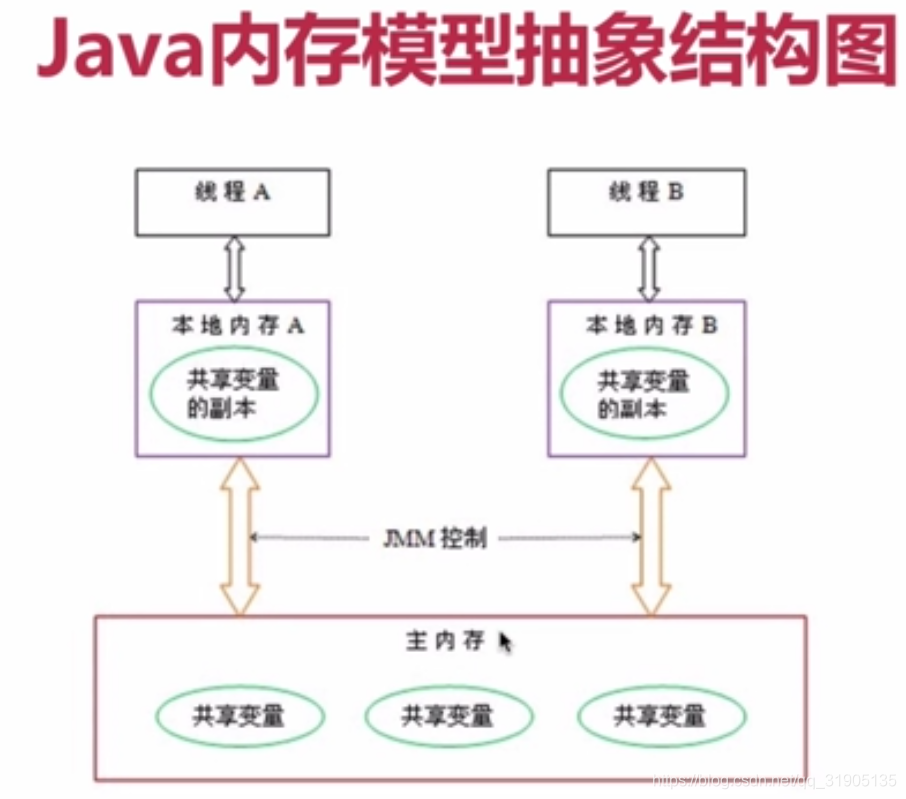
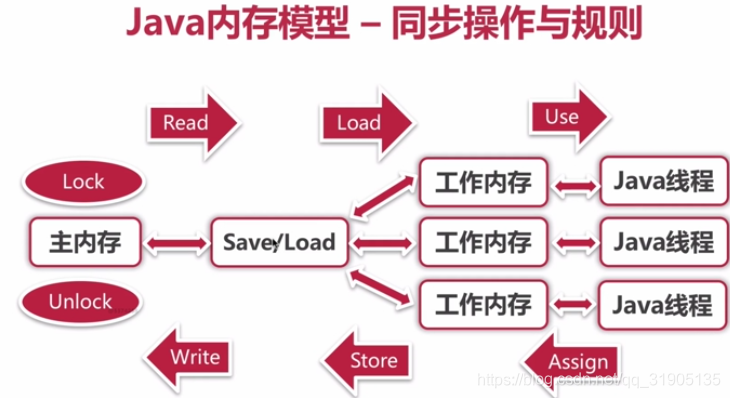






文章来源: blog.csdn.net,作者:血煞风雨城2018,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:blog.csdn.net/qq_31905135/article/details/84143986
【版权声明】本文为华为云社区用户转载文章,如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)