Flume快速入门系列(9) | 如何自定义Sink
这篇文章我们讲解的是如何自定义Sink。
1. 介绍
Sink不断地轮询Channel中的事件且批量地移除它们,并将这些事件批量写入到存储或索引系统、或者被发送到另一个Flume Agent。
Sink是完全事务性的。在从Channel批量删除数据之前,每个Sink用Channel启动一个事务。批量事件一旦成功写出到存储系统或下一个Flume Agent,Sink就利用Channel提交事务。事务一旦被提交,该Channel从自己的内部缓冲区删除事件。
Sink组件目的地包括hdfs、logger、avro、thrift、ipc、file、null、HBase、solr、自定义。官方提供的Sink类型已经很多,但是有时候并不能满足实际开发当中的需求,此时我们就需要根据实际需求自定义某些Sink。
官方也提供了自定义source的接口:
https://flume.apache.org/FlumeDeveloperGuide.html#sink
根据官方说明自定义MySink需要继承AbstractSink类并实现Configurable接口。
实现相应方法:
configure(Context context)//初始化context(读取配置文件内容)
process()//从Channel读取获取数据(event),这个方法将被循环调用。
- 1
- 2
使用场景:读取Channel数据写入MySQL或者其他文件系统。
2. 需求
使用flume接收数据,并在Sink端给每条数据添加前缀和后缀,输出到控制台。前后缀可在flume任务配置文件中配置。
流程分析:
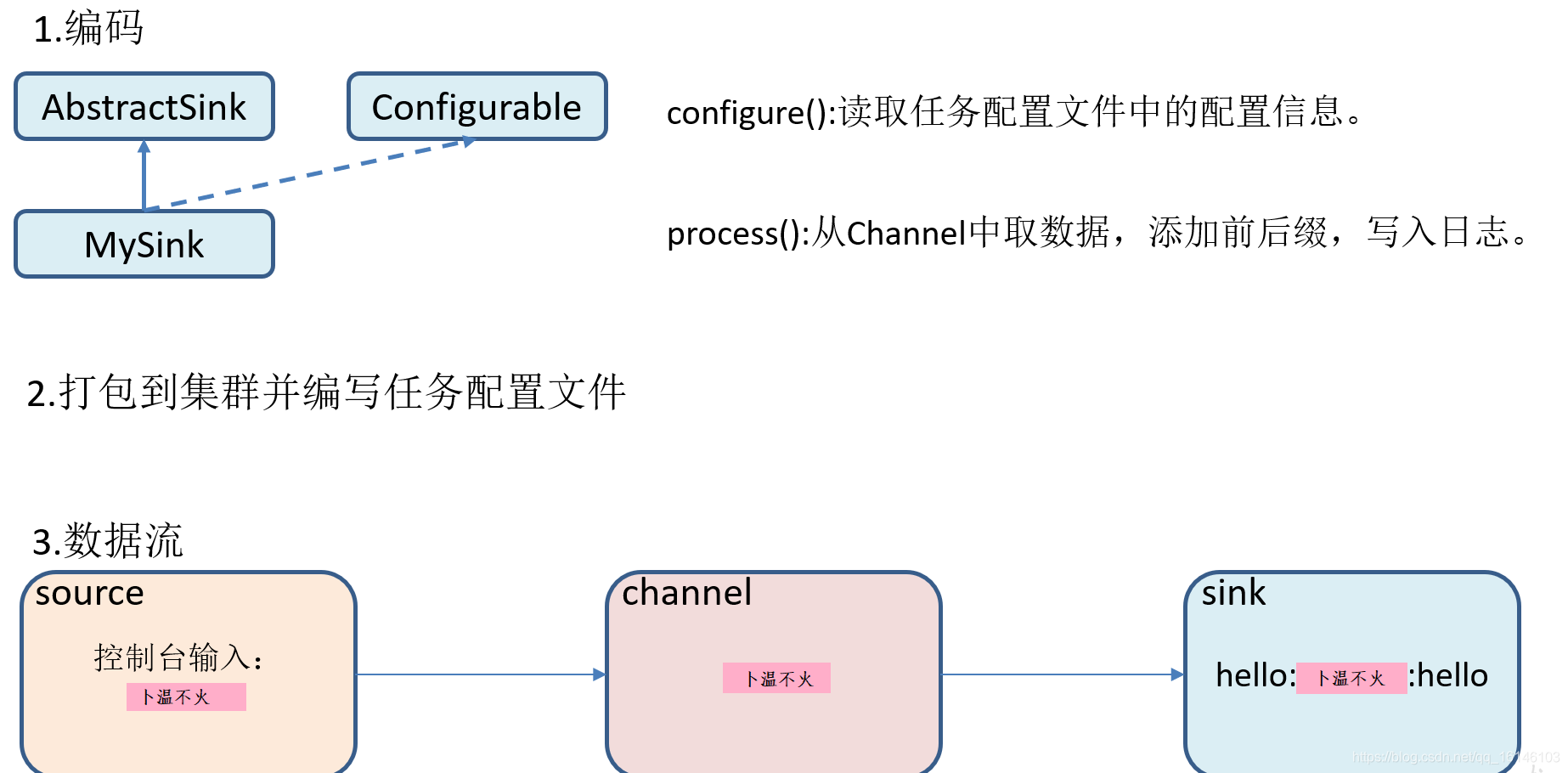
3. 编码
package com.buwenbuhuo;
import org.apache.flume.*;
import org.apache.flume.conf.Configurable;
import org.apache.flume.sink.AbstractSink;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
/**
* @author 卜温不火
* @create 2020-05-04 17:06
* com.buwenbuhuo - the name of the target package where the new class or interface will be created.
* flumeplugins0504 - the name of the current project.
*/
public class MySink extends AbstractSink implements Configurable { //创建Logger对象 private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AbstractSink.class); private String prefix; private String suffix; @Override public Status process() throws EventDeliveryException { //声明返回值状态信息 Status status; //获取当前Sink绑定的Channel Channel ch = getChannel(); //获取事务 Transaction txn = ch.getTransaction(); //声明事件 Event event; //开启事务 txn.begin(); //读取Channel中的事件,直到读取到事件结束循环 while (true) { event = ch.take(); if (event != null) { break; } } try { //处理事件(打印) LOG.info(prefix + new String(event.getBody()) + suffix); //事务提交 txn.commit(); status = Status.READY; } catch (Exception e) { //遇到异常,事务回滚 txn.rollback(); status = Status.BACKOFF; } finally { //关闭事务 txn.close(); } return status; } @Override public void configure(Context context) { //读取配置文件内容,有默认值 prefix = context.getString("prefix", "hello:"); //读取配置文件内容,无默认值 suffix = context.getString("suffix"); }
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
4. 测试
- 1. 打包
将写好的代码打包,并放到flume的lib目录(/opt/module/flume/lib)下。


- 2. 配置文件
[bigdata@hadoop002 job]$ cp flume-netcat-logger.conf flume-netcat-mysink.conf
[bigdata@hadoop002 job]$ vim flume-netcat-mysink.conf # Name the components on this agent
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = netcat
a1.sources.r1.bind = localhost
a1.sources.r1.port = 44444
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = com.buwenbuhuo.MySink
a1.sinks.k1.prefix = buwenbuhuo:
a1.sinks.k1.suffix = :buwenbuhuo
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 3. 开启任务
[bigdata@hadoop002 flume]$ [bigdata@hadoop002 flume]$ bin/flume-ng agent -c conf/ -f job/flume-netcat-mysink.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
- 1
- 2
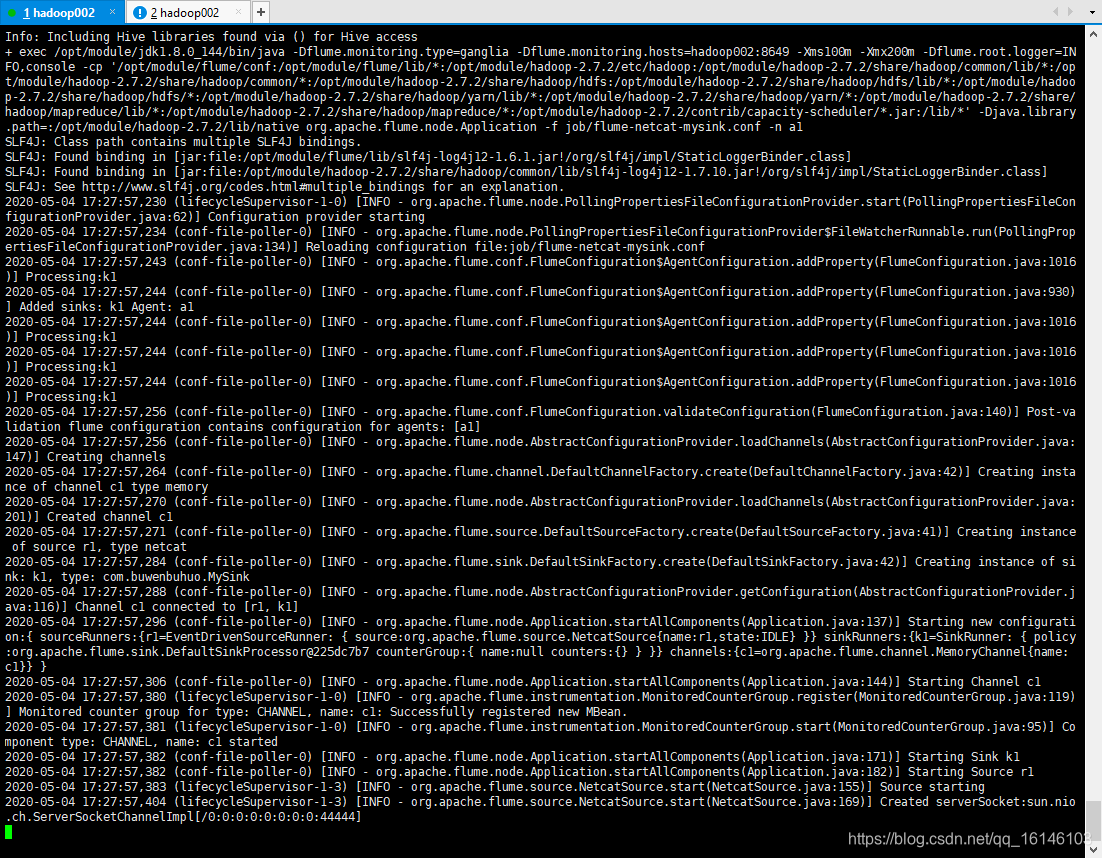
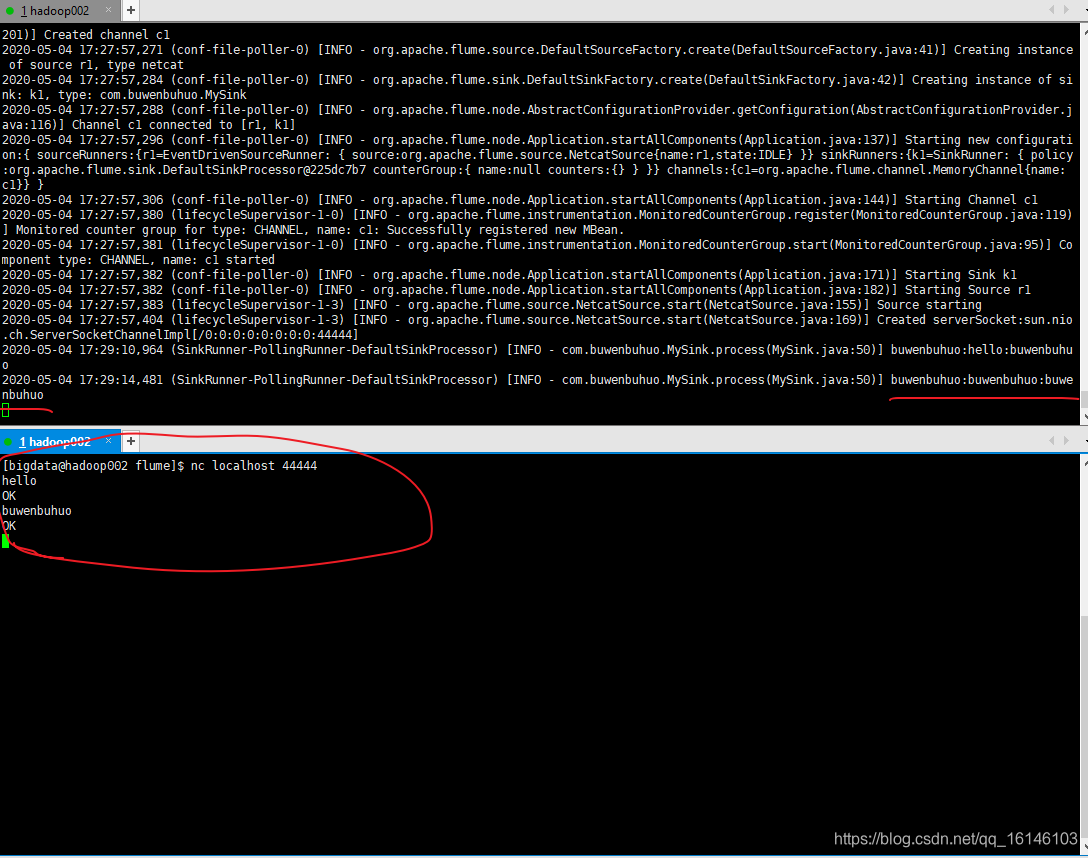
- 4. 结果展示(另开窗口)
[bigdata@hadoop002 flume]$ nc localhost 44444
- 1
本次的分享就到这里了,

看 完 就 赞 , 养 成 习 惯 ! ! ! \color{#FF0000}{看完就赞,养成习惯!!!} 看完就赞,养成习惯!!!^ _ ^ ❤️ ❤️ ❤️
码字不易,大家的支持就是我坚持下去的动力。点赞后不要忘了关注我哦!
文章来源: buwenbuhuo.blog.csdn.net,作者:不温卜火,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:buwenbuhuo.blog.csdn.net/article/details/105919850
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)