java nio 基础用法
传统的io模型问题:
在传统的IO模型中,每个连接创建成功之后都需要一个线程来维护,每个线程包含一个while死循环,那么1w个连接对应1w个线程,继而1w个while死循环,这就带来如下几个问题:
- 线程资源受限:线程是操作系统中非常宝贵的资源,同一时刻有大量的线程处于阻塞状态是非常严重的资源浪费,操作系统耗不起
- 线程切换效率低下:单机cpu核数固定,线程爆炸之后操作系统频繁进行线程切换,应用性能急剧下降。
- 除了以上两个问题,IO编程中,我们看到数据读写是以字节流为单位,效率不高。
NIO编程模型
NIO编程模型中,新来一个连接不再创建一个新的线程,而是可以把这条连接直接绑定到某个固定的线程,然后这条连接所有的读写都由这个线程来负责,那么他是怎么做到的?我们用一幅图来对比一下IO与NIO
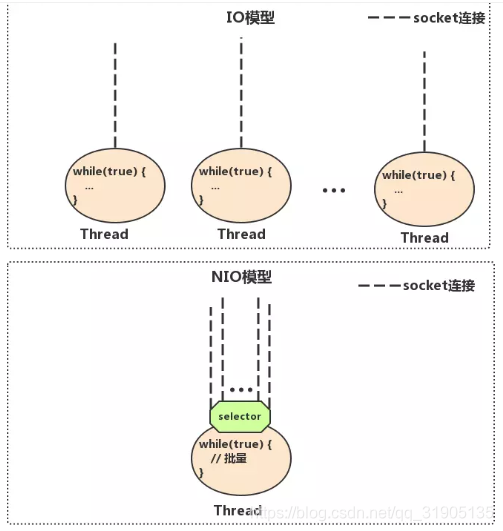
如上图所示,IO模型中,一个连接来了,会创建一个线程,对应一个while死循环,死循环的目的就是不断监测这条连接上是否有数据可以读,大多数情况下,1w个连接里面同一时刻只有少量的连接有数据可读,因此,很多个while死循环都白白浪费掉了,因为读不出啥数据。
而在NIO模型中,他把这么多while死循环变成一个死循环,这个死循环由一个线程控制,那么他又是如何做到一个线程,一个while死循环就能监测1w个连接是否有数据可读的呢?
这就是NIO模型中selector的作用,一条连接来了之后,现在不创建一个while死循环去监听是否有数据可读了,而是直接把这条连接注册到selector上,然后,通过检查这个selector,就可以批量监测出有数据可读的连接,进而读取数据,下面我再举个非常简单的生活中的例子说明IO与NIO的区别。
在一家幼儿园里,小朋友有上厕所的需求,小朋友都太小以至于你要问他要不要上厕所,他才会告诉你。幼儿园一共有100个小朋友,有两种方案可以解决小朋友上厕所的问题:
- 每个小朋友配一个老师。每个老师隔段时间询问小朋友是否要上厕所,如果要上,就领他去厕所,100个小朋友就需要100个老师来询问,并且每个小朋友上厕所的时候都需要一个老师领着他去上,这就是IO模型,一个连接对应一个线程。
- 所有的小朋友都配同一个老师。这个老师隔段时间询问所有的小朋友是否有人要上厕所,然后每一时刻把所有要上厕所的小朋友批量领到厕所,这就是NIO模型,所有小朋友都注册到同一个老师,对应的就是所有的连接都注册到一个线程,然后批量轮询。
这就是NIO模型解决线程资源受限的方案,实际开发过程中,我们会开多个线程,每个线程都管理着一批连接,相对于IO模型中一个线程管理一条连接,消耗的线程资源大幅减少
由于NIO模型中线程数量大大降低,线程切换效率因此也大幅度提高
NIO解决这个问题的方式是数据读写不再以字节为单位,而是以字节块为单位。IO模型中,每次都是从操作系统底层一个字节一个字节地读取数据,而NIO维护一个缓冲区,每次可以从这个缓冲区里面读取一块的数据,
这就好比一盘美味的豆子放在你面前,你用筷子一个个夹(每次一个),肯定不如要勺子挖着吃(每次一批)效率来得高。
一、Buffer demo
-
public class BufferTest {
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
//静态方法常见 buffer
-
IntBuffer buf = IntBuffer.allocate(10);
-
int[] array = new int[]{3, 5, 1};
-
-
//put一个数组到buffer中,使用put方式将
-
// buf.put(array);
-
-
//使用wrap方式会直接更改原数组
-
buf = buf.wrap(array);
-
-
//IntBuffer.wrap(array, 0, 2);
-
-
buf.put(0, 7);
-
-
int length = buf.limit();
-
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
-
System.out.print(buf.get(i));
-
}
-
-
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
-
System.out.print(array[i]);
-
}
-
-
System.out.println(buf);
-
/**
-
* limit = position;
-
* position = 0;
-
*/
-
buf.flip();
-
/**
-
* position = 0;
-
* limit = capacity;
-
*/
-
buf.clear();
-
System.out.println(buf);
-
//创建一个新的字节缓冲区,共享此缓冲区的内容
-
IntBuffer newBuffer = buf.duplicate();
-
System.out.println(newBuffer);
-
}
-
-
}
二、FileChannel demo
-
public class FileChannelTest {
-
-
-
public static void testFileChannel() throws IOException {
-
RandomAccessFile aFile = new RandomAccessFile("D:/nio-data.txt", "rw");
-
FileChannel channel = aFile.getChannel();
-
//分配一个新的缓冲区
-
ByteBuffer allocate = ByteBuffer.allocate(48);
-
int bytesRead = channel.read(allocate);
-
while (bytesRead != -1) {
-
System.out.println("Read " + bytesRead);
-
allocate.flip();
-
while (allocate.hasRemaining()) {
-
System.out.print((char) allocate.get());
-
}
-
allocate.clear();
-
bytesRead = channel.read(allocate);
-
}
-
aFile.close();
-
}
-
-
-
public static void fileChannelDemo() throws IOException {
-
-
//定义一个byteBuffer
-
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
-
-
FileChannel inputChannel = new FileInputStream("D:/nio-data.txt").getChannel();
-
-
FileChannel outputChannel = new FileOutputStream("D:/nio-data.txt", true).getChannel();
-
-
//读取数据
-
byteBuffer.clear();
-
int len = inputChannel.read(byteBuffer);
-
-
System.out.println(new String(byteBuffer.array(), "UTF-8"));
-
System.out.println(new String(byteBuffer.array(), 0, len, "UTF-8"));
-
-
ByteBuffer byteBuffer2 = ByteBuffer.wrap("奥会计师八度空间".getBytes());
-
-
outputChannel.write(byteBuffer2);
-
-
outputChannel.close();
-
inputChannel.close();
-
}
-
-
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
try {
-
FileChannelTest.fileChannelDemo();
-
} catch (Exception e) {
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}
-
}
-
}
三、不使用 选择器 selector 的 ServerSocketChannel 和 SocketChannel 的demo
服务端:
-
public class NioChannelServer {
-
-
private ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
-
-
//获取一个intBuffer视图,操作视图的同时原缓冲区也会改变
-
private IntBuffer intBuffer = byteBuffer.asIntBuffer();
-
-
private SocketChannel socketChannel = null;
-
-
private ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = null;
-
-
-
/**
-
* 打开服务端的通道
-
*
-
* @throws Exception
-
*/
-
public void openChannel() throws Exception {
-
serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
-
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(8888));
-
System.out.println("服务端通道已经打开");
-
}
-
-
/**
-
* 等待新的连接
-
*
-
* @throws Exception
-
*/
-
public void waitReqConn() throws Exception {
-
-
while (true) {
-
socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
-
if (null != socketChannel) {
-
System.out.println("新的连接加入!");
-
}
-
//处理请求
-
processReq();
-
socketChannel.close();
-
-
}
-
}
-
-
private void processReq() throws IOException {
-
System.out.println("开始读取和处理客户端数据。。");
-
byteBuffer.clear();
-
socketChannel.read(byteBuffer);
-
int result = intBuffer.get(0) + intBuffer.get(1);
-
byteBuffer.flip();
-
byteBuffer.clear();
-
//修改视图,byteBuffer也会变化
-
intBuffer.put(0, result);
-
socketChannel.write(byteBuffer);
-
System.out.println("读取处理完成");
-
-
}
-
-
public void start() {
-
try {
-
//打开通道
-
openChannel();
-
//等待客户端连接
-
waitReqConn();
-
socketChannel.close();
-
System.out.println("服务端处理完毕");
-
} catch (Exception e) {
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}
-
}
-
public static void main(String[] args){
-
new NioChannelServer().start();
-
}
-
-
}
客户端:
-
public class NioChannelClient {
-
-
private SocketChannel socketChannel = null;
-
-
private ByteBuffer buff = ByteBuffer.allocate(8);
-
-
private IntBuffer intBuffer = buff.asIntBuffer();
-
-
-
public SocketChannel connect() throws IOException {
-
return SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8888));
-
}
-
-
-
public int getSum(int a, int b) {
-
int result = 0;
-
try {
-
socketChannel = connect();
-
sendRequest(a, b);
-
result = receiveResult();
-
} catch (Exception e) {
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}
-
return result;
-
}
-
-
private int receiveResult() throws IOException {
-
buff.clear();
-
socketChannel.read(buff);
-
return intBuffer.get(0);
-
}
-
-
private void sendRequest(int a, int b) throws IOException {
-
buff.clear();
-
intBuffer.put(0,a);
-
intBuffer.put(1,b);
-
socketChannel.write(buff);
-
System.out.println("客户端发送请求 ("+a+"+"+b+")");
-
}
-
-
-
-
public static void main(String[] args){
-
-
Random random = new Random();
-
-
for (int i = 0; i <10 ; i++) {
-
int result = new NioChannelClient().getSum(random.nextInt(100),random.nextInt(100));
-
System.out.println(result);
-
}
-
}
-
}
四、使用 selector 方式 实现 ServerSocketChannel 和 SocketChannel
选择器(Selector) 是 SelectableChannle 对象的多路复用器,Selector 可以同时监控多个 SelectableChannel 的 IO 状况,也就是说,利用 Selector可使一个单独的线程管理多个 Channel,selector 是非阻塞 IO 的核心。
选择器(Selector)的应用:
当通道使用register(Selector sel, int ops)方法将通道注册选择器时,选择器对通道事件进行监听,通过第二个参数指定监听的事件类型。
其中可监听的事件类型包括以下:
读 : SelectionKey.OP_READ (1)
写 : SelectionKey.OP_WRITE (4)
连接 : SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT (8)
接收 : SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT (16)
如果需要监听多个事件是:
int key = SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_WRITE ; //表示同时监听读写操作
服务端:
-
public class SelectorServer {
-
private Selector selector = null;
-
private ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = null;
-
private int keys = 0;
-
-
public void initServer() throws IOException {
-
selector = Selector.open();
-
serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
-
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8888));
-
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
-
//服务端通道注册accept事件
-
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
-
}
-
-
private void listen() throws IOException {
-
System.out.println("服务端已经启动");
-
while (true) {
-
//让通道选择器至少选择一个通道,阻塞的方法
-
keys = this.selector.select();
-
//selector.wakeup();//可以唤醒阻塞的select()方法
-
//设置超时时间,非阻塞
-
//this.selector.select(1000);
-
System.out.println(keys);
-
Iterator<SelectionKey> itor = this.selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
-
-
if (keys > 0) {
-
//进行轮询
-
while (itor.hasNext()) {
-
try{
-
SelectionKey key = itor.next();
-
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
-
//serverSocketChannel = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
-
//获取和客户端连接的服务端渠道
-
SocketChannel channel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
-
channel.configureBlocking(false);
-
channel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("hello".getBytes()));
-
//还需要读取客户端发过来的数据,所以需要注册一个读取数据的事件
-
channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
-
} else if (key.isReadable()) {
-
read(key);
-
}
-
}finally {
-
//处理完一个key,就删除,防止重复处理
-
itor.remove();
-
}
-
}
-
} else {
-
System.out.println("select finished without any keys");
-
}
-
-
}
-
-
-
}
-
-
private void read(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
-
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
-
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
-
int len = socketChannel.read(byteBuffer);
-
String msg = new String(byteBuffer.array(), 0, len);
-
System.out.println("服务端接收到的消息是" + msg);
-
}
-
-
-
public void start() {
-
try {
-
initServer();
-
listen();
-
} catch (IOException e) {
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}
-
}
-
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
new SelectorServer().start();
-
}
-
-
-
}
客户端:
-
public class SelectorClient {
-
private Selector selector;
-
-
private ByteBuffer outBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
-
private ByteBuffer inputBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
-
-
private int keys = 0;
-
-
private SocketChannel socketChannel = null;
-
-
public void initClient() throws IOException {
-
selector = Selector.open();
-
-
socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
-
//客户端通道配置为非阻塞
-
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
-
//连接服务端
-
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8888));
-
//注册客户端连接服务器的事件
-
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
-
}
-
-
-
private void listen() throws IOException {
-
while (true) {
-
keys = this.selector.select();
-
System.out.println(keys);
-
if (keys > 0) {
-
Iterator<SelectionKey> iter = this.selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
-
-
while (iter.hasNext()) {
-
try{
-
SelectionKey key = iter.next();
-
if (key.isConnectable()) {
-
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
-
if (channel.isConnectionPending()) {
-
channel.finishConnect();
-
System.out.println("完成连接");
-
}
-
//连接完成之后,肯定还要做其它的事情,比如写
-
channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
-
-
} else if (key.isWritable()) {
-
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
-
outBuffer.clear();
-
System.out.println("客户端正在写数据。。");
-
-
//从控制台写消息
-
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
-
while (true) {
-
String msg = scanner.next();
-
channel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(msg.getBytes()));
-
if("end".equals(msg)) {
-
break;
-
}
-
}
-
channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
-
System.out.println("客户端写数据完成。。。");
-
} else if (key.isReadable()) {
-
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
-
inputBuffer.clear();
-
int len = socketChannel.read(inputBuffer);
-
System.out.println("读取服务端发送的消息:" + new String(inputBuffer.array()));
-
}
-
}finally{
-
iter.remove();
-
}
-
}
-
} else {
-
System.out.println("select finished without any keys");
-
}
-
}
-
-
}
-
-
-
public void start() {
-
try {
-
initClient();
-
listen();
-
} catch (Exception e) {
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}
-
}
-
-
public static void main(String[] args){
-
new SelectorClient().start();
-
}
-
-
-
}
nio的非阻塞是对于网络通道来说的,需要使用Channel.configureBlocking(false)来设置通道为非阻塞的,如果没设置,默认是阻塞的。
文章来源: blog.csdn.net,作者:血煞风雨城2018,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:blog.csdn.net/qq_31905135/article/details/88862106
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)